Mr. Editor:
The process of nutritional transition in Peru is somewhat paradoxical: an alarming number of chronic malnutrition cases coexist with a high prevalence of overweight and obesity, as reported in several studies in recent years.1-3 Huicho et al.4 recently published Child health and nutrition in Peru within an antipoverty political agenda: a Countdown to 2015 country case study, where they stated that the success of Peru in reducing mortality in infants and children under 5 years old was achieved thanks to the strategies implemented by the government through social and health programmes aimed to tackle malnutrition, mainly in vulnerable populations.
This “breakthrough” of Peru in terms of infant mortality and reducing malnutrition and its comorbidities is “counteracted” by the maintenance of the prevalence in childhood overweight and obesity. A study using as source of information the reports of the Peruvian Demographic and Family Health National Survey between 1996 and 2011, concluded that overweight in Peruvian children decreased both in urban and rural settings until 2005 before stabilizing in 2011.3 In recent years, there have been no epidemiological studies regarding the national prevalence of overweight, obesity, and chronic child malnutrition; therefore, we conducted an analysis of the Information System of Nutritional Status (SIEN) data between 2010 and 2015 of children under 5 years that attended healthcare facilities at a national level.5
The national prevalence of overweight has changed over the analysis period in a range of 6.22% to 6.84%. In 2010, the national prevalence of overweight was 6.22%. This was followed by an annual growth and reaching its peak in 2014 with 6.84%, to decrease in 2015 to 6.24%. In the case of obesity, the prevalence oscillated between 1.52% to 2.72%, with the highest figure recorded in 2013 and the lowest in 2015. We must be watchful because a high adolescent prevalence of overweight (34%) and obesity (14%) in a Peruvian urban area had recently been reported6 and it is very likely that our children will continue that path. On the other hand, although the prevalence of chronic malnutrition shows a decreasing trend, this still remains at alarming percentages (range 19.44% - 23.94%) and, unquestionably, far exceeds the national rate of obesity and overweight (Fig. 1).
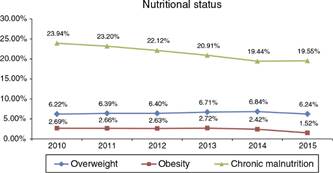
Figure 1 Prevalence of overweight, obesity and chronic malnutrition in children under 5 years, Peru 2010-2015.
The overall results show the persistence of a large proportion of children with nutritional problems in Peru. This is dangerous for the benefits of reducing malnutrition because they could be lost if the prevalence of infantile overweight and obesity remains its frequencies or even increases them deriving in other problems, as it had happened in countries with similar epidemiological characteristics to the Peruvian.7 Nevertheless, some efforts have been made, such as Law 30021 for the promotion of healthy eating in children and adolescents.8 Under this law, nationwide surveillance mechanisms, promotion of healthy foods, and clear indications of nutritional contents in food labels were established. Still, its implementation and publication was delayed by several months,8 which could be revealing bureaucratic barriers and lobbies against it.
Therefore, to mitigate this risk, we need multidisciplinary participation, awareness, and involvement in the design of strategies for longitudinal policies. We also need to involve decision makers, stakeholders and academics to fight against this double burden of malnutrition, which steals the opportunities for a better future to the children from Peru.














