INTRODUCTION
A balanced diet and appropriate hydration are fundamental to sport performance, but specific needs will depend on several factors, such as individual physiological conditions, intensive physical activity, time of the season and training or competition period 4,5. An average daily water intake of 2.2 to 2.6 ml/d in men and 1.9 to 2.4 ml/d in women meets the needs of most adult people 1. However, strenuous physical exercise and heat stress can greatly increase daily water needs, and individual variability between athletes can be substantial 6.
Dehydration can negatively affect different physiological systems including the nervous system 7,8, cardiovascular, thermoregulation and endocrine systems or metabolism 3, which may have negative consequences on health 9, affect athletic performance 10,11,12 and increase the risk of exertional heat injury 13 in both anaerobic and aerobic sports 14. Physical and mental performance during physical exercise and sport practice is impaired in the under-hydrated individual 15 and to avoid this, as well as the negative effects on physical performance, the athlete must drink enough fluids before 16,17,18, during 19,20,21 and after practicing physical exercise, maintaining proper hydration throughout the day 3. Furthermore, not only the amount of beverage is important, but also the type of beverage to be drunk.
Currently, many people practice some kind of recreational intensive activity sport, such as basketball, for more than one hour a day 4, but there are few studies evaluating whether drinking habits are in line with the recommendations made by national and international sports institutions. Basketball is an aerobic-anaerobic sport, characterized by high-intensity intermittent exercise 22 and mainly played indoors, so dehydration may also be affected by high temperature and humidity. Health and disease prevention do not only depend on physical activity practice 23, but also on eating and hydration habits 20. Therefore, the aim of this work was to assess the drinking habits of amateur basketball players before, during and after exercise on both training and competition days.
METHODS
STUDY DESIGN
The study was a population-based cross-sectional study carried out in the city of Barcelona between October 2011 and February 2012.
SELECTION OF PARTICIPANTS, RECRUITMENT AND APPROVAL
Barcelona city's basketball clubs (n = 50) were contacted by e-mail and phone and all players registered as senior category (1st, 2nd and 3rd) in the Catalan Federation of Basketball (CFB) and aged between 19 to 29 years were invited to participate in the study. One hundred and eighty-three players (96 men and 87 women), from 45 clubs, performing intensive physical activity 2-3 times per week, accounting for 60 to 120 min/d, agreed to participate.
ETHICS
This study was conducted according to the guidelines laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki, and the URL's Committee of Ethics in Research (CER-URL, Barcelona, Spain, ref. 2010_05) approved all procedures involving human subjects. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENTS
Anthropometric characteristics are part of the biological variables related to sport performance. Anthropometric characterization of subjects was included in Table I. All anthropometric variables were measured according to the protocol recommended by the International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry (ISAK) 24. All the anthropometric measurements were objectively obtained by trained personnel. Height was determined using a mobile anthropometer (Seca 217(r), Hamburg, Germany), to the nearest millimeter, with the subject's head in the Frankfurt plane. Body mass was determined to the nearest 100 g using a digital scale (Seca 874(r), Hamburg, Germany). The subjects were weighed in bare feet and light underwear. Height and weight measures were used to calculate the body mass index (BMI, kg/m2). Waist circumference (WC) was also measured. Height and WC measures were used to calculate the waist-to-height ratio (WHtR).
Table I. Anthropometric characteristics of the amateur basketball players

BMI: body mass index; whtr: waist-to-height ratio. values are the *median (1st quartile-3rd quartile) and †mean ± standard deviation. ‡statistical significant differences between genders were assessed by means of unpaired student t test or mann-whitney u test.
The three somatotype components (endomorphy, mesomorphy and ectomorphy) were calculated according to the Carter and Heath anthropometric somatotyping method 25. The ten variables used to calculate the anthropometric somatotype were height, mass, four skinfolds (triceps, subscapular, supraspinale, medial calf), biepicondylar breadth of humerus and femur, and arm (flexed and tensed) and calf circumferences. Skinfold thicknesses were measured using a skinfold caliper (Holtain(r), Croswell, UK), to the nearest 0.2 mm. Circumferences were measured using a non-stretch measuring tape (Lufkin Executive(r) w606pm, Lufkin, USA) to the nearest 1 mm. Bone widths were measured with a small sliding bone caliper (Holtain(r) Ltd., Crosswell, UK) to the nearest 1 mm. The subjects were asked to stand erect in a relaxed position with both feet together on a flat surface. The median was used for statistical analysis if the measurements had to be taken three times, while the mean was used if the first two measurements were within the acceptable range 26.
Assessment of beverage consumption
A drinking habits questionnaire based on a previously published questionnaire 27 was self-administered by computer. This questionnaire included the following questions about beverage intake before, during and after exercise on both training and competition days:
Type of beverage, which was categorized into five groups: fruit juice (i.e., natural fruit juice and fruit juice sweetened with sugar), water (i.e., tap, bottled and spring water), energy drinks (i.e., cola and guarana drinks), soda (i.e., carbonated soft drinks) and others (i.e., carrot juice, alcohol-free beer, chocolate, vanilla and strawberry milkshakes and diet milkshakes, soya milk, rice milk, oat milk, fermented milk drinks with sugar, fermented milk drinks, kefir and sweetened iced tea).
The amount of fluid drunk, which was categorized into three groups: < 250, 250-500, and ≥ 500 ml.
The beverage time, which was categorized into four groups before and after the exercise: < 10, 10-20, 20-30, and > 30 min; and into three groups during the exercise: 1-3, 4-6 and > 6 times. Fluid intake was only considered if it occurred within four hours before starting or after finishing physical exercise.
According to the drinking habits recommendations published by the American College of Sport Medicine (ACSM) 28,29 and the Spanish Federation of Sports Medicine (FEMEDE) 4, the following criteria were established to assess healthy hydration habits:
Before exercise: less than one glass (< 250 ml) between 10-30 minutes beforehand, or more (≥ 250 ml), 30 minutes before exercise.
During exercise: less than one glass (< 250 ml) more than six times; between one to two glasses (250 to 500 ml) 4-6 times; or more than two glasses (≥ 500 ml) regardless of the frequency.
After exercise: more than one glass (≥ 250 ml) within 30 minutes after exercise ended.
STATISTICS
Analyses were performed with the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences version 24.0 (IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Armonk, NY: IBM Corp USA). All tests were stratified by gender. Categorical variables were presented as frequencies and/or proportions. Significant differences in prevalence were calculated by means of χ2 or Fisher's exact test. Normality of data was assessed using Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Continuous variables were expressed as follows: mean (standard deviation [SD]) for normally distributed data (somatotype components: endomorphy, mesomorphy, ectomorphy), and median (1st-3rd quartile) for non-normally distributed data (age, weight, height, BMI, and WHtR). For normally distributed data, the unpaired Student's t-test was used to compare the mean of two independent groups. For non-normally distributed data, the Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare the median of two independent groups. The level of significance was established for p values at < 0.05.
RESULTS
Table II shows the type of beverage consumed before, during and after exercise on both training and competition days. Overall, 20.8%, 5.5% and 2.7% of the subjects reported that they did not drink before, during and after exercise on training days, respectively. More women than men reported that they did not drink before exercise (27.6% vs 14.6%, p < 0.05) while more men than women did not drink during exercise (9.4% vs 1.2%, p < 0.05). No statistically significant difference in the prevalence of non-drinkers was found between men and women after exercise (2.1% and 3.4%, respectively). In competition days, 17.5% of subjects reported that they did not drink before exercise, with a higher prevalence among women than in men (25.3% vs 10.4%, p < 0.01). Almost none of them reported that they did not drink during or after exercise on competition days.
Table II. Type of beverages consumed before, during and after the exercise in training and competition days among amateur basketball players
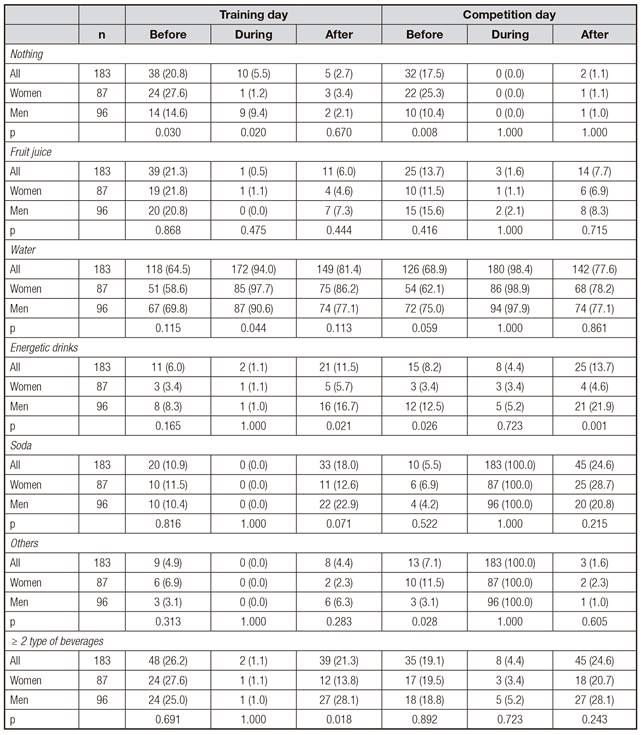
Values are: n (%). Statistical significant differences between genders were assessed by χ2 or Fisher's exact test.
Water was the preferred beverage before, during, and after exercise on both training and competition days. In fact, 64.5% of the subjects reported that they drank water before exercise on training days, followed by fruit juice (21.3%), soda (10.9%), energy drinks (6.0%) and other beverages (4.9%). Overall, a quarter of the subjects reported more than one type of beverage before exercise on training days. On competition days, 68.9% of the subjects also reported that they drank water before exercise, followed by fruit juice (13.7%), energy drinks (8.2%), other beverages (7.1%) and soda (5.5%). However, men were more likely to show a preference for energy drinks than women. Almost all of the subjects reported that they only drank water during exercise on training days. However, all the subjects reported that they also drank soda and other beverages during exercise on competition days. Despite the fact that the preferred beverage after exercise on both training and competition days included water (81.4% and 77.6%, respectively), some subjects reported that they also drank soda (18.0% and 24.6%), energy drinks (11.5% and 13.7%), fruit juice (6.0% and 7.7%) and/or other beverages (4.4% and 1.6%). After exercise, men were also more likely to prefer energy drinks than women were.
The overall amount of beverage intake before, during and after exercise on both training and competition days is shown in Figure 1. Overall, 1.4%, 41.4% and 57.2% of the subjects reported that they drank < 250, 250-500, and ≥ 500 ml, respectively, before exercise on training days, with no statistically significant differences between genders (p = 0.265). On competition days, 62.3% of subjects reported that they drank ≥ 500 ml before exercise. On the other hand, statistically significant differences in the distribution of the sample according to the amount of beverage intake during exercise were obtained on both training (p = 0.006) and competition (p = 0.042) days, with men more likely to drink ≥ 500 mlthan women were. After exercise, around 70% of the subjects reported that they drank ≥ 500 ml.

Figure 1. Amount of beverage consumed before, during and after exercise in training (A) and competition (B) days among amateur basketball players.
Figure 2 shows the time of fluid intake for those subjects who reported drinking some beverage before (A), during (B) and after (C) exercise on both training and competition days. Most of the subjects reported that they drank < 10 or > 30 minutes before exercise on both training and competition days. During exercise, most subjects (89.0%) reported that they drank 1-3 times on training days, while only 52.1% of men and 28.7% of women did so 1-3 times on competition days. Furthermore, 21.9% of men and 25.3% of women reported that they drank > 6 times during exercise on competition days. Overall, 80.3% and 83.4% of the subjects reported that they drank < 30 minutes after exercise on training and competition days, respectively.

Figure 2. Time of the fluid intake among amateur basketball players who reported to drink several beverages before (A), during (B) and/or after (C) the exercise in training and competition days.
Table III shows the prevalence of good hydration habits before, during and after exercise on training days according to the recommendations released by the ACSM and FEMEDE. Good hydration habits were found in 54.6%, 74.2% and 76.5% of the subjects, respectively.
DISCUSSION
The first main finding of this study was that 20.8%, 5.5% and 2.7% of amateur basketball players reported that they did not drink before, during and after exercise on training days, respectively. Furthermore, 17.5% of the subjects reported that they did not drink before exercise on competition days, with a higher prevalence among women than in men. To our knowledge, there is little previous data regarding the drinking habits of amateur sportspeople. Previously, Alarcon et al. 27 assessed the drinking habits of 35 basketball players (14-32 years) from the Polaris World basketball Club (Murcia, Spain) on a competition day. In this study, 94.3% of the participants drank some fluid before exercise against the 82.5% from this study.
In agreement with the research by Alarcon et al. 27, water was the preferred beverage before, during, and after exercise on both training and competition days. Moreover, fruit juice was the second most-consumed beverage on both training and competition days prior to exercise. However, in contrast to the study by Alarcon et al. 27, all the subjects in our work reported that they also drank soda and other beverages during exercise on competition days. Finally, beverage intake in the Alarcon et al. study 27 included water (40%), fruit juice (22.8%), soda (20%) and energy drinks (17.1%) after exercise. Likewise, in this study participants also reported that they drank water, soda, energy drinks, fruit juice and other beverages after exercise on both training and competition days. Finally, 31.8% of the subjects in our study reported that they drank some type of beverage 30 minutes before exercise on competition days, against the 8.6% seen in the Alarcon et al. study 27. Furthermore, 16.6% of the subjects in this study reported that they drank some type of beverage 30 minutes after exercise on competition days, against the 22.8% observed in the study by Alarcon et al. 27.
The National Athletic Trainers Association (NATA) 13 proposed that, to ensure proper pre-exercise hydration, athletes should consume approximately 500-600 ml of water or sport drinks 2-3 hours before exercise. If hydration levels are low, athletes should drink 200-300 ml of water or sport drinks 10-20 minutes before exercise. In this study, most subjects reported drinking at least 250 ml before exercise; however, only 26 subjects reported that they drank it 10-20 minutes before exercise. The NATA 13 recommended that, during exercise, fluid replacement generally requires 200-300 ml of water or sports drinks every 10-20 minutes and proposed that post-exercise hydration should aim, within two hours afterwards, to correct fluid losses accumulated during the practice or event and that, ideally, rehydration should contain water to restore hydration levels.
A review by Rowland 17 pointed out that the amount of liquid intake could be calculated as a fluid intake of 13 ml/kg body weight/h. According to the ACSM 28,29 and FEMEDE 4, prior to exercise individuals should drink beverages at least four hours before exercise and around 5-7 ml/kg body weight (300-600 ml) or 3-5 ml/kg body weight approximately two hours before exercise. In the present study, about 60% of the subjects reported that they drank at least 500 ml before exercise. However, post-exercise fluid intake is equally important to avoid commencing subsequent bouts of exercise in a dehydrated state 4,17,26. In fact, the ACSM 29 and FEMEDE 4 also pointed out that, 30 minutes after exercise starts, it is necessary to compensate fluid loss, and after one hour it is essential to drink 400-500 ml/h or 150-200 ml/20 min. Moreover, post-exercise hydration should aim to restore fluid losses accumulated during the practice or event within two hours. In this study, around 70% of the subjects reported that they drank at least 500 ml after exercise, but around 80% of basketball players rehydrated by drinking water and 25% drank also soda. Ideal rehydration should contain water to restore hydration levels. Finally, good hydration habits were found in 54.6%, 74.2% and 76.5% amateur basketball players before, during and after exercise on training days, respectively.
STRENGTHS AND LIMITATIONS
The main strength of this study is that there are many studies regarding the relationship between hydration and health and performance in the field of elite sport, but few studies have been conducted on adults in the field of recreational sports. However, this study has also several limitations. Firstly, good hydration habits should consider the intake of liquid throughout the day to learn about the level of hydration before starting exercise in order to determine the amount of liquid that each subject should drink after completing the exercise. This should be 150% 4 of the amount of weight lost during exercise. Secondly, the evaluation of good hydration was only carried out on a training day, because not all subjects played for more than one hour on a competition day.
CONCLUSIONS
Good hydration habits were found in 54.6%, 74.2% and 76.5% of subjects before, during and after the training day, respectively. It is difficult to instil hydration habits into all sportsmen, and even more so in non-professional categories and in the lower divisions. Because good hydration substantially contributes to the improvement of physical performance, and drinking water ad lib is not enough, hydration patterns should be an important part of training 30. These results should be taken into account to establish recommendations by sports organizations in relation to the amount and quality of liquid to drink before, during and after exercise, taking into account the type of sport, duration and climate.















