Introduction
Disability has become the most important component of the burden of disease.1 In 2010, low back pain and major depressive disorders were ranked as the third and fourth leading causes of disability worldwide, after HIV/AIDS and road injuries, according to disability adjusted life years (DALYs).1 Although DALYs help to compare the relative magnitude of the disease burden across diseases and countries, they might not adequately capture the welfare impact of some diseases, for instance mental disorders, as they have a large impact on functioning and quality of life.2-4 According to the World Report on Disability,5 infectious diseases (e.g., malaria, tuberculosis and sexually transmitted diseases); non-communicable diseases (e.g., arthritis, hearing disorders, asthma) and injuries (road traffic injuries, occupational injuries and violence) are important causes of health-related disability in developed countries.
The World Mental Health (WMH) Surveys Initiative was launched by the World Health Organization (WHO) to collect comparable data on the burden of mental disorders around the world.6 Two WHO-WMH reports3,4 have provided information on the individual and societal-level impact of the disability due to 19 physical and mental conditions in the general population. By means of the WHO-Disability Assessment Schedule 2.0,7 the full and the partial inability to perform daily activities, as measures of functional impairment, were assessed. Both reports have emphasized, in agreement with the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2010 study1 that back and neck pain, among physical conditions, and depression, among mental disorders, were the most burdensome non-communicable conditions worldwide.
In Europe, nearly 42 million persons of working-age from 15 European countries (16.4%) reported having a long-standing health problem or disability in 2002.8 However, good sources of data on disability are not available in all European countries and cross-country comparisons are limited due to methodological differences.9 While harmonization of data on disability among European countries are underway by the European Health Interview Survey, 2008 (EHIS), there is still limited comparable information about the disability burden of health conditions in the working-age population of Europe.
Here data from 10 European countries participating in the World Mental Health surveys initiative (EU-WMH)10,11 were analysed with two general objectives: first, to describe the distribution of disability in the population aged 18 to 64 years; and second, to examine the contribution of health conditions to disability. We analysed the contribution of mental disorders and physical conditions on two self-reported measures of disability: complete inability (i.e., full role limitation) and partial ability (i.e., partial role limitation) to perform daily activities in three European regions.
Materials and methods
Survey method and samples
Ten European countries (Belgium, Bulgaria France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Northern Ireland, Portugal, Romania and Spain) participated in the European World Mental Health Surveys Initiative (EU-WMH). Household interview surveys were conducted between 2001 and 2009 on probability samples of each country's population aged 18 years or older living in private households. Institutionalized individuals as well as those not able to understand the language of each country, were excluded from the study. Computer-assisted personal interviewing (CAPI) were used except for Bulgaria, were paper-and-pencil (PAPI) format was used. Respondents were selected using stratified multistage clustered-area probability sampling methods (Table 1). Response burden was reduced by splitting-up the single interview into a two-part process in all countries except for Romania (in which the interview was administered in one part). Part 1 was administered to all participants and included the core diagnostic assessment of mood and anxiety disorders. Part 2 was administered to all respondents with a certain number of mood and anxiety symptoms and to a random proportion of those who had none, and included questions about disability, additional mental disorders and information on physical conditions. Part 2 individuals were weighted by the inverse of their probability of selection to adjust for differential sampling, and therefore provide representative data on the target adult general population. Additional details about sampling methods are available elsewhere.10 The EU-WMH total sample size was 37,289, ranging from 2,357 (Romania) to 5,473 (Spain). Response rates ranged from 45.9% (France) to 78.6% (Spain), with an overall weighted response rate of 63.4%. For this particular work, the 13,666 individuals aged 18 to 64 years, who completed Part 2 of the interview were analysed (Table 1).
Table 1 EU-WMH surveys: sample characteristics, field dates, and samples sizes by country groups.

CAPI: computer-assisted personal interviewing; ESEMeD: European Study of the Epidemiology of Mental Disorders; NISHS: Northern Ireland Study of Health and Stress; NMHS: Portugal National Mental Health Survey; NSHS: Bulgaria National Survey of Health and Stress; PAPI: pencil and paper interviewing; RMHS: Romania Mental Health Survey.
aMost WMH surveys are based on stratified multistage clustered area probability household samples in which more subsequent stages of geographic sampling (e.g., towns within counties, blocks within towns, households within blocks) to arrive at a sample of households, in each of which a listing of household members was created and one or two people were selected from this listing to be interviewed. No substitution was allowed when the originally sampled household resident could not be interviewed. These household samples were selected from Census area data in all countries other than France (where telephone directories were used to select households) and the Netherlands (where postal registries were used to select households). Several WMH surveys (Belgium, Germany, Italy) used municipal resident registries to select respondents without listing households.
bRomania did not have an age restricted Part II sample.
cThe response rate is calculated as the ratio of the number of households in which an interview was completed to the number of households originally sampled, excluding from the denominator households known not to be eligible either because of being vacant at the time of initial contact or because the residents were unable to speak the designated languages of the survey.
Institutional Review Boards (IRB) of each country approved this study.
European regions
Countries were grouped into three regions according to the United Nations Statistic Division: (i) Central-Western Europe (Belgium, France, Germany, the Netherlands and Northern Ireland); (ii) Southern Europe (Italy, Portugal and Spain); and (iii) Central-Eastern Europe (Bulgaria and Romania).
Measurements
-
Mental disorders
DSM-IV mental disorders were assessed using the WHO Composite International Diagnostic Interview (CIDI),12 version 3.0, a fully structured research diagnostic interview designed for use by trained lay interviewers to provide diagnoses of mental disorders according to the definitions and criteria of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV). Standardized common procedures were followed to guarantee cross-survey comparability of data.13 Mental disorders evaluated were: Depressive disorder (major depressive episode), and any anxiety disorder (panic disorder and/or agoraphobia, social phobia, specific phobia, generalized anxiety disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder).
-
Physical conditions
Physical conditions were assessed with a checklist based on the U.S. National Health Interview Survey.14 Respondents were asked about a number of symptom-based conditions and a number of silent conditions, diagnosed by a health professional. Seven conditions or groups of conditions were included: arthritis, cardiovascular disorders (heart attack, heart disease, hypertension and stroke), severe headaches or migraines, insomnia, chronic pain (back or neck pain or other chronic pain), respiratory disorders (seasonal allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, emphysema), and other physical conditions with low prevalence estimates (<2%), which included cancer, neurological diseases, diabetes, or digestive disorders (stomach or intestine ulcer or irritable bowel disorder).
Both mental disorders and physical conditions had to be present in the 12-months before the interview.
-
Disability
Role limitation was assessed with a modified version of the WHO Disability Assessment Schedule 2 (WMH-WHODAS),7 based on the conceptual model of the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF). Respondents were asked about the number of days in the last 30 days, in which they were totally unable to carry out their daily life activities (full role limitation) or they were able to perform their daily life activities, but only partially (partial role limitation). A day with partial role limitation was defined as a day on which respondents had either (a) to cut down on what they did, (b) to cut back on quality of what they did, and (c) needed extreme effort to perform as usual. An aggregate measure of partial role limitation was computed: ([0.50]*quantity cut down days)+([0.50]*quality cut back days)+([0.25]*extreme effort days). If this sum exceeded 30, it was set to 30 giving the measure a range from 0 to 30.3,4
Statistical analysis
We used a two-part modelling approach to separately assess the association of full and partial role limitation with health conditions, controlling for age, sex, employment status, education, marital status and country. Interactions with sex were tested in all models but interaction terms did not reach statistical significance in any model. First, a logistic regression equation was used to predict the probability of reporting days with role limitations in the total sample. Subsequently a Generalized Linear Regression Model equation was used to predict the scores in those individuals reporting days with full and with partial role limitation (the specification for both outcomes was a normal distribution with an identity link function).15 Each model included the health conditions, the covariates, and the number of conditions starting at two to avoid colinearity. For each of the outcomes, four models were built (all 10 countries together plus one for each region).
Population attributable fraction (PAF) as a societal-level measure
PAFs16,17 were estimated to evaluate the expected effect of either preventing or successfully treating one or more of the health conditions included as predictors in our regression equations. PAF can be interpreted as the proportion of days with full/partial role limitation that would not have occurred in the absence of the predictor disorders. As the outcome was continuous, the calculation of PAF was done as follows: the predicted value of a health condition on the dependent variables (i.e., full or partial role limitation) was distributed across a number of coefficients from two distinct models, logistic and GLM. (More detail is presented in the Supplementary Box, in the Appendix online).
Data were weighted to account for known probabilities of selection as well as to restore age and gender distributions of the population within countries. An additional weight was added to restore the relative dimension of the population across countries.15 The standard errors were calculated using the Jackknife Repeated Replication method, implemented in a SAS macro (SAS Version 9.2).
Results
Sample characteristics are displayed in Table 2. Regions were similar in gender distribution (about 50-51% were women) and in mean age (40.2 years). Approximately one third of the participants reported not being married at the time of the interview (32.2%), with a significantly lower proportion of married participants in Central-Eastern Europe (26.8%). Completed high school or more varied from 92.7% in Central-Western to only 50% in Southern Europe. Unemployment also varied: from the lowest rate in Central Western Europe (26.5%) to the highest rate in Central-Eastern (48.8%). Almost one in ten individuals (9.5%) reported a full role limitation day and about 18.0%, a partial role limitation day in the previous month. Central-Western Europe was the region with more full and partial role limitation days.
Table 2 Sample characteristics of the population sample aged 18-64 years in the WMH surveys in the 10 European countries (EU-WMH).

N: unweighted; %: weighted.
aEducation in France was collected differently from the other countries.
bNon-employees included students, unemployed, early retirement, permanently disabled, fulfilling domestic tasks and care responsibility.
cThe proportion of individuals reporting either a full or a partial role limitation day in the previous month.
About half of the sample (48.2%) had a health condition (Central-Western Europe, 51.1%; Southern, 45.8%; and Central-Eastern Europe, 42.7%) (Fig. 1). Physical conditions were three times more prevalent than mental disorders (43.9% vs. 11.9%, respectively). Prevalence of mental disorders varied among regions, from 14.3% in Central-Western, 10.1% in Southern, and 6.5% in Central-Eastern Europe. Regional differences were observed for arthritis (Central-Eastern, 22.1% compared to Central-Western and Southern Europe). Central-Eastern Europe showed marked differences in regard to cardiovascular diseases as a highly prevalent condition (15.1%), and headache/migraine (6.6%) and chronic pain disorders (11.5%) as low prevalence conditions, in comparison with the other two regions.

Figure 1 Prevalence rates and 95% Confidence Intervals of health conditions by European regions (EU-WMH).
As shown in Figure 2, about 30% of individuals reporting health conditions had any role limitation. Among those with any role limitation due to health conditions, around 60% reported partial, 15% reported full, and 25% reported both. Role limitation, particularly partial limitation, was significantly higher among individuals with any mental disorder (43.3%), than among those with a physical condition (29.1%). Mental disorders categories presented similar proportion of any role limitation. Among physical conditions, insomnia and other physical conditions presented the highest while cardiovascular and respiratory the lowest proportion of any role limitation.
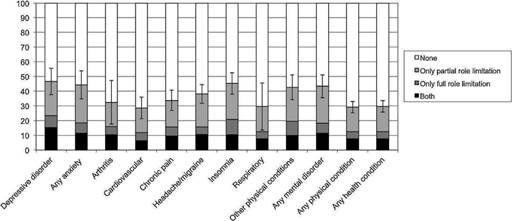
Figure 2 Distribution of role limitation's categories by health conditions (EU-WMH). Error bars (95%CI) are calculated for any role limitation.
Figure 3 shows the Population Attributable Fraction (PAFs) of full (Fig. 3 A) and partial (Fig. 3 B) role limitation for physical conditions and mental disorders. In the overall sample (black column) the PAFs for all the health conditions were 62.6% for full role limitation and 46.6% for partial role limitation. This PAF difference was statistically significant at the overall level but not within the regions. Figure 3 A shows that the PAFs of full role limitation were similar for both types of conditions (physical and mental). This was also the case in two of the regions, but not for Central-Eastern Europe (white column) where the PAF for full role limitation attributable to mental disorders was lower than that attributable to physical conditions. In Figure 3 B no statistically significant differences were observed across regions on the contributions from each type of disorder to partial role limitation, again, with the exception of Central-Eastern Europe.

Figure 3 Full role limitation (A) and partial role limitation (B) expressed as population attributable fractions (PAFs) by European regions (EU-WMH).
Table 3 presents PAFs of full and partial role limitation for each health condition and by region. Results should be interpreted as follows: of 100% of the role limitation reported by participants, depressive disorders contribute to explain 12.7% of full role limitation and 12.1% of partial role limitation in Europe. Overall, anxiety, depression, chronic pain and other physical conditions contributed the highest PAFs to full role limitation. While chronic pain, depression, arthritis, anxiety, insomnia, headache/migraines and other physical conditions had the highest PAFs of partial role limitation. In Central-Western and in Southern Europe, depression and anxiety were substantial contributors to full role limitation. In Southern Europe, mental disorders also significantly contributed to partial role limitation. In Central-Eastern Europe almost all physical conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases and chronic pain, contributed importantly to full and partial role limitation. Chronic pain was the health condition that substantially and consistently contributed to full and to partial role limitation in all European regions.
Table 3 Population attributable Fraction (PAF) of days with full and partial role limitation due to common health conditions by European region (EU-WMH).

n: unweighted; %: weighted.
The societal predicted values for both outcomes come from a two-part modelling approach and were obtained by multiplying predicted values of the logistic (first part) and GLM (second part) equations. The estimates of both role limitation variables were calculated based on the actual data, and then under the counterfactual assumption that the condition no longer existed.
All models adjusted by age, sex, employment status, country, marital status, education and the number of conditions starting by two.
aStatistical significance <0.05.
bStatistical significance <0.05 between any mental disorder and any physical condition.
Discussion
Our paper has four major findings. First, about two-thirds of the total full role limitation and about one-half of the partial role limitation are associated with nine health conditions in Europe. Theoretically, role limitations could be largely reduced by treating or successfully preventing these nine health conditions. Other burdensome health conditions not included in this study (for instance, hearing loss and visual impairment),5 as well as non-health related determinants (work-related and non-work related factors18,19) could cause role limitations left unexplained in this study. Second, chronic pain was the single condition that contributed the most to both disability measures in all European Regions. This is very consistent with the Global Burden of Disease Study results,1 in which low back pain is the leading cause of disability in Europe, and with previous studies reporting that musculoskeletal conditions, especially back and neck pain, are the most common cause of physical disability in Western countries.1 Third, regional differences were observed: depressive and anxiety disorders were important contributors to full and to partial role limitation in Central-Western and Southern Europe, while in Central-Eastern Europe cardiovascular diseases and headache/migraine were more important contributors. Previous studies have also reported that mental disorders represent a substantial burden in some European countries20-22 and in other countries.23 And fourth, Central-Eastern Europe was the region in which mental disorders contributed the lowest share of full and partial role limitation. This finding is in contrast with the GBD study, which ranked depression as one of the ten leading causes of disability in Bulgaria and in Romania. Reasons for this difference are not easy to grasp from our data, but we speculate with possible explanations below.
Our analysis was restricted to a population sample of working age individuals (18-64 years), thus, while this is not a sample of workers, full and partial role limitation estimates might be interpreted as proxy measures of absenteeism and presenteeism, respectively. Accordingly, health conditions have a much larger impact on absenteeism than on presenteeism. This is because, in general, other non-health related factors frequently account for work performance.18,19 Work-related factors (e.g., shift work, physical work, employment position, among others) together with non work-related characteristics (e.g., family life, financial situation, adverse life events, among others) have also been shown to be relevant in explaining work performance. Nevertheless, the proportion of reduced functioning explained by common and treatable health conditions is far from negligible. Moreover, given that partial disability predicts future full disability,24 our findings carry important policy-making implications. A previous study25 of over one million workers showed that the cost of productivity losses associated to health conditions would be about 40% of the medical costs generated by the same health conditions. Thus, reducing the impact of prevalent disorders should be a priority in occupational health policies in all European regions.
Chronic pain, anxiety, and depression explained almost half of all health-related full role limitation reported in Central-Western (46.3%) and in Southern Europe (53.8%); and chronic pain, cardiovascular diseases and headache/migraines did so in Central-Eastern Europe (48.0%). The most important cross-regional difference was the small proportion of disability explained by mental disorders in Central-Eastern Europe in comparison with the other two regions. WMH survey data are cross-nationally comparable as they were assembled using a standardized protocol for sampling, interviewing, coding and analysing.15 So, it is likely that this cross-regional difference might be explained by reasons other than methodological issues. All health conditions that significantly contributed to full role limitation in our study were respectively listed among the top-ten highly disabling conditions in the 2010 GBD study, except for mental disorders in Central-Eastern Europe. In terms of DALYs, major depressive disorders ranked eighth and sixth as the most disabling condition in Bulgaria and Romania, respectively. Similarities and differences between 2010 GBD study and WMH have been extensively discussed26 but, in general, DALYs and PAFs are population-based disability measures that can be compared. It is known that prevalence and disability are not directly correlated; in particular, mental disorders are conditions with low prevalence but associated with large limitations in functioning.21 However, post hoc analyses of our data (not presented) showed a significantly lower proportion of partial role limitation in Romania compared to other countries with low prevalence of mental disorders (Italy and Germany). We speculate that specific cultural traits of the Romani population could account for this difference27,28 that fosters an underestimation of functional limitations associated with health conditions. Such underestimation would lead to underreporting functional limitations, resulting in measurement bias (i.e., a possible differential item functioning). Future research should address these country-specific differences in order to elucidate the true burden of mental disorders in Central-Eastern countries.
The impact of co-morbid conditions on health status is usually sub-additive.29 This could imply that to accomplish a more substantial decrease of the impact of co-morbid conditions on disability, all conditions, not only one in particular, should be addressed. We tested this hypothesis by including the number of co-morbid conditions in all models. For full role limitation, the coefficient of the number of co-morbid conditions was negative and statistically significant, while for partial limitation, the coefficient was non-significant. Our results would therefore be consistent with findings reported by Alonso et al.29 Nevertheless, we are aware that a simple co-morbidity count term is not the optimal way of controlling for co-morbidity: in addition to consider all co-morbid conditions at once, as we did here, it would also be necessary to consider which co-morbidity patterns are associated to higher or lower decrements in health. A previous study30 showed that depression in combination with certain chronic conditions (asthma, diabetes, angina) produced a greater decrement in health than any of these conditions alone or depression alone. Further exploration of patterns of chronic conditions and impact on disability is necessary.
Limitations of the study
Some limitations should be taken into account when interpreting our findings. First, only a limited number of physical conditions and mental disorders were included in the analysis. Future research should include the above-mentioned conditions along with an expansion (e.g., substance use disorders, psychotic disorders) and disaggregation (e.g., anxiety disorders) of those already included. Second, while mental disorders were assessed with a well-established measure,12 physical conditions were self-reported. Although there is evidence of good correspondence between self-reported31 conditions (diabetes, heart disease and asthma), and clinical records, we might have underestimated the effect of physical conditions on role limitation. Additionally, the collection of the data was done in different years in some countries within the same region, so this may have had an influence in the differences observed between regions. Third, Eastern Europe was the region with the lowest prevalence estimates of DSM-IV mental disorders and also, as mentioned above, was where the lowest association with disability was observed. Such cross-regional variation in mental disorders prevalence should be interpreted with caution. An extensive discussion on cross-national variations in prevalence estimates of mental disorders in the WMH Surveys can be found in Kessler et al.13 It remains possible that a greater reluctance of respondents in Eastern countries to admit emotional problems to a stranger. This issue would be supported by some evidence about stigma being a major problem in Central-Eastern countries.32 It is also possible that the CIDI would not be completely adequate to capture psychopathological syndromes in Eastern countries.15 A high proportion of sub-threshold cases with psychiatric treatment in countries with low prevalence estimates has been reported.33 This suggests that there is still room for improvement in the diagnosis of mental disorders. Finally, the data were collected before the peak of the recent financial crisis, which is associated with important health impacts.34 Changes in health and economic conditions might modify associations described here. In this sense, weighting for non-response was done using general characteristics (e.g., age, sex, and country) while non-response is higher among the less educated, the unemployed and the immigrant populations, characteristics which also are linked with poor mental health. Moreover, in some countries, there was a low response rate that may also have contributed to a selection bias resulting in conservative estimates on the relationship between role limitation and physical and mental diseases.
Conclusions
Notwithstanding these limitations, our results are relevant for health policy, as most of these health conditions are treatable, so the large role limitation impact associated to them might be avoidable. They are also important for research, in particular about the differences in prevalence and in associated disability found in countries from Central-Eastern Europe.














