Introduction
The survival time of renal transplant recipients has gradually increased because of the improved survival rate during the perioperative period and enhancements in treatment with anti-rejection drugs1-4; as a result, long-term complications and the quality of life of transplant recipients have recently received more attention.
Posttransplantation diabetes mellitus (PTDM) is a serious and frequent metabolic complication after a renal transplant and is officially considered a risk factor for patients undergoing renal transplantation.5 PTDM severely affects the quality of life and long-term survival rate of renal transplant recipients.6-9
Variable rates in the prevalence of PTDM after kidney transplantation were reported in many studies.10,11 Porrini et al.12 reported the prevalence of PTDM was 27, 21, 21 and 30%, at 3, 12, 24 and 36 months, respectively.
The variation in the reported incidence may be due in part to the lack of a standard definition of the condition, the duration of follow-up, the presence of both modifiable and non-modifiable risks factors, and the type of organ transplants.13
The aim of this study was to investigate the frequency of development of PTDM among the renal transplant patients in our center, to determine the characteristics of the patients with PTDM and the duration of PTDM diagnosis and to evaluate the risk factors for PTDM.
Materials and methods
Patients’ characteristics
In this retrospective study, we included all adult kidney allograft recipients at the Division of Nephrology and the Transplantation Unit of Istanbul Bilim University, between February 2005 and February 2014. Exclusion criteria were known history of diabetes, age under 18 years at the time of transplantation, multiorgan transplantation, follow up period < 6 months, patients who underwent two or more renal transplantations.
Demographic characteristics such as age, gender, body mass index (BMI), etiologies of primary renal disease, history of dialysis, type of renal transplantation (living or deceased), degrees of related living donors, pharmacologic therapy (induction and maintenance therapy) family history of diabetes and follow-ups were recorded from the patients’ medical charts.
Detailed clinical history, pretransplant parameters, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), total cholesterol (T.Chol), triglycerides (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-Chol), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), intact parathormone (iPTH), impaired fasting glucose (IFG) during the first week after transplantation, serum creatinine levels at discharge from hospital and at the last visit, acute rejection attacks and its treatments were also noted.
Definitions
The diagnosis of PTDM was based on the following diagnostic criteria for diabetes proposed by international consensus meeting on posttransplantation diabetes mellitus in 2013; symptoms of diabetes i.e. polyuria, polydipsia, or unexplained weight loss plus random blood glucose ≥ 200 mg/dl or presence of fasting plasma glucose (FPG) of ≥ 126 mg/dl, or second hour plasma glucose ≥ 200 mg/dl during oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).14
In addition, it was considered that PTDM developed when the patients used glucose lowering medications (insulin and/or oral hypoglycemic agents for > 1mo) which were given by the nephrologist or endocrinologist at anytime during the study. Diagnosis was always confirmed by measuring FBG and/or HbA1c of these patients.
As OGTTs were time consuming and impractical in a large transplant program we did not use OGTTs routinely in our unit. We use OGTTs in specific cases such as with patients who had impaired fasting glucose within the first week after transplantation. OGTTs were performed after week six (meanly in week eight) depending on the transient hyperglycemia which was frequently seen in the first six weeks when intensive immunosuppressive therapy was used. Also, OGTTs were performed on the patients with body mass index (BMI) > 30 kg/m2 who had a family history of diabetes and the patients who were diagnosed with impaired fasting glucose at any time during the follow-up period.
OGTT detects the possibility of uncovering IGT which is a prediabetic condition. It is defined by a 2-h plasma glucose (2hPG) of 140-199 mg/dl.
As this study was a retrospective analysis, the patients with transient hyperglycemia were not accepted as PTDM and these patients were included in non-PTDM group. In other words, the patients who were still diabetic and treated with antidiabetic agents on the day of the study were included in PTDM group.
HbA1c was certainly not used as a diagnostic criterion in the first three months after transplantation. Then it was used as a diagnostic criterion in combination with elevated FBG level.
PTDM group was divided to four subgroups according to the time of developing PTDM such as, the first 3 months, 3-6 months, 6-12 months and 12 months after renal transplantation. Patients and laboratory characteristics of PTDM were compared with the patients who did not develop post-transplant diabetes, to investigate the incidence of PTDM and find out various risk factors associated with occurrence of PTDM.
Immunosupression
Induction therapy was given all patients. Immunosuppression comprised rabbit antithymocyte globuline (ATG) or IL-2 receptor monoclonal antibody (basiliximab) according to induction therapy, methylprednisolone (1000 mg given intraoperatively, followed by sequential tapering to daily oral prednisone 30 mg by one week, 10mg at one month and 5 mg on the 12th week posttransplantation period), Mycophenolate-mofetil (MMF) or mycophenolate sodium (MMY) at 2 × 1000 mg/d or 2 × 720 mg/d postoperatively with dose adjustment for side effects, calcineurin inhibitors (CNI) (tacrolimus or cyclosporin-A started within 24 h after surgery). Cyclosporin-A (CsA) was started at 8 mg/kg/day, Tacrolimus at 0.2 mg/kg/day, and then adjusted according to total blood levels. Target CsA levels at 3 months were 150-250 ng/ml and then tapered to 100-150 ng/ml by 1 year. Target tacrolimus levels were 7-10 ng/ml in the three months, and then tapered to 4-7 ng/ml. The standard immunosuppressive protocol (maintenance therapy) mainly consists of triple therapy composed of steroids, a calcineurin inhibitor (cyclosporine or tacrolimus), and MMF/MMY.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed with SPSS software version 17.0 for windows. All continuous data were expressed as mean ± SD and were analyzed by unpaired t test. Categorical data were expressed as number (percentage) and were analyzed by χ 2 test. Univariate vs multivariate logistic regression analysis were done to evaluate odds ratio of various parameters associated with increased risk of PTDM among study population. p value of <0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Results
We retrospectively analyzed the records of 570 patients who underwent a renal transplantation at Istanbul Bilim University, School of Medicine, from 2005 to 2014. The following patients were excluded: 4 patients whose age were under 18, 55 patients whose follow-up period less than 6 months, 3 patients who underwent 2 or more renal transplants, and 88 patients who were diabetic before surgery. The data of the remaining 420 non-diabetic patients who underwent a renal transplant for the first time and had a renal graft survival time of more than 6 months, were included for analysis. Totally 420 patients (152 female; mean age was 44.5 ± 12.3) had an average follow-up time of 42.2 ± 21.8 months years until the endpoints of follow-up.
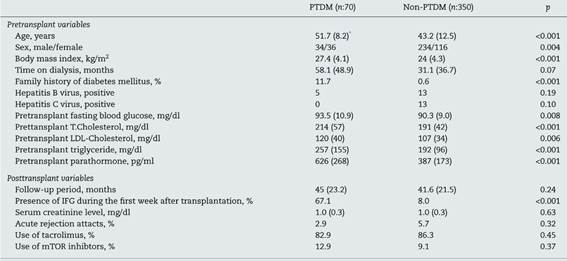
Seventy (16.6%) of total patients had onset of PTDM, of them 36 were female. Mean age was 51.7 ± 8.2 years, mean BMI was 27.4 ± 4.1 kg/m2 and mean follow-up time was 45 ± 23.2 months. 37 of these cases (52.8%) developed PTDM within the first three months, 11 of them (15,7%) developed during the 3-6 months, 4 of them (5.7%) developed during 6-12 months and 18 of them (25.8%) developed PTDM 12 months later after renal transplantation. During the follow-up period, 3 patients died with functioning graft, 10 patients had transferred dialysis due to graft loss, 8 patients were followed in other centers and remaining 49 patients were followed in our unit.
Remaining 350 patients were non-PTDM. 116 of these were female, mean age was 43.2 ± 12.5 years, mean BMI was 24 ± 4.3 kg/m2 and mean follow-up time was 41.6 ± 21.5 months. Compared with the non-PTDM group, the PTDM group was older, had higher body mass index values, and had higher proportions of female patients (p < 0.001, <0.001 and 0.004, respectively). Follow-up period was similar between the two groups (p = 0.24). During the follow-up period, 15 patients died with functioning graft, 30 patients had transferred dialysis due to graft loss, 25 patients were followed in other centers and remaining 280 patients were followed in our unit.
The most common causes of primary renal failure were chronic glomerulonephritis and cyctic renal diseases in each groups (p = 0.54). While 88.6% of PTDM group received dialysis treatment before transplantation for a period of 58.1 ± 48.9 months; that was 90.6% in non-PTDM group, for a period of 31.1 ± 36.7 months. History of dialysis and duration of this therapy were similarly found between patients with PTDM and non-PTDM (p = 0.07). While 11.7% of PTDM group had a family history of diabetes, only 0.6% of other group had a family history of diabetes (p < 0.001).
Eight patients had cadaveric kidneys in PTDM group, live donor transplant were performed in 62 patients, [75.8% first-degree relatives (mother, father, siblings, childrens), 8.1% second degree relatives (grandparents, grandmother, uncle, etc.) and remaining 16.1% patients unrelated donor]. In the non-PTDM group 33 patients had cadaveric kidney and live donor transplant were performed in 317 patients (78.1% first-degree relatives, 7.7% second degree relatives and 14.2% patients unrelated donor). There were no significant difference between two groups according to type of donor and degrees of related living donors (p = 0.64 and 0.91, respectively).
The patients’ clinical and laboratory parameters are shown in Table 1. PTDM group had higher preoperative FPG and lipid profile (T.Chol and LDL-Chol and TG levels). IFG during the first week after transplantation was determined in 47 (67.1%) of PTDM developed patients and 28 (8%) in non-PTDM group (p < 0.001).
OGTTs were performed on a total of 94 patients (75 patients with IFG in the first week after transplantation, 9 patients with BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 and had family history of diabetes, 10 patients with IFG during the follow-up period). Among these patients PTDM was diagnosed in 56 patients and IGT was diagnosed in 10 patients.
Five patients were hepatitis B virus (HBV) positive and none of them was hepatitis C (HCV) positive before transplantation in PTDM group. In non-PTDM group, 13 were HBV and 13 were HCV positive before transplant. Incidence of HBV and HCV were found similarly between two groups (p = 0.19 and 0.10).
As induction treatment, 29 patients received ATG and 41 patients received basiliximab (IL-2 receptor antagonist) in PTDM groups, whereas 160 patients received ATG and 190 patients received basiliximab (IL-2 receptor antagonist) in non-PTDM groups (p = 0.54). It was found that 82.9% of patients with PTDM, 86.3% of patients with non-PTDM used tacrolimus as calcineurin inhibitors while 87.1% and 92.3% of patients used MMF/MMY, respectively. The use of mTOR inhibitors was found 12.9% and 9.1% in both groups respectively. The ratio of using mTOR inhibitors, tacrolimus and cyclosporine were found similar in each group (p:0.37, 0.45 and 0.24, respectively).
Maintenance therapy was found similar among groups (p > 0.05). 2.9% of patients in PTDM group and 5.7% of patients in non-PTDM group had acute rejection attacks during the follow-up period. Incidence of acute rejection attacks was similar between two groups (p = 0.32).
Older age, gender, high BMI, presence of IFG during the first week period after transplantation, presence of hypertriglyceride, hypercholesterolemia and hyperparathyroidism during the pretransplant period, presence of family history of diabetes were predictors of development of PTDM in univariate logistic regression analysis. Multivariete logistic regression analysis were shown in Table 2. Older age, high BMI, presence of IFG during the first week period after transplantation, presence of hypertriglyceride and hyperparathyroidism during the pretransplant period were predictors of development of PTDM in multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Table 2 Multivariate logistic regression analysis.
| Parameter | p | Odds Ratio (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.031 | 1.04 (1.00-1.08) |
| BMI | 0.045 | 1.10 (1.00- 1.21) |
| Pretransplant triglyceride (for every 100mg/dl increased) | 0.02 | 1.46 (1.06- 2.02) |
| Posttransplant IFG | <0.001 | 19.95 (8.73-45.60) |
| Pretransplant PTH | <0.001 | 1.02 (1.00-1.04) |
Discussion
We observed an incidence of 16.6% of PTDM in our cohort. Development of PTDM was highest at the six months period following transplantation. Significant relationships were found between PTDM and presence of family history of diabetes, pretransplant glucose levels, hyperparathyroidism and dyslipidemia, presence of IFG during the first week period after transplantation. Older age, obesity, presence of IFG during the first week period after transplantation, presence of hypertriglyceridemia and hyperparathyroidism during the pre transplant period were predictors of development of PTDM. No association was observed between onset of PTDM and immunosuppressive treatment.
PTDM is a serious metabolic complication and is the major factor leading to dysfunction of the renal graft and patient death moreover, it is a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases in these patients.15-17 Several in-depth clinical and animal studies have been conducted to study the prevalence rate, risk factors, and pathogenesis of PTDM.18-21
The true incremental incidence of diabetes occurs mainly during the first 6 months posttransplantation, when patients are treated with high doses of immunosuppression. There is a five-to sixfold higher incidence of new-onset of diabetes mellitus among transplant recipients during the first year after transplantation.22 In our study it was observed that more than half of the patients (52.8%) had diagnosis of PTDM in the first three months and also 68.5% of patients had PTDM during the six months period after transplantation.
The literature describes various modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors for the development of PTDM.23 Non-modifiable risk factors include race, older age, male recipient, positive family history of diabetes, presence of certain HLA phenotypes, increasing HLA mismatches, deceased donor, presence of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, and impaired pre-transplant FPG or OGTT. Modifiable risk factors are type of immunosuppressive therapy, obesity, male gender of donor, pre-transplant hypertriglyceridemia, HCV infection and cytomegalovirus (CMV) disease.23 In our study, older age, presence of hypertriglyceride, obesity, hyperparathyroidism during the pre transplant period, presence of IFG during the first week period after transplantation were established as the risk factors of PTDM.
Among the non-modifiable risk factors, age is considered as the strongest risk factor for the development of PTDM.23,24 A study by Cosio et al.25 that included 2078 allograft recipients, showed that individuals older than 45 were 2.9 times more likely to develop PTDM than those younger at the time of transplantation. Age increased the risk for development of diabetes 1.5-fold for every 10-year increase in age.37,39 In our study, older age was established as a risk factor of PTDM.
Obesity represents a modifiable risk factor and has been shown to be associated with the development of PTDM in many studies.24,26,27 Analysis of the USRDS database revealed that obesity, defined as a BMI of >30 kg/m2 is one of the strongest risk factors for PTDM (relative risk (RR) of 1.73, p < 0.0001).24,26 Although some studies failed to demonstrate an association between obesity and the development of PTDM, obesity and its associated peripheric insulin resistance state is a known risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Shah et al.28 also found that the risk of PTDM increased as BMI increased. Compared with patients with a BMI < 25 kg/m2, the risk of developing PTDM was higher in patients with a BMI within the range of 25-30 kg/m2 (RR:1.51; p < 0.001) and in patients with a BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 (RR:1.64; p < 0.001). In our study, obesity or being overweight were determined as risk factors of PTDM.
In this study we observed that pre-transplant TG levels were a risk factor for PTDM. Cosio et al.29 found that elevated triglyceride levels before transplantation correlated strongly with the development of PTDM in a retrospective analysis of 1811 renal transplant recipients. Porrini et al.30 also found that pretransplantation hypertriglyceridemia was a risk factor for PTDM in patients treated with tacrolimus as a primary immunosuppressant. Hypertriglyceridemia is strongly linked with insulin resistance, one of the two central pathophysiological defects of PTDM, which would explain why hypertriglyceridemia seems to be associated with an increased risk of PTDM.31
We determined an association between PTDM and presence of IFG during the first week after transplantation and that was a risk factor of developed PTDM. IFG or IGT are strong predictors for the development of PTDM.5,32 Cosio et al.33 showed that hyperglycemia during the first week after transplantation is the strongest predictor of PTDM at 1 year. In this study PTDM was present in 3% of patients who were euglycemic 1 week after transplantation, 14% of patients who had IFG 1 week after transplantation, and 50% of patients who had diabetes 1 week after transplantation, at 1 year.
Earlier studies reported that there was a high incidence of de novo hyperglycemia immediately after transplantation which can be associated with the exposure of pancreatic β-cells to several stress factors, collectively the surgical procedure, weight gain due to physical inactivity immediately after surgery (insulin sensitivity), high doses of corticosteroids and initiation of CNIs.34 Pre-transplant impaired OGTT has also been reported as risk factor for PTDM.35 However, routine OGTT analysis during pre-transplant work-up was not done at our center; hence we could not analyze impact of this potential factor.
Primary hyperparathyroidism (pHPT) and secondary hyperparathyroidism are both associated with abnormalities in glucose metabolism, such as glucose intolerance and insufficient insulin release.36-39 Ivarsson et al.40 found that intact parathormone (iPTH) values above twice the upper limit of the normal range were associated with PTDM. Hyperparathyriodism was established as a risk factor for the development of PTDM in our study. Hyperparathyroidism and hypophosphatemia along with additional diabetogenic factors such as immunosuppressive agents might induce glucose intolerance and insufficient insulin release and thereby trigger the development of PTDM.41,42
There is strong evidence suggesting that positive family history of diabetes among first-degree relatives is an important risk factor for development of PTDM in transplant recipients.13,26 Although some researchers have reported that a family history of diabetes mellitus is associated with an up to sevenfold increase in the risk of developing PTDM43,44 others have not found any positive relationship between family history of diabetes and risk for PTDM.11 Family history of diabetes was observed at a higher rate in our PTDM patients. In our study family history of diabetes was not determined as a risk factor for development of PTDM in multivariate analysis. Although family history plays a significant role in predicting PTDM, it has not been evaluated in registry reports; however multivariate analysis of quite a few studies showed family history of diabetes as a significant risk factor.43,45
Several immunosuppressive agents that are commonly used in the transplant arena have been noted to have diabetogenic potential. Herein, commonly used drugs include glucocorticoids, calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs), the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors. Diabetogenic effects of all of these drugs have been explored in detail and their effect on the development of PTDM has been elucidated in several major studies.46 In DIRECT trial, incidence of PTDM was significantly higher among patients treated with tacrolimus as compared to cyclosporine group.12 However, interaction between CNI and PTDM development is quite complex and there are multiple confounding variables reported.12,47-49 Thirty-three percent dose reduction of tacrolimus resulted in enhanced insulin secretion without change in therapeutic concentration of tacrolimus levels (5-10ng/ml). This suggests that diabetogenic effect of tacrolimus is dose dependent.49 However, in some studies, authors did not observe any association between tacrolimus and PTDM.50,51 In our study, there was no significant difference between tacrolimus and cyclosporine. Moreover usage of CNI was not detected as a risk factor of PTDM. Majority of patients were receiving tacrolimus based immunosuppressive therapy and therapeutic concentration of tacrolimus levels were targeted at the low dose range. For these reasons, it might not be detected as a risk factor.
Our study was retrospective and reflects a single center experience. These are the most important limitations of our study. Although we tried to keep the immunosuppressive drugs between target levels, in this study we did not evaluate the effect of drug levels on the development of PTDM. In addition, we could not analyze the effect of posttransplant changes of BMI on the development of PTDM. These are the other limitations of our study.
As a conclusion, PTDM is a common metabolic disorder. PTDM is diagnosed most frequently during the first six months after transplantation. Older age, presence of hypertriglyceridemia, obesity, hyperparathyroidism during the pre transplant period, presence of IFG during the first week period after transplantation are the risk factors of PTDM. All of transplant recipient patients should be screened for IFG within the first week of intensive immunosuppression. Patients with dyslipidemia, elderly and obese patients during the pretransplant period should be closely monitored for the risk of development of PTDM.