Mi SciELO
Servicios Personalizados
Revista
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Accesos
Accesos
Links relacionados
-
 Citado por Google
Citado por Google -
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO -
 Similares en Google
Similares en Google
Compartir
Nutrición Hospitalaria
versión On-line ISSN 1699-5198versión impresa ISSN 0212-1611
Nutr. Hosp. vol.29 no.6 Madrid jun. 2014
https://dx.doi.org/10.3305/nh.2014.29.6.7486
INFORNUT® Process; improves accessibility to diagnosis and nutritional support for the malnourished hospitalized patient; impact on management indicators; two-year assessment
Proceso INFORNUT®; mejora de la accesibilidad del paciente hospitalizado desnutrido a su diagnóstico y soporte nutricional; repercusión en indicadores de gestión; dos años de evaluación
Juan Luis Villalobos Gámez1-3, Cristina González Pérez3, José Manuel García-Almeida1,2,4, Alfonso Martínez Reina5, José del Río Mata5, Efrén Márquez Fernández3, Rosalía Rioja Vázquez1,2,4, Joaquín Barranco Pérez6, Alfredo Enguix Armada2,7, Luis Miguel Rodríguez García2,8, Olga Bernal Losada4, Diego Osorio Fernández2,9, Alfredo Mínguez Mañanes2,10, Carlos Lara Ramos3, Laila Dani3, Antonio Vallejo Báez2,11, Jesús Martínez Martín12, José Manuel Fernández Ovies3, Francisco Javier Tinahones Madueño5 and Joaquín Fernández-Crehuet Navajas13
1Nutritional Support Team.
2Nutrition Committee.
3Hospital Pharmacy /Nutrition Section.
4Endocrinology and Nutrition.
5Clinical Documentation.
6Information Systems.
7Laboratories.
8Internal Medicine.
9General Surgery.
10Anesthesiology / Reanimation.
11Intensive Care Medicine.
12Financial Control.
13Preventive Medicine.
Hospital Clínico Universitario Virgen de la Victoria (Virgen de la Victoria University Hospital). Complejo Hospitalario de Málaga (Hospital Complex of Malaga). Spain.
ABSTRACT
Introduction: The high prevalence of disease-related hospital malnutrition justifies the need for screening tools and early detection in patients at risk for malnutrition, followed by an assessment targeted towards diagnosis and treatment. At the same time there is clear undercoding of malnutrition diagnoses and the procedures to correct it.
Objectives: To describe the INFORNUT program/ process and its development as an information system. To quantify performance in its different phases. To cite other tools used as a coding source. To calculate the coding rates for malnutrition diagnoses and related procedures. To show the relationship to Mean Stay, Mortality Rate and Urgent Readmission; as well as to quantify its impact on the hospital Complexity Index and its effect on the justification of Hospitalization Costs.
Material and methods: The INFORNUT® process is based on an automated screening program of systematic detection and early identification of malnourished patients on hospital admission, as well as their assessment, diagnoses, documentation and reporting. Of total readmissions with stays longer than three days incurred in 2008 and 2010, we recorded patients who underwent analytical screening with an alert for a medium or high risk of malnutrition, as well as the subgroup of patients in whom we were able to administer the complete INFORNUT® process, generating a report for each. Other documentary coding sources are cited. From the Minimum Basic Data Set, codes defined in the SEDOM-SENPE consensus were analyzed. The data were processed with the Alcor-DRG program. Rates in of discharges for 2009 and 2010 of diagnoses of malnutrition, procedure and procedures-related diagnoses were calculated. These rates were compared with the mean rates in Andalusia. The contribution of these codes to the Complexity Index was estimated and, from the cost accounting data, the fraction of the hospitalization cost seen as justified by this activity was estimated.
Results: Results are summarized for both study years. With respect to process performance, more than 3,600 patients per year (30 of admissions with a stay > 3 days) underwent analytical screening. Half of these patients were at medium or high risk and a nutritional assessment using INFORNUT® was completed for 55 of them, generating approximately 1,000 reports/year. Our coding rates exceeded the mean rates in Andalusia, being 3.5 times higher for diagnoses (35); 2.5 times higher for procedures (50) and five times the rate of procedure-related diagnoses in the same patient (25). The Mean Stay of patients coded with malnutrition at discharge was 31.7 days, compared to 9.5 for the overall hospital stay. The Mortality Rate for the same patients (21.8%) was almost five times higher than the mean and Urgent Readmissions (5.5%) were 1.9 times higher. The impact of this coding on the hospital Complexity Index was four hundredths (from 2.08 to 2.12 in 2009 and 2.15 to 2.19 in 2010). This translates into a hospitalization cost justification of 2,000,000€; five to six times the cost of artificial nutrition.
Conclusions: The process facilitated access to the diagnosis of malnutrition and to understanding the risk of developing it, as well as to the prescription of procedures and/or supplements to correct it. The interdisciplinary team coordination, the participatory process and the tools used improved coding rates to give results far above the Andalusian mean. These results help to upwardly adjust the hospital Complexity Index or Case Mix-, as well as to explain hospitalization costs.
Key words: Disease-related malnutrition. Nutritional screening. Hospital costs. Diagnostic-related group. Mean Complexity or Complexity Index.
RESUMEN
Introducción: La alta prevalencia de desnutrición hospitalaria relacionada con la enfermedad justifica la necesidad de herramientas de cribado y detección precoz de los pacientes en riesgo de desnutrición, seguido de una valoración encaminada a su diagnóstico y tratamiento. Existe asimismo una manifiesta infracodificación de los diagnósticos de desnutrición y los procedimientos para revertirla.
Objetivos: Describir el programa/proceso INFORNUT® y su desarrollo como sistema de información. Cuantificar el rendimiento en sus diferentes fases. Citar otras herramientas utilizadas como fuente de codificación. Calcular las tasas de codificación de diagnósticos de desnutrición y procedimientos relacionados. Mostrar su relación con Estancia Media, Tasas de Mortalidad y Reingreso urgente; así como cuantificar su impacto en el Índice de Complejidad hospitalario y su efecto en justificación de Costes de Hospitalización.
Material y métodos: El proceso INFORNUT® se basa en un programa de cribado automatizado de detección sistemática e identificación precoz de pacientes desnutridos al ingreso hospitalario, así como de su valoración, diagnóstico, documentación e informe. Sobre el total de ingresos con estancias mayores de tres días habidos en los años 2008 y 2010, se contabilizaron pacientes objeto de cribado analítico con alerta de riesgo medio o alto de desnutrición, así como el subgrupo de pacientes a los que se les pudo completar en su totalidad el proceso INFORNUT® llegando al informe por paciente. Se citan otras fuentes documentales de codificación. Del Conjunto Mínimo de la Base de Datos se analizaron los códigos definidos en consenso SENPE-SEDOM. Los datos se procesaron con el programa Alcor-GRD. Se calcularon las tasas en altas dadas para los años 2009 y 2010 de diagnósticos de desnutrición, procedimientos y diagnósticos asociados a procedimientos. Se compararon dichas tasas con las tasas medias de la comunidad andaluza. Se estimó la contribución de dichos códigos en el Indice de Complejidad y, a partir de los datos de contabilidad analítica, se estimó la fracción del coste de hospitalización que se ve justificada por esta actividad.
Resultados: Resumimos aquí un resultado para ambos años estudiados. En cuanto al rendimiento del proceso, más de 3.600 pacientes por año (30 de los ingresos con estancia > 3 días) fueron objeto de cribado analítico. La mitad de ellos resultaron de riesgo medio o alto, de los cuales al 55 se les completó una valoración nutricional mediante INFORNUT®, obteniéndose unos 1.000 informes/año. Nuestras tasas de codificación superaron a las tasas medias de Andalucía, siendo 3,5 veces superior en diagnósticos (35 ); 2,5 veces en procedimientos (50 ) y quintuplicando la tasa de diagnósticos asociados a procedimientos en el mismo paciente (25 ). La Estancia Media de los pacientes codificados al alta de desnutrición fue de 31,7 días, frente a los 9,5 de global hospitalaria. La Tasa de Mortalidad para los mismos (21,8 %) fue casi cinco veces superior a la media y la de Reingresos "urgentes" (5,5 %) resultó 1,9 veces superior. El impacto de dicha codificación en el Índice de Complejidad hospitalario fue de cuatro centésimas (de 2,08 a 2,12 en 2009 y de 2,15 a 2,19 en 2010). Esto se traduce en una justificación de costes de hospitalización por 2.000.000 €; cinco a seis veces el coste de la nutrición artificial.
Conclusiones: El proceso ha facilitado el acceso al diagnóstico de la desnutrición o al conocimiento del riesgo de padecerla, así como a la prescripción de los procedimientos y/o suplementos para remediarla. La coordinación interdisciplinar del equipo, lo participativo del proceso y las herramientas utilizadas mejoran las tasas de codificación hasta resultados muy por encima de la media andaluza. Estos resultados contribuyen a ajustar al alza el IC hospitalario, así como a la justificación de costes de hospitalización.
Palabras clave: Desnutrición relacionada con la enfermedad. Cribado nutricional. Costes hospitalarios. Grupo relacionado con el diagnóstico. Complejidad media o Índice de Complejidad.
Introduction
Hospital malnutrition is a common problem in patients admitted to hospital. Values of hospital malnutrition range between 10% and 85% depending on the type of patients studied (elderly, children, medical, surgical, oncology, etc.), the category of hospital to which they are admitted, and the nutritional assessment markers used for patient evaluation. There is consensus that the prevalence of disease-related malnutrition ranges from 20 to 50%1-6. When nutritional status is deficient, recovery is delayed, hospital stays are pro-longed and readmission rates increase, negatively affecting health care costs.7,8
In developed countries the problem of malnutrition particularly affects hospitalized persons. As early as 1994 the high prevalence of malnutrition (40%) and the poor documentation of nutritional information in medical records was made evident, with coding at less than 50% in malnourished patients.9
Pérez de la Cruz et al.10 found a malnutrition prevalence of 0.3% using only anthropometric measurements, and 13.4% considering body mass index. When analyzing biochemical markers, the rate rose to 65.7%.
There was an increase in corresponding costs in relation to duration of hospital stay (68.04% higher in malnourished patients than in normally nourished patients). The same authors studied the relationship of malnutrition on admission to mean stay (MS) and premature readmission rates (RR), finding an increase of 2.7 days in MS.11
The PREDyCES12 multicenter study recently concluded that 23.7% of 1597 patients evaluated presented malnutrition on hospital admission (rising to 37% in those >70 years and 47% in those >85 years). Patients with malnutrition (on admission or discharge) had a significantly higher MS (11.5 days versus 8.5 days, p <0.001, and 12.5 days versus 8.3 days, p <0.001 respectively).
Given the importance of the problem of malnutrition, both because of its prevalence, and the clinical and economic consequences involved, various international agencies13,14 and scientific societies15-18 have highlighted the need for a screening method that is valid, reliable, reproducible, convenient and coordinated with specific action protocols. There are clinical, automated and mixed screening methods. Most clinical screening methods include subjective and objective data (weight, height, weight changes, changes in food intake, comorbidities, etc.). Automated methods are fundamentally based on analytical data, but also collect other useful objective screening data (diagnosis, age, duration and evolution of illness, resources used, etc.) available in the database of the hospital computer system.16 In 2005, the II SENPE Discussion Forum15 noted that given the positive predictive value of filters such as CONUT® 19 and FILNUT® 20 where weighing and measuring all patients on admission is not possible, these types of information systems must be used to identify those patients who can most benefit from a complete nutritional assessment.
By applying the CONUT® analytical nutritional filter, Ulíbarri et al. detected malnutrition on admission in more than a quarter of patients. Among the various causal elements of malnutrition they describe, they highlighted the existence of widespread ignorance about this problem. Thus disease-related malnutrition is common, fails to be detected and worsens during hospital stays, except for a small group of patients (<10%), from among those who would have been detected by the filter method had it been used.19,21,22
The INFORNUT® process is based on an automated screening program of systematic detection and early identification of malnourished patients on hospital admission, as well as for documentation and reporting.16 It has three phases.
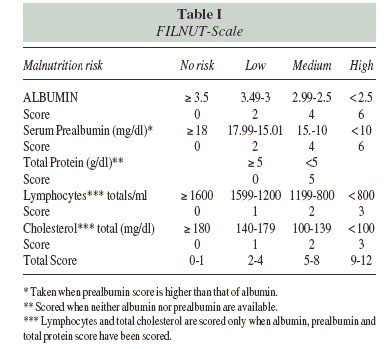
In the first phase, the analytical nutritional filter, the conditions applied are: albumin <3.5 g/dL and/or total protein <5 g/dL and/or prealbumin <18 mg/dL with or without total lymphocytes <1600 cells/ml and/or total cholesterol <180 mg/dL. The FILNUT-Scale23 assessment scale is then applied to the positive results. These conditions have been validated as an analytical filter for risk of malnutrition, with a positive predictive value of 94.1%, sensitivity of 92.3% and specificity of 91.2%.20 The good cost/benefit ratio of implementing analytical screening at hospital admission, with a cost of less than 0.60 €, seems clear, especially when it increases efficiency and early detection of at-risk patients24. The second and third phases of the INFORNUT® process are explained in the materials and methods section of this paper.
The resolution on Food and Nutritional Care in Hospitals, issued by the Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe in 2003,13 considers that the lack of cooperation between the different groups and levels of professionals involved is one of the factors causing hospital malnutrition and urges the different professionals to work together to provide nutritional care.25
We know that coding is a key exercise in health management that is governed by well-established procedures. Proper coding of hospital malnutrition, as a primary or secondary diagnosis, and of therapeutic procedures employed, contributes an understanding of the reality of healthcare activity and resource consumption at each center.26 Aware of the importance of these measures, the Spanish Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (SENPE), together with the Spanish Society of Medical Documentation (SEDOM), has contributed to the EU strategy by developing the Consensus Document on Coding Malnutrition SENPE-SEDOM27. This document has enabled standardization of the coding process for this condition by assigning specific codes to specific defining terms and optimizing the information on malnutrition, its types and degrees and the methods used for prevention and treatment in hospitals in our National Health System. In 2011, the Multidisciplinary Consensus on Addressing Hospital Malnutrition in Spain1 ratified the malnutrition criteria established in the SENPE-SEDOM consensus when performing malnutrition screening.
Villalobos Gámez et al.28 in 2004 measured the impact of coding malnutrition and nutritional support procedures showing a Complexity Index (CI) or Case Mix Index increase from 1.84 to 1.89. This also affected a drop in the Hospital Stay Usage Index from 1.05 to 1.03. Of 21,121 total discharges, they found that this coding caused a change in Diagnosis-Related Group (DRG) in 721 patients (3.41% of the discharges and 24.47% of those coded). The authors concluded that the integrated action of the nutritional support teams with pharmacy, clinical documentation and information systems development services, greatly improved management results. Álvarez Hernández et al.29 evaluated 10,451 discharges, recoding a sample of 134 patients using information from the nutrition unit. The impact found was an increase of 0.035 in CI.
Another 2004 study in Singapore30 applied the Subjective Global Assessment (SGA) screening31 to 658 patients. The authors estimated an overall prevalence of malnutrition of 15%. Malnutrition coding showed increased complexity in 23% of episodes, measured in terms of costs and expected duration of stay. For patients whose complexity increased through malnutrition coding, an increased case-mix funding of 59.7% was estimated. If none of the cases of malnutrition had been coded, it was estimated that the hospital would have experienced the equivalent of $16,617 in lost reimbursement.
Following the precedent set by similar studies such as those conducted in the US,32 the Ockenga group,33 in 2005, evaluated the effect of the identification and coding of malnutrition in the DRG system adapted to Germany. To do this, they performed SGA31 screening in 541 patients in the gastroenterology area of a German hospital. The malnutrition rate detected increased from 4% to 19%. Malnourished patients showed a significantly longer hospital stay. The additional malnutrition coding raised the case mix index from 1.53 to 1.65, given that it was only relevant in 27% of patients, because in patients with comorbidities, which in themselves are already complex, the effect of malnutrition may not add differences in severity. However, the malnutrition coding resulted in an overall reimbursement increase of 360€ per malnourished patient. The authors note that this additional reimbursement covered about 75% of the nutritional interventions necessary.
In a study conducted in Portugal,34 469 patients from two hospitals were assessed with Nutritional Risk Screening (NRS) 2002.35 Of these, 42% were classified as nutritionally at-risk patients. Using a multivariate model, it was estimated that the cost of treating a nutritionally at-risk patient was 19% higher than the average for the respective german DRG. Moreover, the hospitalization costs for nutritionally at-risk patients were double those who were not at nutritional risk. From the sample analyzed, and considering the observed case-mix, this may represent a cost increase of between 200 and 1500 €. From an economic point of view, given the low cost of most nutritional interventions, these results support the need for appropriate nutritional screening and nutritional treatment.
In 2011 Rowell36 published the results of a study involving 256,865 Australian patients admitted between 2003 and 2004. Hospitalization costs were estimated by a least squares regression model that included malnutrition coding, coded malnutrition treatment and severity of disease as factors. Approximately 1.87% of patients were coded as malnourished, but up to 17.3% had a documented diagnosis and/or treatment for malnutrition. Adjusting the model, they estimated the cost to their health system of malnutrition at 10.7 million Australian dollars.
More recently, the prevalence of malnutrition and its impact on outcomes and hospital costs was evaluated in 818 patients at a hospital in Singapore.37 Through SGA, 235 malnourished patients (29%) were detected, of whom only 3 had been coded as such. Forty-five percent had a longer than recommended hospital stay, according to their DRG, compared to 21% of the normally nourished. Adjusting for age, gender, race and DRG, a greater MS (6.9 vs 4.6 days) and a longer stay by DRG, RR 15 days from discharge, Mortality Rate (MR) in the first year, and annual hospitalization costs per patient were detected and found to be statistically significant. The authors believe that the adjustment for DRG minimizes the confounding effect of the disease and its complexity. Thus they argue that malnutrition is an independent predictor of hospital stay, readmission, mortality and hospital costs.
Regarding consumption costs for nutritional support, Villalobos et al.38 studied the difference between 1996 and 1998 produced by the implementation of an instruction protocol. Use of enteral nutrition increased and an approximate cost savings of 99,000€ in parenteral nutrition was seen. The cost per admission fell from 14.86€ to 12.63€ and the cost per stay from 1.54€ to 1.42€ (Original expressed in pesetas, only the purchase prices of components are considered).
Objectives
To describe the INFORNUT® program/process and the tables and algorithms used: Analytical risk rating scale, scale for scoring nutritional risk, assessment scale -for diagnosis- of analytical and anthropometric parameters and the diagnostic orientation algorithm. To present the INFOrme de Riesgo por desNUTricion (INFORNUT) model for individualized malnutrition risk reporting which, in Spanish, gives the name to the process. To cite other tools used as a coding source.
To quantify performance at different phases of the process, applied to admissions with stays of more than three days, from 2008 through 2010 at the Virgen de la Victoria University Hospital.
To describe the diagnostic coding rates of malnutrition and related therapeutic procedures, according to ICD-9, at our hospital in 2009 and 2010. To compare these coding rates with those described for Andalusia during this period. To quantify the impact of malnutrition on CI, MS, MR and RR at this hospital.
To estimate the justification of hospitalization costs linked to the incidence of coding on the center's CI in 2009 and 2010. Compare this amount with the cost per use of enteral and parenteral nutrition. Calculate the cost of nutritional support given per discharge and per stay.
To show, through its results, that INFORNUT® is a tool for integrated teamwork, improving patient access to early diagnosis of malnutrition, nutritional support treatment and coding at discharge, with implications for management indicators.
Material and Methods
Hospital Information Systems Tools
The project involved several departments, including Information Systems, which provided an analyst-developer tasked with carrying out the applications needed to meet the functionality requested by the Nutritional Support Team for INFORNUT. In the first stage of analysis we agreed to address the following challenges:
- Integration of data from three environments that were not interconnected at that time:
• Laboratory
• Admissions / Hospitalization
• Nutritional Support Team / Pharmacy.
- Creation of tools for input, storage and management of information to allow interdisciplinary work.
The system performs a daily analytical screening, at dawn, from the analytical results of hospitalized patients, to assess the degree of malnutrition risk for each patient. This information is incorporated into the rest of the information on which the nutritional filter algorithm is based. To carry out this integration of information the free software application Talend Open Studio (TOS) was used. This is an ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) system that allows the extraction of information from one system and its processing and loading into another system. There are no license fees for use, which influenced this choice.
Although, traditionally, the Health Language 7 (HL7) messaging protocol has been used for communication between systems handling health information, when the project was launched TOS lacked these HL7 connectors. For this reason a shared space is used where the Laboratory Information System provides the patients' analytical results, from which TOS extracts the necessary information. After determining the degree of malnutrition based on the calculation algorithm, TOS transfers the results to the Hospital Information System.
For a better understanding of the results, we briefly describe the INFORNUT® process and program. In the first phase, or nutritional filter stage, a score from a check of the analyses is given according to the FILNUT-Scale (table I)39 activating a visual risk alarm on the control panel of the ward nurses, as well as on that of the medical department responsible for the patient.
This is followed by a second phase of incorporation of clinical data into the software application (fig. 1) by the nurse, doctor, nutritionist or pharmacist responsible for each patient, through completion of a MUST40-42 test the rating scale which was modified for use in the process (Modified-MUST) (table II).39
On the same screen the survey on intake by quartiles over the preceding five days is completed, as defined in NRS 2002,35 leaving a field for notes. Furthermore, functionality within the hospital information system was developed to allow health care personnel to view nutritional risk alarms and introduce anthropometric data to calculate the Modified-MUST. The transverse solutions require more initial analysis and coordination effort, but they provide a greater benefit.
The possibility of carrying out the MUST assessment on any patient admitted, particularly those displaying obvious thinness, regardless of whether an analytical alert was produced, provides the opportunity to detect cases of calorie malnutrition exclusively, as would be the case with anorexia nervosa, that do not affect analytical parameters. There are clinical nutrition care processes recommended by the Health Systems for the different geographical areas of responsibility that prescribe structured tests as a screening measure in hospitalization. In this sense INFORNUT® does not contradict these recommendations as the possibility exists of performing this screening test on any patient admitted, regardless of the analytical data. This feature enables the incorporation of this system into other nutritional assessment strategies on admission.
Based on the laboratory data and information collected by the nursing staff, the system performs a recalculation using the scoring algorithm and establishes a modified-MUST nutritional risk for the patient. This nutritional risk is visible through alerts in key points of the patient's dietary treatment, such as in the care processes, pharmacy and kitchen. The alerts are displayed in different colors depending on the seriousness of the malnutrition (fig. 1).
Each individual parameter is analyzed according to a "modified" scale (table III)39 based on the scale contained in the SENPE-SEDOM agreement.27 This scale then assigns a diagnostic (fig. 2) and therapeutic orientation based on local algorithms incorporated into the program, depending on the type of malnutrition and intake capacity.39 Although there are no universally accepted criteria for nutritional diagnosis, the INFORNUT® process is open to recalculating diagnostic criteria according to changes in worldwide recommendations. There are analytical data such as the prealbumin/ C-reactive protein ratio performed systematically in our laboratory that are helping to bring us closer to the acute disease-related malnutrition concepts of the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN) recommendations.43
Regardless of the name of the relevant information format from the nutritional point of view, MUST, NRS, etc., anthropometric and laboratory data on malnutrition are similar for risk screening, nutritional assessment and diagnostic guidance; hence albumin levels and weight loss are two standards used throughout the entire process. Linking screening with assessment, diagnosis and treatment is, because of its importance, the aim of INFORNUT®.
Finally, in the third phase, which gives its name to the program, the Malnutrition Risk Report (MRR) becomes part of the Clinical Course in the patient history (Appendix 1). In this annex the MRR is compressed to fill a single page. It usually takes two pages with automatic digital validation of the person responsible for the process and the signature of the physician responsible for the patient. The MRR has another page for the nurse's progress notes containing guidance on nursing care.
Coding of Clinical Episode: Lastly the system automatically associates an episode with the ICD-9 CM44 codes corresponding to the degree and type of malnutrition of the patient through the diagnostic algorithm developed. Nutritional information is also automatically included in the care reports at discharge so the primary care professionals can continue to respond to the specific needs of these patients.
Calculation of process performance in its different phases
Of total admissions with stays longer than three days incurred in the years 2008 and 2010, the absolute number and percentages were calculated for: patients who underwent analytical screening with an alert for a medium or high risk of malnutrition, as well as the subgroup of the latter for which, having undergone assessment questionnaires as described for the second phase of the process, the corresponding MRR was obtained.
To quantify and improve the coding rates for malnutrition and nutritional support procedures, a joint action plan was implemented between the Clinical Management Unit (CMU) Endocrinology and Nutrition / Nutritional Support Team, CMU Pharmacy / Nutrition Section, Clinical Documentation Department, Committee on Nutrition and Information Systems Department. The following coding tools were used:
- Discharge reports and documentation in response to inter-office consultations.
- MRR for the INFORNUT® program already described; (there is an improvement project for autocoding after digital validation).
- Nutritional Case Reports after completing parenteral nutrition (PN) obtained by the NUTRIDATA® program, including assessment of nutritional status and PN or enteral nutrition (EN) procedures used.
- Treatment Forms of patients in Critical Care Units, coded from the Pharmacy through password access into the documentation program, as well as previous reports of PN.
- Finally, a local software application was also used as a coding tool, analyzing prescription data dumps in the X-FARMA® and Dominion® application, and coding all parenteral nutrition, binary PN a 2000 ml, and EN ≥ 1000 kcal.
Calculation of rates and impact on Complexity Index
The codes used for malnutrition and nutritional support procedures were those specified in the SENPE-SEDOM agreement27 detailed below:
For the calculation of coding rates, the Minimum Basic Data Set (MBDS) from both our center and from the overall figures for Andalusia registered in the Health Product Department of the Andalusian Health Service were used. These were measured in of discharges in 2009 and 2010, differentiating those related to diagnoses of malnutrition, methods of nutritional support, diagnoses associated with procedures (in the same patient), and also the rate of those who had an ICD-9-CM code44 as defined in the SENPE-SEDOM consensus.27 Finally, we obtained the percentage of malnutrition diagnoses coded as "unspecified degree" out of all the codes. All data were processed by the clinical documentation department with the Alcor-DRG® program and grouped using version 27.0 of the DRG grouper program.
Calorie malnutrition:
Mild: 263.1.
Moderate: 263.0.
Serious or severe: 261 Unspecified degree: 263.9
Protein malnutrition:
Any degree: 260 Hypoalbuminemia: 273.8
Mixed or protein-calorie malnutrition:
Mild: 263.8.
Moderate: 263.8.
Serious or severe: 262 Unspecified degree: 263.9
Unspecified malnutrition:
Mild: 263.1.
Moderate: 263.0.
Serious or severe: 261 Unspecified degree: 263.9
Parenteral nutrition: 99.15.
Enteral nutrition: 96.6
For the calculation of the RR, readmission was considered as readmission of a patient within 365 days from the discharge date for the index event, whether urgent or scheduled. Urgent readmission was defined as occurring within 30 days from the date of the index event. The annual overall RR from any cause and mode of entry and urgent RR caused by processes belonging to the same Major Diagnostic Category (MDC) were calculated. The MDC consists of 25 groups, plus a pre-major diagnostic category, of DRGs based on organs, systems or broad disease areas (nervous system, digestive system diseases, pregnancy, delivery and postpartum, infectious and parasitic diseases, multiple significant trauma).
A hospital's Complexity Index or CI is the average DRG weight, or Case Mix, of all episodes, excluding those patients grouped by DRG weight = 0 (nonspecific DRG). The assignment of ICD-9-CM44 codes for malnutrition and/or support procedures could affect the case mix converting an uncomplicated process into one with a complication or comorbidity (CC) or a process with major complications or comorbidities (MCC), the latter only with codes 260, 261, 262, 263.8. This would imply that processes with complications are related to increased demand for resources and associated costs.12,34,37 However in some circumstances a process is not altered by malnutrition because the process per se would already have a high complexity. This occurs, for example, in certain malignancies. From a DRG perspective, the hospital case mix is related to the demand for resources and the costs associated with these patients. A more complex case mix means that the hospital treats patients who require more hospital resources. For its calculation, a weight is assigned to each DRG that considers that complexity. The impact on the CI is derived by removing these codes from the database to obtain a CI free of their influence; the difference is expressed in hundredths or as a percentage of the CI.
The MBDSs from 2009 and 2010 were updated in 2012 and their complexity is the result of grouping the MBDSs from 2009 and 2010 with the AP-DRG version 27.0. They therefore have a complexity index with differences, either upwards or downwards, with respect to the official Andalusian Health Service data for those years that were processed with AP version 23.0 for 2009 (Minimal Basic Data Set at Hospital Discharge. Diagnosis-Related Groups, Andalusia 2009). http://www.sas.junta-andalucia.es/publicaciones/Listadodeterminado.asp?idp=377) and AP 25.0 in 2010 (Minimal Basic Data Set at Hospital Discharge. Diagnosis-Related Groups, Andalusia 2010. http://www.sas.junta-andalucia.es/publicaciones/Listadodeterminado.asp?idp=439).
Justification of Hospitalization Costs
A portion of the total hospital costs are charged to hospitalization costs. Excluded are: outpatient consultations, major ambulatory surgery, oncology day hospital, radiotherapy sessions, outpatient emergency room care, etc. At the same time this could be considered a net cost of hospitalization excluding proportional costs that correspond to basic services (maintenance, catering and cleaning or general administration) and Intermediate Services (pharmacy, x-rays, laboratory, etc.) which therefore would include only: chapter 1, consumables, medicines, prosthetics, reagents and cleaning supplies related to hospitalization. For the calculation of cost justification, the total cost of hospitalization was used, not the net cost.
From Financial Control Department data, recorded according to the Andalusian Analytical Accounting System 45 (Coanhyd©), the known net hospitalization costs and total DRG hospitalization points were used to calculate the cost per DRG point. Once the impact in hundredths of malnutrition and procedures coding in the CI is known and its percentage calculated, this impact percentage is multiplied by the total DRG hospitalization points giving us the score resulting from this coding. Multiplying the number of points by the per point cost, we obtain the cost figures that would be explained by this activity; otherwise this value would be attributed to inefficiency.
From the consumption data reported to the Financial Control Department by Pharmacy, costs for nutritional support consumption were obtained. These costs were then compared to the costs justified by coding. Due to changes in programs and databases in both departments, we could not obtain data for the years 2009 and 2010. Therefore, costs by discharge and by stay were calculated for more recent annual periods. Although it is not the same period, these costs serve as a reference.
The care model itself as material and method
The authors believe that the main tool for this work was, and continues to be, our own purely participatory care model. A support team, dedicated to the rational use of nutritional support and management of malnutrition, with the interdisciplinary features inherent in Clinical Nutrition, promotes early detection of hospital malnutrition as well as good clinical practice and greater autonomy for health center professionals. This team advises and monitors practices without assuming the exclusive control of this therapeutic tool, although intervening automatically or in response to interconsultations, in this way exercising clinical leadership in nutrition.39 This philosophy, in place for over two decades, has been presented by members of our team, not only in the works already cited, but at many communications, conference presentations, courses, congresses and working group recommendations in which we have participated. Since implementing this care model at our center we have imparted ten courses in "Basics in artificial clinical nutrition" for medical staff, in addition to having published several posters and pocket guides to the basic protocols; all with the collaboration of the members of our hospital Nutrition Committee. Our own performance, always of an educational nature, contributes to the training and subsequent autonomy of health professionals. Other centers have already joined this shift in focus.46
Results
Performance in the different phases of the INFORNUT® process in 2008 and 2010 is shown in table IV.
The coding rates for diagnoses of malnutrition and nutritional support procedures for the years 2009 and 2010, for all hospitals in Andalusia as well as for Virgen de la Victoria University Hospital, expressed in ‰ of discharges, are listed in table V.
Table VI shows the impact of diagnosis coding for malnutrition and nutritional support procedures on the hospital CI in 2009 and 2010, mediated by changes in the average weight of the DRGs. Also, for the same years, Table VI shows the overall MS, MR and RR of the hospital and for those patients who, at discharge, had malnutrition coding in the MBDS by the clinical documentation department; all from the coding tools and documentation described above.
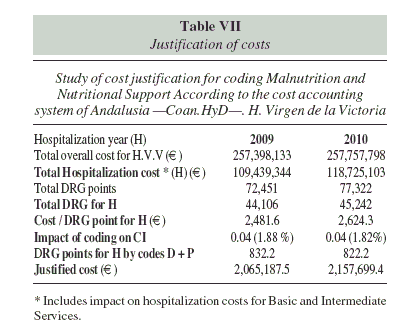
Table VII shows the results of the hospitalization costs justification study in 2009 and 2010, specifying the amount justified by the effect of our activity.
Finally, table VIII shows the costs for nutritional support consumption from in the last two years (November to October accounting period), including overall, by discharge and by stay.
Discussion
The INFORNUT® process had two critical points that decreased performance in the successive phases of screening and assessment. For continuous improvement we planned to implement the following measures, among others:
a) On generating the hospital admission in the admission program, through the DIRAYA program (clinical management program used in the Andalusian Health Service), a printed or digital request for nutrition screening analysis will be produced automatically.
b) Link nursing productivity incentives to performance of the modified-MUST in response to the risk alarm to obtain the MRR according to the INFORNUT® program.
c) As an alternative to the above measure, implement a motivational campaign geared towards physicians responsible for patients with a risk alarm so that they fill in the patient data needed to generate the MRR.
Requests for analytical screening on admission should be made universal since, in our view, there is a very positive cost-benefit relationship. In our center, the 2013 cost of tests that score on the FILNUT-Scale 22 was as follows: albumin 0.11€; total cholesterol 0.097€; blood count 0.51€; total protein (TP) 0.10€ and prealbumin (PR) 0.74€. Given that at a minimum, a blood count is ordered for all admitted patients, the additional request for albumin and cholesterol has a cost of 0.207€. There is an unquestionable benefit of a nutritional screening that, for a few extra cents on admission, prevents a much higher cost; namely, the time needed to perform other types of screening based on questionnaires that also require weighing and measuring all patients admitted23. According to the scoring system of our filter, TP and PR are not essential but useful because at any time during the hospital stay they may result in scoring.22 With analytical screening we would focus the process on those patients with a medium or high risk. The program and process is designed to enable response by the patient's nurse, the physician responsible, and nursing or medical staff belonging to the nutritional support team or unit.
Even though it has some limitations, the process facilitated access to the diagnosis of malnutrition and to the knowledge of the risk of developing it, as well as to the prescription of procedures and/or supplements to correct it, reaching more than 3,600 patients annually. We understand that efficiency is high, since staff effort and time is reduced by targeting only patients at medium and high risk and we achieve the maximum benefit from the subsequent intervention, given that by merging analytical data with the modified-MUST, we obtain sufficient information to achieve a diagnostic and therapeutic target unlike with simple screening. The perennial difficulty of implementing screening based on patient height and weight on admission is well known. In 200842 we reported the results we obtained on performing the MUST screening test on FILNUT positives: of 568 patients at a medium or high risk on the FILNUT Scale, 100% proved to be medium (25.9) or high (74.1) MUST. This, plus the issue of staff cost, affirmed our idea of starting with the analytical filter to detect patients requiring some form of nutritional intervention.
The interdisciplinary coordination of the team, the decentralized nature of our process, the agreements reached and the tools used improve coding rates to give results far above the Andalusian average; three times higher in diagnosis, two in procedures and five in diagnosis-related procedures; that is, care activity related to malnutrition. Even so, our malnutrition coding rates remain well below the actual prevalence. Rates in 2010 were 11.6%c in Andalusia and 35.5%c in our center, both well below those described in the literature. Much remains to be done to overcome this important under-coding.27,28,32,36
Our results help to adjust the CI, or Mean Complexity, of the hospital upwards, with the resulting economic implications and justification for stays27 which would otherwise be considered inefficient. On removing the malnutrition and procedure codes from the MBDS for the years studied we see that the CI decreases by four hundredths or, equivalently, the contribution of their coding to the index is these four hundredths, which to us is an important contribution and consistent with previous findings.27,28 The fact that in 2010 PN and EN coding did not add complexity to that already produced by malnutrition may be due to the usual approximation of the number to only two decimal places. Our higher rate of diagnosis-related treatments that would not add complexity also had an influence; as well as the fact that in certain clinical situations their coding, and even malnutrition itself, no longer adds weight per DRG, as has already been described by other authors with a DRG change in 24% or 27% of cases.27,29,32 Nevertheless, it is very notable to see (table VI) how the complexity of a supposed virtual hospital with only those patients whose MBDS had a malnutrition code at discharge is three times greater than the average complexity. We must consider that our center, with a CI of 2.19 in 2010, is the most complex in Andalusia, where the average complexity of all hospitals in the Andalusian Health Service is 1.76, according to the Cost Accounting data of centers in the Andalusian Health Service. InforCoan System (18 December 2012).
The results of MS and MR indicate that diseases that present with malnutrition (and which are recorded in the MBDS) have much higher morbidity and mortality, reaching a 3-fold increase in MS and a 4-fold increase in MR. These results are consistent with those of the PREDyCES11 study and those of Ockenga32 and Lim.36 It should also be noted that when the calculation is adjusted for age, mortality rates change. With regard to RR we prefer to focus, as do other authors,10 on the urgent RR; i.e., within 30 days after discharge of the episode under study, but with one specification: that it be produced by the same MDC corresponding to the DRG, so as to not record a subsequent admission caused by a clinical picture unrelated to the MDC as caused by malnutrition. An example is a patient with a gastric tumor who is readmitted for cataract surgery. This "urgent" RR is 1.9 times higher in patients with a record of malnutrition. Logically readmissions to other hospitals escape this rate. Other authors,36 however, used the RR at 15 days of discharge, with similar results.
Comparing these results with previous studies is not easy, due to differences in the method of screening or assessment used, baseline characteristics of the study population and primary diagnosis, definition of malnutrition followed, economic terms used and DRG systems applied in different countries. The fact that our results refer to all discharges, with no exclusion criteria, obtained through the standardized work system, with no ad hoc coding, means we believe they have an added value as they can be considered structural results. Awareness of the prevalence and economic impact of malnutrition,9,25,33 requires tools to improve its diagnosis and subsequent coding, which would generate an opportunity for economic reimbursement32 in a hospital financing system based on complexity.
The four hundredths that the coding of our diagnostic activity and nutritional therapy contributes to the CI, translated into justified hospitalization cost, involve a number (two million euros) five to six times higher than the cost generated by support treatments that are, or would have been, necessary. This supports the efficiency of this activity, in addition to its clinical efficacy.
The INFORNUT® process uses its own applications and free software; similar development would, in theory, be achievable in other centers. DIRAYA is the information system that supports the Single Digital History of Andalusia. As a challenge for the future we can say that we are currently taking the first steps to transferring all the knowledge gained through implementation of the system in our hospital to DIRAYA and thereby extend its benefits to other public hospitals in Andalusia. To that end we are participating in a functional development team within the program. DIRAYA has an Analytical Requests Module (ARM) that enables management of all requests going to the clinical analysis laboratories, as well as distribution to the various laboratories and receipt of the results provided by them. Analytical tests are uniquely coded throughout Andalusia, thus the filtering of measurement results required for the malnutrition detection algorithm is immediate. Management of messaging between the various systems and modules that make up DIRAYA uses HL7, which facilitates the information arriving at its destination successfully. However, as mentioned above, the fact that TOS does not work with HL7 would need to be resolved. Once the algorithm is applied, the system will generate necessary patient alerts and recommendations, with the advantage that this information will be accessible from anywhere in the Andalusian Public Health System. We think this could also be extended to information systems in other Spanish autonomous regions.
Conclusions
Aware that quality healthcare implies equality, we believe the INFORNUT® process promotes equal access to the diagnosis of malnutrition and its nutritional support treatment and reaches more patients, making efficient use of human and economic resources, taking into account the current economic situation.
The interdisciplinary coordination of the team, the multidisciplinary and participatory nature of the process and the tools used, improve coding rates to give results far above the Andalusian average. These results help to adjust the hospital Complexity Index -or Case Mix- upwards, having a significant impact on the justification of hospital costs and demonstrating the efficiency of the clinical activity of these teams.
References
1. García de Lorenzo A, Alvarez Hernandez J, Planas M, Burgos R, Araujo K. Multidisciplinary consensus on the approach to hospital malnutrition in Spain. Nutr Hosp 2011; 26: 701-10. [ Links ]
2. Edington J, Boorman J, Durrant ER, Perkins A, Giffin CV, James R, et al. The Malnutrition Prevalence Group. Prevalence of malnutrition on admission to four hospitals in England. Clin Nutr 2000;19:191-5. [ Links ]
3. Naber TH, Schermer T, de Bree A, Nusteling K, Eggink L, Kruimel JW, et al. Prevalence of malnutrition in nonsurgical hospitalized patients and its association with disease complications. Am J Clin Nutr 1997; 66: 1232-9. [ Links ]
4. Korfali G, Gundogdu H, Aydintug S, Bahar M, Besler T, Moral AR, et al. Nutritional risk of hospitalized patients in Turkey. Clin Nutr 2009; 28: 533-7. [ Links ]
5. Marco J, Barba R, Zapatero A, Matia P, Plaza S, Losa JE, et al. Prevalence of the notification of malnutrition in the departments of internal medicine and its prognostic implications. Clin Nutr 2011; 30: 450-4. [ Links ]
6. Norman K, Pichard C, Lochs H, Pirlich M. Prognostic impact of disease-related malnutrition. Clin Nutr 2008; 27: 5-15. [ Links ]
7. Ocón J, Celaya S. Implicaciones clínicas de la desnutrición hospitalaria. In: García de Lorenzo A, García Luna PP, Marsé P, Planas M (eds.). Libro blanco de la desnutrición clínica en España. Acción Médica: Madrid 2004; 61-70. [ Links ]
8. Burgos R, Sarto B, Elío I, Planas M, Forga M, Cantón A, et al. Prevalence of malnutrition and its etiological factors in hospitals. Nutr Hosp 2012; 27: 469-76. [ Links ]
9. McWhirter JP, Pennington CR. Incidence and recognition of malnutrition in hospital. BMJ 1994; 308: 945-8. [ Links ]
10. Pérez de la Cruz A, Lobo Tamer G, Orduna Espinosa R, Mellado Pastor C, Aguayo de Hoyos E, Ruiz Lopez MD. Desnutrición en pacientes hospitalizados: prevalencia e impacto económico. Med Clin (Barc) 2004; 123: 201-6. [ Links ]
11. Lobo Tamer G, Ruiz Lopez MD, Pérez de la Cruz AJ. Desnutrición hospitalaria: relación con la estancia media y la tasa de reingresos prematuros. Med Clin (Barc) 2009; 132: 377-84. [ Links ]
12. Álvarez-Hernandez J, Planas Vila M, Leon-Sanz M, García de Lorenzo A, Celaya-Perez S, García-Lorda P, et al. Prevalence and costs of malnutrition in hospitalized patients; the PREDyCES Study. Nutr Hosp 2012; 27: 1049-59. [ Links ]
13. Committee of Ministers. Resolution ResAP (2003) on food and nutritional care on hospitals. Council of Europe: Strasbourg 2003. Available at: https://wcd.coe.int/ViewDoc.jsp?id=85747. [ Links ]
14. National Collaborating Centre for Acute Care. Nutrition support in adults: Oral nutrition support, enteral tube feeding and parenteral nutrition. London. National Collaborating Centre for Acute Care at the Royal College of Surgeons of England: 2006. Available at: http://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/pdf/cg032niceguideline.pdf. [ Links ]
15. García de Lorenzo A, Alvarez J, Calvo MV, Ulibarri JI, del Rio J, Galban C, et al. Conclusions of the II SENPE discussion forum on: hospital malnutrition. Nutr Hosp 2005; 20: 82-7. [ Links ]
16. Ulibarri JI, Burgos R, Lobo G, Martínez MA, Planas M, Pérez de la Cruz A, et al. Recomendaciones sobre la evaluación del riesgo de desnutrición en los pacientes hospitalizados. Nutr Hosp 2009; 24: 467-72. [ Links ]
17. Kondrup J, Allison SP, Elia M, Vellas B, Plauth M. ESPEN guidelines for nutrition screening 2002. Clin Nutr 2003; 22: 415-21. [ Links ]
18. ASPEN Board of Directors and the Clinical Guidelines Task Force. Guidelines for the use of parenteral and enteral nutrition in adult and pediatric patients. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2002; 26: 1SA-138SA. [ Links ]
19. Ulibarri Pérez JI, González-Madroño Giménez A, González Pérez P, Fernández G, Rodríguez Salvanés F, Mancha Alvarez-Estrada A, et al. Nuevo procedimiento para la detección precoz y control de la desnutrición hospitalaria. Nutr Hosp 2002; 17: 179-88. [ Links ]
20. Villalobos Gámez JL, García-Almeida JM, Guzmán de Damas JM, Rioja Vázquez R, Osorio Fernández D, Rodríguez-García LM, et al. Proceso INFORNUT®: validación de la fase de filtro -FILNUT- y comparación con otros métodos de detección precoz de desnutrición hospitalaria. Nutr Hosp 2006; 21: 491-504. [ Links ]
21. Ulibarri Pérez JI, Picón César MJ, García Benavent E, Mancha Alvarez-Estrada A. Detección precoz y control de la desnutrición hospitalaria. Nutr Hosp 2002; 17: 139-46. [ Links ]
22. Ulibarri J, González-Madroño A, de Villar NG, González P, González B, Mancha A, et al. CONUT: a tool for controlling nutritional status. First validation in a hospital population. Nutr Hosp 2005; 20: 38-45. [ Links ]
23. Villalobos Gámez JL, Guzmán de Damas JM, García-Almeida JM, Galindo MM, Rioja Vázquez R, Enguix Armada A, et al. FILNUT-escala: justificación y utilidad en el cribaje de riesgo por desnutrición dentro del proceso INFORNUT®. Farm Hosp 2010; 34: 231-6. [ Links ]
24. Enguix Armada A, Villalobos Gámez JL, Guzmán de Damas JM. Costes y beneficios de la implantación de un perfil nutricional de laboratorio. Valoración del estado nutricional por el laboratorio. Comité de Publicaciones de la Sociedad Española de Bioquímica Clínica y Patología Molecular-SEQC Ed. Mayo 2007. [ Links ]
25. Commission of the European Communities. Together for Health: a Strategic Approach for the EU 2008-2013.: Brussels 2007. Available at: http://ec.europa.eu/health/ph_overview/Documents/strategy_wp_en.pdf. [ Links ]
26. Alvarez J, Planas M, García de Lorenzo A. Importancia de la codificación de la desnutrición hospitalaria en la gestión clínica. Actividad Dietética 2010; 14: 77-83. [ Links ]
27. Alvarez J, Del Rio J, Planas M, García Peris P, García de Lorenzo A, Calvo V, et al. Documento SENPE-SEDOM sobre la codificación de la desnutrición hospitalaria. Nutr Hosp 2008; 23: 536-40. [ Links ]
28. Villalobos Gámez JL, del Río Mata J, García-Almeida J. Cambios en los índices de complejidad y de utilización de estancias de 2004. Plan de colaboración del equipo de soporte nutricional con servicios de documentación clínica y farmacia. Nutr Hosp 2006; 21: 22. [ Links ]
29. Álvarez-Hernández J, Ortiz P, Salido C, Martínez V, Ausbaugh R. Impacto de la codificación de la desnutrición hospitalaria en la microgestión sanitaria. Nutr Hosp 2005; 20 S1: 25-26. [ Links ]
30. Raja R, Lim AV, Lim YP, Lim G, Chan SP, Vu CK. Malnutrition screening in hospitalised patients and its implication on reimbursement. Intern Med J 2004; 34: 176-81. [ Links ]
31. Norman K, Schutz T, Kemps M, Josef Lubke H, Lochs H, Pirlich M. The Subjective Global Assessment reliably identifies malnutrition-related muscle dysfunction. Clin Nutr 2005; 24: 143-50. [ Links ]
32. Funk KL, Ayton CM. Improving malnutrition documentation enhances reimbursement. J Am Diet Assoc 1995; 95: 468-75. [ Links ]
33. Ockenga J, Freudenreich M, Zakonsky R, Norman K, Pirlich M, Lochs H. Nutritional assessment and management in hospitalised patients: implication for DRG-based reimbursement and health care quality. Clin Nutr 2005; 24: 913-9. [ Links ]
34. Amaral TF, Matos LC, Tavares MM, Subtil A, Martins R, Nazare M, et al. The economic impact of disease-related malnutrition at hospital admission. Clin Nutr 2007; 26: 778-84. [ Links ]
35. Kondrup J, Rasmussen HH, Hamberg O, Stanga Z. Ad Hoc ESPEN Working Group. Nutritional risk screening (NRS 2002): a new method based on an analysis of controlled clinical trials. Clin Nutr 2003; 22: 321-36. [ Links ]
36. Rowell DS, Jackson TJ. Additional costs of inpatient malnutrition, Victoria, Australia, 2003-2004. Eur J Health Econ 12: 353-61. [ Links ]
37. Lim SL, Ong KC, Chan YH, Loke WC, Ferguson M, Daniels L. Malnutrition and its impact on cost of hospitalization, length of stay, readmission and 3-year mortality. Clin Nutr 2012; 31: 345-50. [ Links ]
38. Villalobos JL, Tutau F, Mora R, Mazure R, Minguez A, Rodriguez F, et al. Prescripción y costes de nutrición artificial antes y después de un nuevo protocolo de utilización. Nutr Hosp 2000; 15: 71-8. [ Links ]
39. Villalobos Gámez JL, García-Almeida JM, del Río Mata J, Rioja Vázquez R, Barranco Pérez J, Bernal Losada O. Proceso IN-FORNUT®. In: García-Almeida JM, Villalobos Gamez JL (eds.). Minivademecum nutricional: Málaga 2012; 27-50. ISBN: 978-84-695-7441-6. Available at: http://www.senpe.com/minivademecum2013/miniVademecum_hvv.pdf. [ Links ]
40. Stratton RJ, Hackston A, Longmore D, Dixon R, Price S, Stroud M, et al. Malnutrition in hospital outpatients and inpatients: prevalence, concurrent validity and ease of use of the 'malnutrition universal screening tool' ('MUST') for adults. Br J Nutr 2004; 92: 799-808. [ Links ]
41. King CL EM, Stroud MA, Stratton RJ. The predictive validity of the malnutrition universal screening tool (MUST) with regard to mortality and length of stay in elderly patients. Clin Nutr 2003; 22 (Supl. 1): S4. [ Links ]
42. Elia M. The "MUST" report: nutritional screening of adults: a multidisciplinary responsability. Development and use of the "Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool" ("MUST") for adults. A report by the Malnutrition Advisory Group of the British Association for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. Redditch: British Association for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (BAPEN) 2003. [ Links ]
43. White JV, Guenter P, Jensen G, Malone A, Schofield M. Consensus statement: Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition: characteristics recommended for the identification and documentation of adult malnutrition (undernutrition). JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr36: 275-83. [ Links ]
44. Clasificación Internacional de Enfermedades 9a Revisión Modificación Clínica -9a edición-. Enero 2014. Madrid: Ministerio de Sanidad, Servicios Sociales e Igualdad. Dirección General de Salud Pública, Calidad e Innovación Subdirección General de Información Sanitaria e Innovación. Available at: https://eciemaps.mspsi.es/ecieMaps/browser/index_9_mc.html. [ Links ]
45. Muñoyerro Muñiz MD SPM, Serrano Garrido A, Martín Fernández D y López Ruiz A. Coanhyd©, Manual de la aplicación. Servicio Andaluz de Salud, DG de Gestión Económica. Depósito legal: SE-1030-04. 2003. Available at: http://www.juntadeandalucia.es/servicioandaluzdesalud/contenidos/publicaciones/datos/142/pdf/ManualCoanhyd.pdf. [ Links ]
46. Gómez-Candela C, Serrano Labajos R, García-Vazquez N, Valero Perez M, Morato Martinez M, Santurino Fontecha C, et al. Proceso completo de implantación de un sistema de cribado de riesgo nutricional en el hospital universitario La Paz de Madrid. Nutr Hosp 2013; 28: 2165-74. [ Links ]
![]() Correspondence:
Correspondence:
Juan Luis Villalobos Gámez.
Hospital Virgen de la Victoria.
Servicio de Farmacia.
Sección de Nutrición.
Campus Universitario de Teatinos.
29010 Málaga.
E-mail: juanluisvillalobos@gmail.com
Recibido: 3-IV-2014.
Aceptado: 23-IV-2014.











 texto en
texto en