INTRODUCTION
As the only effective treatment for pancreatic cancer and periampullary cancer, pancreatoduodenectomy (PD) has increasingly matured (1,2). However, although operative mortality has dropped significantly, the incidence of postoperative complications is as high as 30-65 % due to the complexity of the surgical procedure and the characteristics of related organs (3,4). The incidence of malnutrition in pancreatic cancer and periampullary cancer is the highest in the oncological setting and is linked to advanced stage and/or obstruction of the digestive tract. Therefore, a possible effect of preoperative nutritional support on restoring nutritional status could be expected in these selected patients with an early stage and early digestive occlusion (5-7). However, no standards have been established for screening nutritional risks of these patients undergoing PD.
In previous studies the survival prognostic value of the Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score, Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index (GNRI), and Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) for patients undergoing PD has been demonstrated (8-10). However, whether the CONUT, GNRI and PNI are related to short-term prognosis, i.e., postoperative complications of PD, and whether CONUT, GNRI and PNI scores have predictive value for complications of PD has not yet been demonstrated. For these purposes we carried out this research.
METHODS
STUDY POPULATION
Between January 2015 and September 2020, 113 preoperatively untreated patients without any severe comorbidities such as end-stage renal disease or liver cirrhosis underwent PD to treat pancreatic cancer or periampullary neoplasms at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University. Patients with distant metastases, chemoradiotherapy, immunotherapy, acute infection, immune system disease, palliative resection, a history of other abdominal surgery procedures (such as colectomy or gastrectomy), an American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) classification exceeding grade III, or without access to information related to CONUT, GNRI, and PNI were excluded. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University (IRB No. JD-HG-2020-12).
MALNUTRITION SCREENING TOOLS
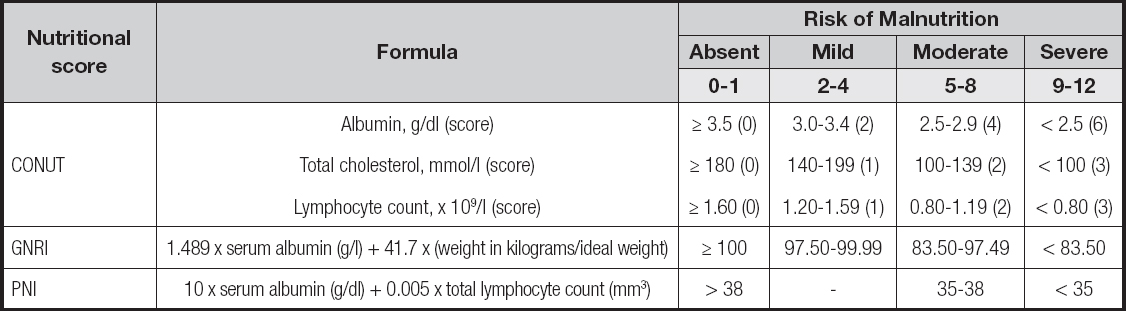
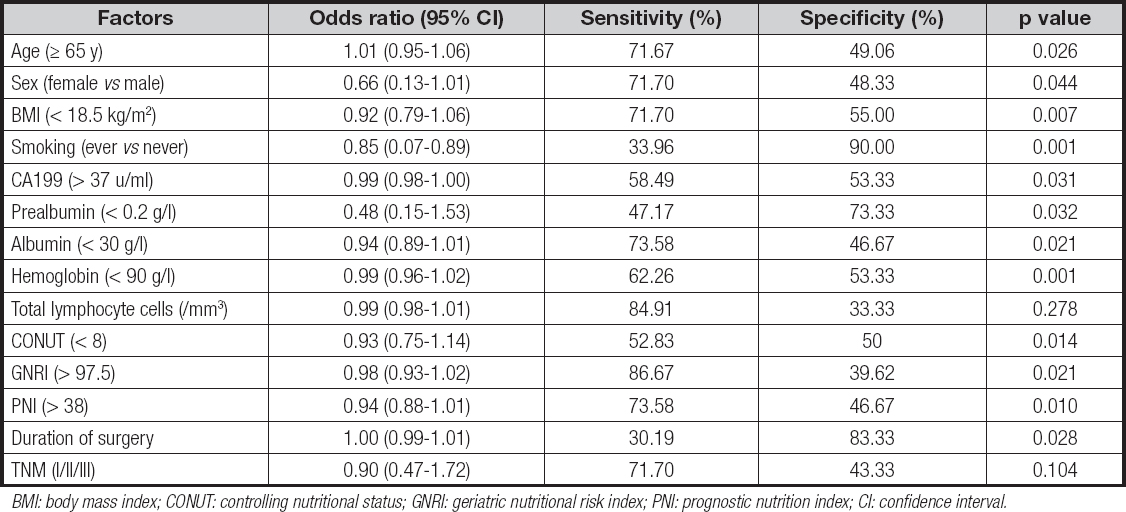
Body mass index (BMI) is defined as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared. According to BMI, patients were classified as underweight (< 18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (18.5-24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25.0-29.9 kg/m2), or obese (≥ 30 kg/m2). In this study, BMI was calculated for all patients. Nutritional status was assessed by the CONUT, GNRI, and PNI scores, and patients were categorized as either at risk or not at risk for malnutrition by each score. Preoperative blood samples were obtained within 2 weeks before surgery. CONUT included total lymphocyte count, cholesterol, and serum albumin. The scores were divided into four nutritional groups, with 0 to 1, 2 to 4, 5 to 8, and 9 to 12 indicating no, mild, moderate, and severe malnutrition, respectively. Besides, in this study the mild, moderate and severe malnutrition categories of the CONUT score were merged into a malnutrition group. GNRI was computed as 1.489 x serum albumin level (g/L) + 41.7 x (weight in kilograms/ideal weight). Ideal weight was height (cm) - 100 - ([height (cm) - 150] / 4) for men and height (cm) - 100 - ([height (cm) - 150] / 2.5) for women (11). When current weight exceeds ideal weight, we set current weight/ideal weight = 1, according to Mizanawa et al.'s study (11). GNRI results were divided into four nutritional groups, as defined in previous studies: no malnutrition (GNRI ≥ 100), mild malnutrition (97.5 ≤ GNRI < 100), moderate malnutrition (83.5 ≤ GNRI < 97.5), and severe malnutrition (GNRI < 83.5). PNI was calculated by the formula 10 x serum albumin (g/dL) + 0.005 x total lymphocyte count (mm3) (12). And there is no mild category for PNI. So, PNI results were divided into three nutritional groups: no nutritional risk (PNI > 38), moderate nutritional risk (35 ≤ PNI ≤ 38), and severe nutritional risk (PNI < 35). According to preoperative CONUT, GNRI and PNI scores, patients were divided into a malnutrition group and non-malnutrition group. More information on malnutrition screening tools is available in table I.
PERIOPERATIVE OUTCOMES
Operation method, operation duration, intra-operative blood loss, major surgical complications including infection, postoperative pancreatic fistula, bile leakage, intra-abdominal bleeding, and delayed gastric emptying were the main perioperative results we compared. Postoperative complications were defined according to the Clavien-Dindo classification (13). Major complications have been defined as those exceeding the Clavien-Dindo grade III. Pancreatic fistula and delayed gastric emptying were classified according to the International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS) criteria (14,15). In brief, the ISGPS classification is characterized by grading each complication into three grades. Grade A complications require only minor adjustments in management and can always be managed conservatively. Grade B complications require a significant change from standard clinical pathway, and grade C complications require major invasive interventions in the case of pancreatic fistula, or markedly prolonged nasogastric drainage in the case of delayed gastric emptying. Pathological data included tumor size, total number of lymph nodes, number of metastatic lymph nodes, lymphatic invasion, neurovascular invasion, tumor differentiation, and histological type.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Categorical variables were represented by counts and percentages. Continuous variables were expressed as median and interquartile range (IQR) (25th to 75th percentile). Spearman's rank correlation test was used to evaluate the correlation between preoperative nutritional status and patient characteristics. The chi-square test, Mann-Whitney U-test, unpaired t-test, or Fisher's exact test were used for variable analysis. Logistic regression models were used to analyze potential predictors of postoperative complications. To predict postoperative complications, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for nutritional factors were generated. The optimal cutoff values were defined using Youden's index. Sensitivity and specificity were weighed equally in this analysis. To determine the influence of independent variables on the prognosis of major postoperative complications, variables with p-values less than 0.05 in the univariate analysis were included in the multivariate regression model. The statistical analysis was performed using the R, version 3.6.3, software (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) and the SPSS software program (version 22.0; SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
RESULTS
PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS
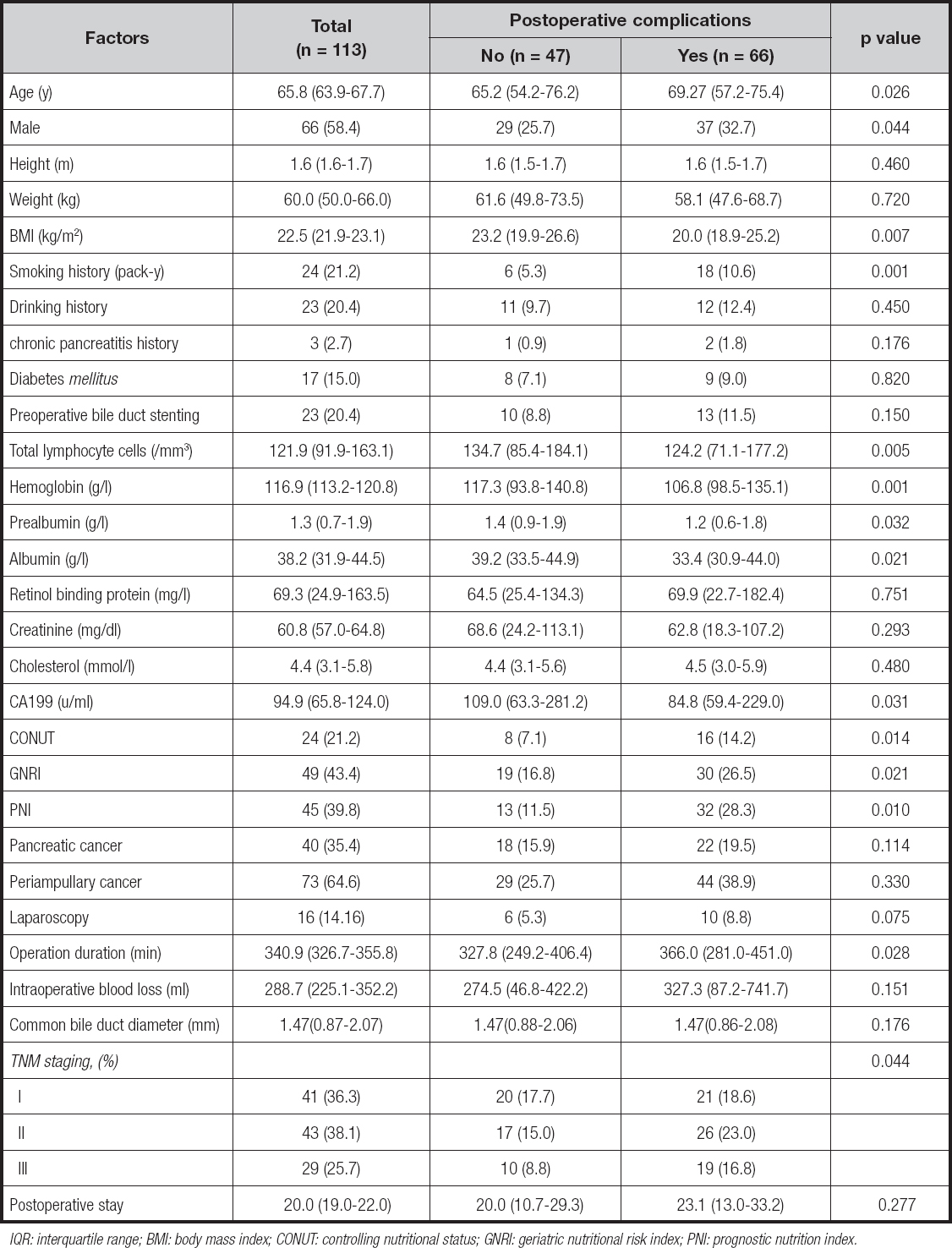
Among the 113 patients enrolled, most patients were men (58.4 %), and the median age was 65.8 years (IQR, 63.9-67.7). The diagnoses of these patients included pancreatic carcinoma (n = 40) and ampullary carcinoma (n = 73). Of the 113 patients, 23 had biliary obstruction, and had undergone preoperative biliary drainage. According to TNM staging, there were 41 patients (36.3 %) in sta- ge I, 43 patients (38.1 %) in stage II, and 29 patients (25.7 %) in stage III. Mean postoperative hospital stay was 20 days. More data on the study population are detailed in table II.
CORRELATION BETWEEN POSTOPERATIVE COMPLICATIONS AND PREOPERATIVE NUTRITIONAL RISK
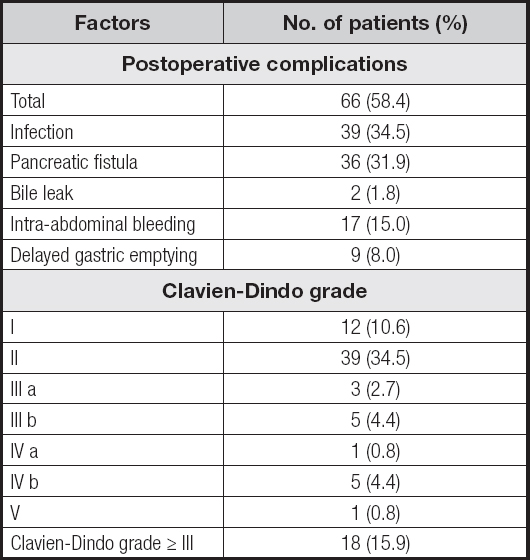
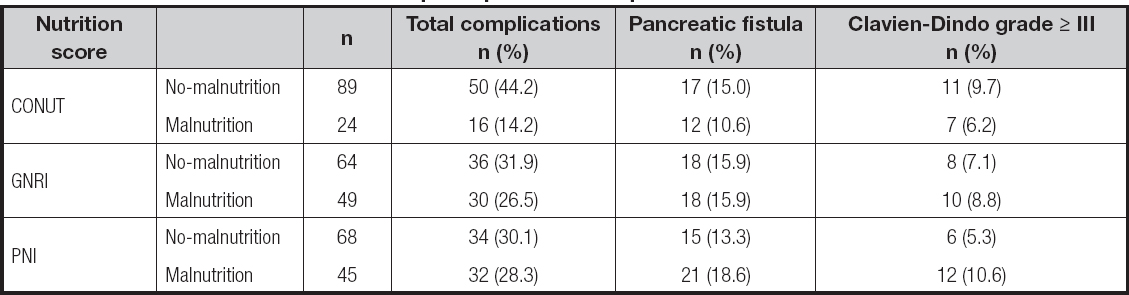
A total of 66 (58.4 %) patients were diagnosed with postoperative complications, with 18 (15.9 %) classified as above Clavien-Dindo grade III.
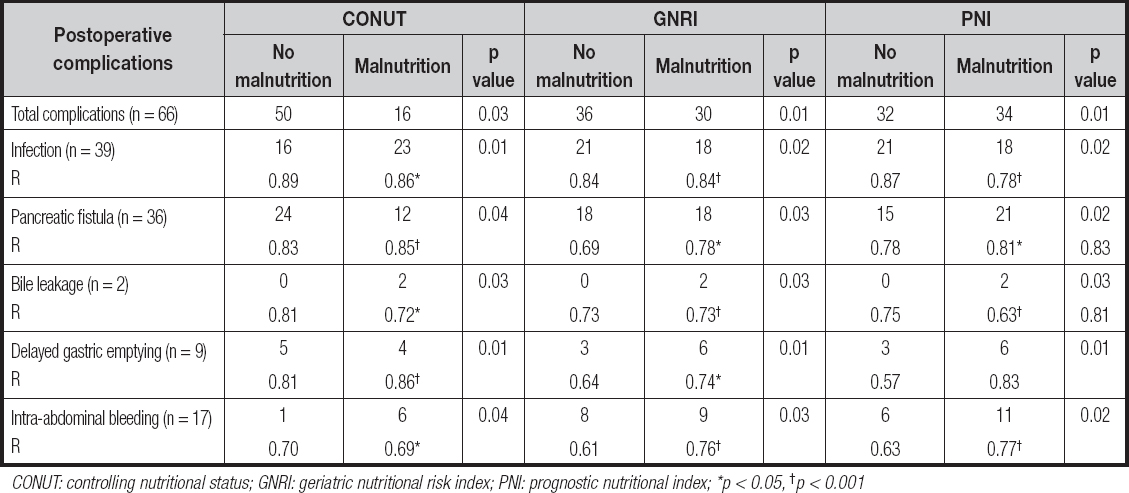
Among them, 39 (34.5 %) patients had infection, 36 (31.9 %) had pancreatic fistula, 2 (1.8 %) had bile leaks, 17 (15 %) had Intra-abdominal bleeding, and 9 (8 %) had delayed gastric emptying. The proportion of malnourished patients ranged from 21.2 % with the CONUT, to 43.4 % with the GNRI, to 39.8 % with the PNI. CONUT, GNRI and PNI scores were closely related to the occurrence of postoperative complications (infection, pancreatic fistula, bile leak, intra-abdominal bleeding, and delayed gastric emptying). Specifically, the incidence of postoperative complications such as infection, pancreatic fistula, bile leakage, hemorrhage, and delayed gastric emptying was relatively high in the malnourished group according to CONUT. Besides, the incidence of postoperative hemorrhage in the malnourished group as defined by PNI and GNRI was significantly high (PNI, p = 0.02, GNRI, p = 0.03). More data on the study population are detailed in tables II and III.
ANALYSIS OF RISK FACTOR ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THREE NUTRITIONAL SCORES AND POSTOPERATIVE COMPLICATIONS
A total of 103 postoperative complications occurred in 66 pa- tients. Among these postoperative complications, the most common types were infection and pancreatic fistula, which were observed in 39 patients and 36 patients. The incidence of postoperative complications in malnourished patients was increased significantly, especially in the PNI score (p = 0.01). Infection and pancreatic fistula were highly correlated with malnutrition and nutritional score. Besides, infection, pancreatic fistula, bile leakage, delayed gastric emptying, and intra-abdominal bleeding had a high correlation with CONUT and PNI scores (Table IV). Univariate analysis showed that the following variables were remarkably correlated with postoperative complications: age, sex, BMI, smoking history, CA199, prealbumin, albumin, hemoglobin, CONUT, GNRI, PNI and duration of surgery (Table V). And the multivariate analysis of postoperative complications showed that CONUT (OR = 0.92, 95 % CI, 0.75-1.12, p = 0.043), GNRI (OR = 0.98, 95 % CI, 0.93-1.02, p = 0.036), PNI (OR = 0.96, 95 % CI, 0.89-1.03, p = 0.024), duration of surgery (OR = 1.01, 95 % CI, 0.99-1.02, p = 0.034) were independent prognostic factors (Table VI).
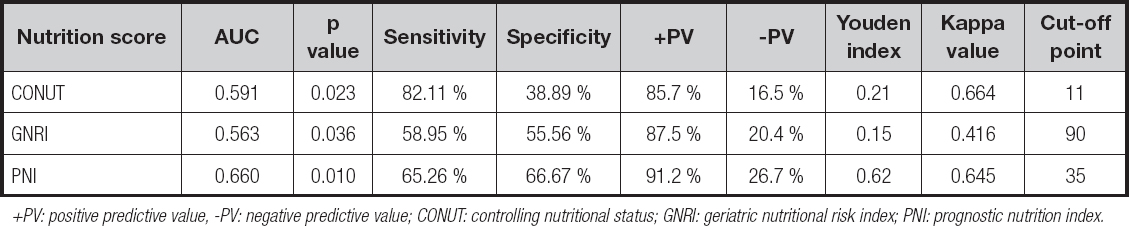
PREDICTABILITY OF THREE NUTRITIONAL SCORING SYSTEMS FOR POSTOPERATIVE COMPLICATIONS
The predictive value of CONUT, GNRI, PNI nutritional screening methods for overall complications of patients with PD had a sensitivity of 31.8 %, 56.06 % and 74.24 %, a specificity of 85.10 %, 68.09 % and 76.81 %, a Youden index of 0.17, 0.24 and 0.71, and a kappa value of 0.460, 0.389 and 0.472, respectively. The PNI score had a higher sensitivity (74.24 %) and specificity (76.81 %) than those of GNRI score, and was consistent with postoperative complications (KCONUT = 0.460, KGNRI = 0.389, KPNI = 0.472), although the area under the AUC curve of it was slightly lower than that of the GNRI and CONUT scores (Table VII, Fig. 1). The predictive value of CONUT, GNRI, PNI nutritional screening methods in predicting the severity of complications in patients with PD had a sensitivity of 82.11 %, 58.95 % and 65.26 %, a specificity of 38.89 %, 55.56 % and 66.67 %, a Youden index of 0.21, 0.15 and 0.62, and a kappa value of 0.664, 0.416 and 0.645, respectively. Among the three nutrition scoring systems, the PNI score had better diagnostic efficiency (0.660 area under the AUC curve) and higher specificity (66.67 %), and was more consistent with postoperative complications (KCONUT = 0.664, KGNRI = 0.416, KPNI = 0.645) when compared to GNRI and CONUT scores (Table VIII, Fig. 2). According to the Clavien-Dindo classification, the PNI nutrition evaluation method can screen more complications with grade III and above (Table IX).
Table VI. Multivariable logistic regression analysis to determine factors associated with major postoperative complications
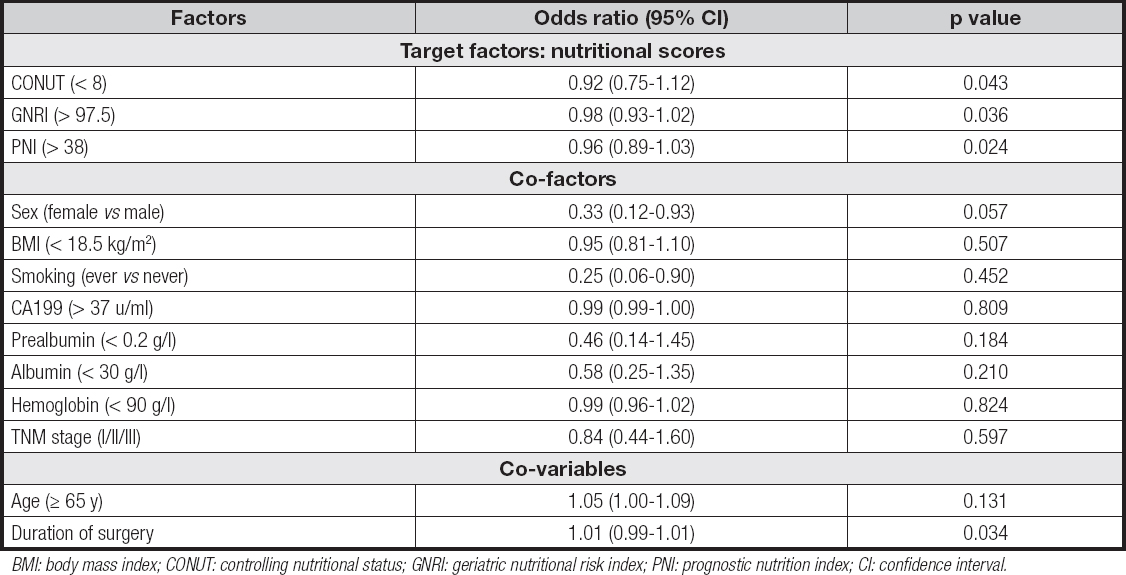
BMI: body mass index; CONUT: controlling nutritional status; GNRI: geriatric nutritional risk index; PNI: prognostic nutrition index; CI: confidence interval.
Table VII. Predictability of three nutritional scoring systems for postoperative complications
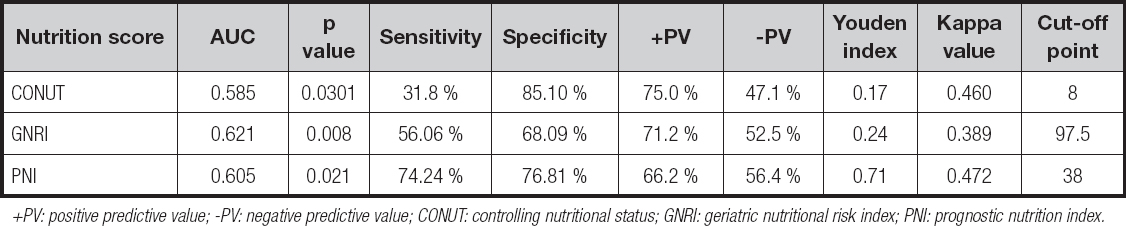
+PV: positive predictive value; -PV: negative predictive value; CONUT: controlling nutritional status; GNRI: geriatric nutritional risk index; PNI: prognostic nutrition index.
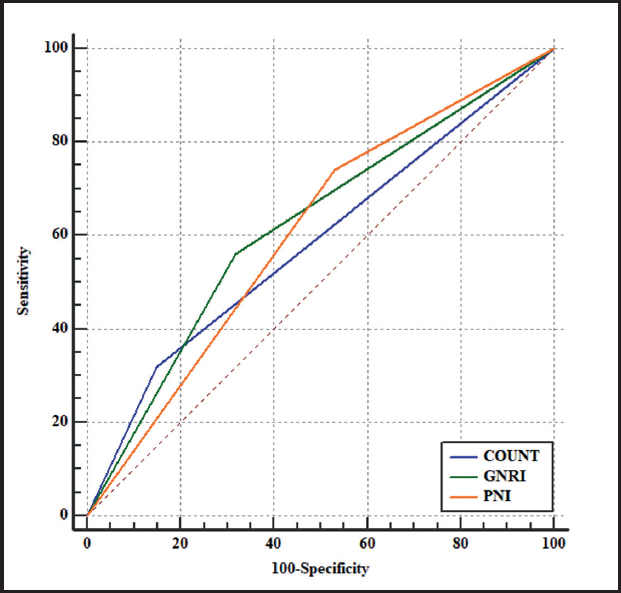
Figure 1. ROC curve of predicting postoperative complications with three nutritional scores (CONUT, GNRI, PNI nutritional screening methods for overall complications of patients with PD had a sensitivity of 31.8 %, 56.06 % and 74.24 %, a specificity of 85.10 %, 68.08 % and 76.81 %, a Youden index of 0.17, 0.24 and 0.71, and a kappa value of 0.460, 0.389 and 0.472, respectively. CONUT: controlling nutritional status; GNRI: geriatric nutritional risk index; PNI: prognostic nutritional index).
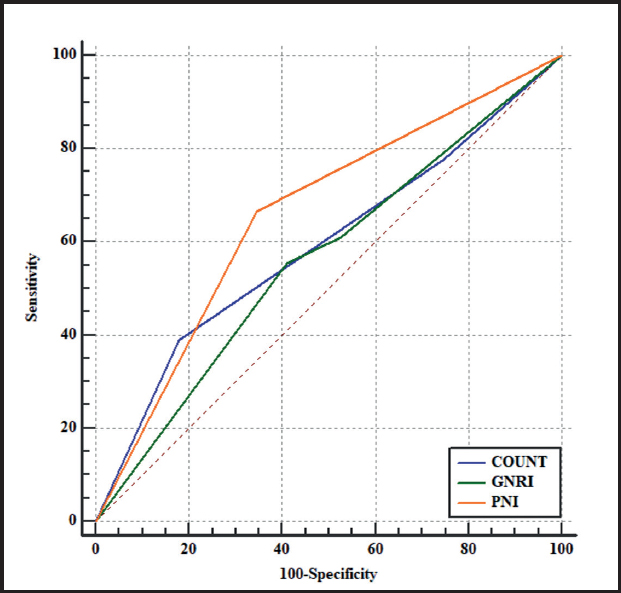
Figure 2. ROC curve for predicting the severity of postoperative complications with three nutritional scores (the predictive value of the CONUT, GNRI, PNI nutritional screening methods in forecasting the severity of complications in patients with PD had a sensitivity of 82.11 %, 58.95 % and 65.26 %, a specificity of 38.89 %, 55.56 % and 66.67 %, a Youden index of 0.21, 0.15 and 0.62, and a kappa value of 0.664, 0.416 and 0.645, respectively. CONUT: controlling nutritional status; GNRI: geriatric nutritional risk index; PNI: prognostic nutritional index).
DISCUSSION
In this study, the COUNT, GNRI, and PNI scores were used to assess preoperative nutritional risk in patients undergoing PD, and to compare their predictive value for postoperative complications. Studies have shown that 40 % of patients with a malignancy are malnourished at the early stage of diagnosis. With the development of a tumor, 70 % to 80 % of patients suffer from cachexia; of these, the patients with pancreatic cancer and gastric cancer show the most serious degree, with their incidence rate reaching 83 % to 85 % (16). Therefore, the concept of using nutritional evaluation as a predictor was put forward by Gordon P (12) in patients after gastrointestinal surgery in 1980. Nowadays, it has been fully proved that preoperative nutritional status is a predictor of postoperative complications and survival in patients after abdominal surgery (17-19). In addition, there is increasing interest in the clinical effects of preoperative nutritional status on postoperative complications following PD. However, currently available data are limited, and the best preoperative nutrition assessment tool for individuals undergoing PD has not yet been determined. Therefore, in this study we explored the predictive values of three typical nutritional assessment methods in the same queue.
In this study, CONUT (OR = 0.92, 95 % CI, 0.75-1.12, p = 0.043), GNRI (OR = 0.98, 95 % CI, 0.93-1.02, p = 0.036) and PNI (OR = 0.96, 95 % CI, 0.89-1.03, p = 0.024) were independent risk factors for complications in patients after PD. And CONUT, GNRI and PNI scores were related to the nutritional status of patients undergoing PD. There was consistency in recent studies. Terasaki et al. (8) studied the postoperative outcomes of 307 patients undergoing surgery for primary pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and their evaluation of the high incidence of postoperative complications and high CONUT values. Utsumi and colleagues (20) reported similar results from a study involving 108 patients undergoing PD. Individuals with a high CONUT score predicted a higher risk of postoperative pancreatic fistula. Funamizu et al. (21) examined a study in 106 patients with PD and suggested that GNRI as calculated by BMI and serum albumin had predictive value for surgical site infection. Additionally, Young et al. (22) showed that preoperative PNI played an important role as an independent prognostic factor for predicting postoperative complications in patients undergoing PD. The mechanism may be as follows. PNI was calculated using total number of lymphocytes and albumin concentration in peripheral blood (23). Serum albumin is a typical nutritional index, which is often used to evaluate the nutritional condition and to predict postoperative pancreatic fistula (24). Hypoalbuminemia is usually associated with decreased collagen synthesis, poor wound healing, and impaired immune regulation (such as granuloma formation and macrophage activation) (25). For this reason, surgical site infection can often be found in patients with hypoproteinemia. Similarly, the total lymphocyte count also reflects nutritional status and immune functions of the body. Menges and colleagues (26) identified that the main feature of lymphopenia, which is caused by systemic inflammatory response, is the striking suppression of cellular immunity. A meta-analysis showed that total lymphocyte count increased and the incidence of postoperative complications decreased after immunization and nutrition intervention (27). Previous research had shown that people with low PNI scores (malnutrition) had a higher incidence of postoperative complications. CONUT is similar to PNI except that it includes cholesterol. Therefore, CONUT reflects protein, lipid metabolism and immune status. Studies have revealed that low serum cholesterol after gastrointestinal surgery was related to postoperative complications (28). In addition to indicating a lack of calories, a reduction in cholesterol also means that cells lack essential nutrients needed to maintain cell membrane integrity and metabolism, as well as hormonal balance (29). The relationship between cholesterol level and postoperative pancreatic fistula can be illustrated by tissue fragility. Masashi et al. showed that CONUT was an independent prognostic factor for surgical site infection in a cohort of 108 patients with PD. GNRI contemplates body weight, which is usually applied to evaluate the metabolic health of patients (9,30). Shinkawa et al. (9) found that GNRI was an independent predictor of the risk of surgical site infection after PD. Naotake et al. (21) demonstrated that in a study of 106 patients aged over 70 years after PD, GNRI had a notable effect on postoperative pancreatic fistula. Our results were consistent with these studies because all variables evaluated were related to postoperative complications.
The second issue to remark is that the three nutritional scores CONUT, GNRI and PNI had high predictive values for the occurrence and severity of postoperative complications after PD. The predictive value of the three nutritional screening methods in overall complications of patients with PD had a sensitivity of 31.8 %, 56.06 % and 74.24 %, a specificity of 85.10 %, 68.09 % and 76.81 %, a Youden index of 0.17, 0.24 and 0.71, and a kappa value of 0.460, 0.389 and 0.472, respectively. The predictive value of the three nutritional screening methods in forecasting the severity of complications in patients with PD had a sensitivity of 82.11 %, 58.95 % and 65.26 %, a specificity of 38.89 %, 55.56 % and 66.67 %, a Youden index of 0.21, 0.15 and 0.62, and a kappa value of 0.664, 0.416 and 0.645, respectively. All data showed that the PNI score had better diagnostic efficiency, higher specificity (66.67 %), and was more consistent with postoperative complications than the GNRI and CONUT scores. Kang et al. (31) found that albumin and lymphocyte count may be strong prognostic factors in patients with renal cell carcinoma. It was pointed out that albumin and lymphocyte count were shown to be significantly predictive in all univariate analyses, whereas the univariate analysis of overall survival or recurrence-free survival using a Cox proportional hazards model showed that serum cholesterol had no significant predictive effect on prognosis. These results indicated that albumin and lymphocyte count may be strong prognostic factors in patients with renal cell carcinoma, and the predictive effect of serum cholesterol may not be as strong as the former two. The predictive value of serum cholesterol levels for the prognosis of postoperative patients is still controversial. We also introduced the possibility of serum cholesterol affecting tumor at present. Therefore, in this study, PNI may be more accurate than CONUT and GNRI scores in predicting postoperative complications. In this study, the similarity of the results shows that CONUT, GNRI and PNI scores can predict postoperative complications and the severity of complications of PD patients to a certain extent, and that PNI is relatively more accurate.
All these findings convincingly sustain the necessity of physicians to identify, reorganize and consolidate patients at risk for malnutrition complications in their daily practice. Furthermore, surgeons also need to bring into equilibrium the risk of delayed surgery, which provides a period of intensive nutritional support preoperatively, with the risk of immediate surgery for untreated malnutrition. Therefore, a preoperative evaluation of nutritional status is of vital importance for patients undergoing elective cancer surgery. This emphasizes the necessity of dynamic assessment for preoperative nutritional status.
This research had some limitations. First of all, this was a retrospective single-center study, and there may have been a potential selection bias in the patients undergoing PD. But a retrospective analysis is ethically and practically the only way to assess the eligibility of patients for PD, given the evidence that surgery is the only curative option for pancreatic and periampullary cancer (32). Secondly, in this study sample size was small. Compared with individuals with benign diseases, the clinical manifestations and time processes of malignant diseases were significantly different. Therefore, a mixed diagnosis could be a confusing factor and might increase study bias. Third, with the increase in long-term survivors of PD, there is still a need to evaluate at a longer term (> 1 year) the nutritional outcomes of patients.
In conclusion, the CONUT, GNRI and PNI scores, especially the PNI score, have good predictive values for the occurrence and severity of postoperative complications in PD patients, and should be used as preoperative nutritional risk screening tools for PD patients.