Mi SciELO
Servicios Personalizados
Revista
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Accesos
Accesos
Links relacionados
-
 Citado por Google
Citado por Google -
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO -
 Similares en Google
Similares en Google
Compartir
Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas
versión impresa ISSN 1130-0108
Rev. esp. enferm. dig. vol.99 no.8 Madrid ago. 2007
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Sigmoid volvulus associated Chilaiditi's syndrome
Vólvulo sigmoide asociado con síndrome de Chilaiditi
Key words: Chilaiditi's syndrome. Hepatodiaphragmatic interposition. Sigmoid volvulus.
Palabras clave: Síndrome de Chilaiditi. Interposición hepatodiafragmática. Vólvulo sigmoide.
Dear Editor:
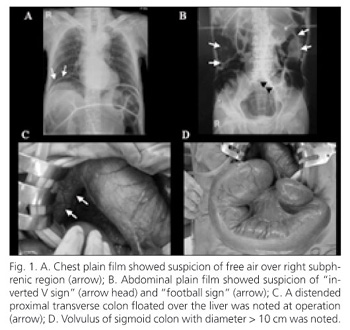
A 78-year-old male was stoked with long-term bedridden for 5 years. He complained of abdominal pain, abdominal distension, vomiting for two days. He was admitted to our hospital for further evaluation. On admission, physical examination revealed distended abdomen and diffuse tympanic percussion. Laboratory investigations revealed leukocytosis, with white blood cell count of 17,000/ mm3; hemoglobin of 10.2 g/dl; platelets count of 157,000/ mm3; creatine phosphokinase of 2,159 U/l; C-reactive protein of 5.0 mg/dl. Chest plain film showed suspicion of free air over right subphrenic region (Panel A, arrow). Abdominal plain film showed suspicion of "inverted V sign" (Panel B, arrow head) and "football sign" (Panel B, arrow). Both signs indicated free intraperitoneal air. Because hollow organ perforation was highly suspected, an exploratory laparotomy was performed. At operation, a distended proximal transverse colon floated over the liver was noted (Panel C, arrow). Volvulus of sigmoid colon with diameter > 10 cm was also noted (Panel D). There was no perforation. Intraoperative colonoscopic reduction and decompression were done but in vain. Resection of sigmoid colon with end-to-end anastomosis was performed without complication. Postoperatively, the symptoms of abdominal pain and distention subsided uneventfully by nasogastric suction, intravenous hydration, and bed rest. During 3 years of following-up, he had no surgical complications or episodes of volvulus and bowel obstruction.
Discussion
Hepatodiaphragmatic interposition of the colon, known as Chilaiditi's sign, is generally asymptomatic and noted as an incidental finding on chest or abdominal plain film. The incidence of Chilaiditi's sign is about 0.1-0.25% occasionally found on chest x-ray and it is more often in male than female (1). This finding is almost noted in adult. When it is accompanied by clinical symptoms such as: abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation, it is known as the Chilaiditi's syndrome. The predisposing factors of Chilaiditi's syndrome include absence of suspensory ligaments of transverse colon, atrophic or small liver, abnormality of the falciform redundant mesocolon, and redundant, dilated colon (2). Volvulus is a complete twisting of a loop of intestine around the mesentery. Such twisting can occur at various sites of the gastrointestinal tract, including the stomach, small intestine, cecum, transverse colon, and sigmoid colon. Sigmoid volvulus is the most common form of volvulus of the gastrointestinal tract. Sigmoid volvulus is more common in elderly than young persons. The symptoms of sigmoid volvulus present with abdominal pain, distension, constipation, and intestinal obstruction. The predisposing factors of colon volvulus include redundant colon, chronic constipation, megacolon, and long mesentery. Abdominal plain radiographs usually show a markedly distended sigmoid loop. Decompression may be achieved with the introduction of a stiff tube per the rectum, aided by endoscopy or fluoroscopy. Early radiographic recognition is important to prevent mortality related to sigmoid volvulus (3). Most people who have hepatodiaphragmatic colonic interposition are asymptomatic, and can be said to have Chilaiditi's sign. A Chilaiditi's sign is often seen as an incidental finding on abdominal plain radiographs. A Chilaiditi's syndrome is an uncommon disease with symptomatic hepatodiaphragmatic colonic interposition. Sigmoid colon volvulus is the most common type of colonic volvulus but less presenting as a Chilaitidi's syndrome. A symptomatic Chilaitidi's syndrome should be considered in a different underlying disease when chest or abdominal plain radiographs revealing a Chilaitidi's sign.
Funding acknowledgement: Civilian Administration Division of Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center.
Chen SY, Liu CT1, Tsai YC2, Yu JC and Lin CH
Division of General Surgery. Department of Surgery.
Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center. Taipei.
1Department of Surgery. Yee-Zen General Hospital. Taoyuan.
2Department of Surgery. Chung-Shan Hospital, Taipei. Taiwan. R.O.C.
References
1. Lekkas CN, Lentino W. Symptom-producing interposition of the colon. Clinical syndrome in mentally deficient adults. JAMA 1978; 240 (8): 747-50.
2. Saber AA, Boros MJ. Chilaiditi's syndrome: what should every surgeon know? Am Surg 2005; 71 (3): 261-3.
3. Frizelle FA, Wolff BG. Colonic volvulus. Adv Surg 1996; 29: 131-9.