INTRODUCTION
The exponential rise in the life expectancy and the poly morbid states has led to an increase in the high-risk patients in the routine dental practice. The life expectancy of an untreated hypertensive patient decreases by one to two decades. Mild hypertension increases risk of complications like apoplectic or cardiac insult, if left untreated. Thus hypertension, among many other co morbidities, is one of the high-risk groups for routine dental procedures. Hypertensive patients are one of the most commonly encountered patients undergoing exodontia. Chances of cardiovascular complication should be anticipated in these patients during tooth extraction which necessitates the need for a well-equipped dental set up1.
Monitoring of patient's vitals and general condition is advocated during traumatic extractions of the teeth or if the psychological condition of patient makes such control desirable to enhance safety. Surgeon can acknowledge and identify increased risk situations with prompt diagnosis and can prevent possible complications during oral surgical procedures. Monitoring the hemodynamic changes in a patient permits the surgeon to operate with increased safety as it can prevent emergency situations in clinical practice2. Local anesthetic solution used in dentistry contains epinephrine which increases the duration and potency of anesthesia. This also reduces the concentration of the anesthetic solution in plasma and improves control over bleeding locally through vasoconstriction3. However, it can induce hemodynamic changes during the surgical exodontia synergistically with other factors, such as anxiety or stress4. Adverse cardiac effects and possibility of systemic absorption, has limited its use in cardiac patients. Moreover, due to the possibility of its massive systemic absorption, the use of this drug has been under criticism as it could result in undesirable cardiovascular effects4.
Since epinephrine is a vasopressor, it was implicated as an etiological agent in certain clinical cases of hypertension 5. The hemodynamic and cardiovascular changes caused due to the administration of exogenous epinephrine makes its use a controversy among hypertensive individuals6. Monitoring the patient's pulse, blood pressure and peripheral oxygen saturation (SPO2) before and during procedure increases the safety factor leading to a more relaxed surgical atmosphere and helps relieve dental anxiety in the patient to a certain extent too 7. There is a lack of evidence comparing the hemodynamic changes in hypertensive and normotensive patients.
This study compares hemodynamic changes namely blood pressure, heart rate, and peripheral capillary oxygen saturation, in normotensive and hypertensive patients prior to, during and after extraction of the teeth using local anesthesia with and without epinephrine.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 100 patients (n = 100) between the age group of 40-70 years reporting to the K.V.G Dental College and Hospital, Sullia were recruited. 50 of whom were diagnosed with Stage I hypertension (blood pressure more than 130/86 mmHg and less than 159/99 mmHg) and another 50 having blood pressure in normal physiological ranges, requiring extraction of tooth, during December 2016-December 2019. The study was approved by institutional review board. Criteria for selection of patients are given in Table 1.
The subjects weredivided into four groups based on ASA (American society of Anesthesiologists) physical status classification8 each consisting of 25 patients as follows:
Group A: patients with controlled hypertension who were administered local anesthesia with epinephrine.
Group B: patients with controlled hypertension who were administered local anesthesia without epinephrine.
Group C: normotensive patients who were administered local anesthesia with epinephrine.
Group D: normotensive patients who were administered local anesthesia without epinephrine.
These patients were evaluated for blood pressure using Electronic Digital Blood Pressure monitor (Omron BP Monitor Upper Arm (Hem 7120), pulse rate and peripheral capillary oxygen saturation using Pulse oximeter (Res Pro-Pulse Oximeter) during preoperatively, intraoperatively and postoperatively.
Local anesthesia (lignocaine with epinephrine 1:80,000, LIGNOX*2 % A and lignocaine plain, LOX*2 %) was used as an anesthetic in an 2 ml syringe (UNOLOK). Standard armamentarium for extraction were also used.
A written informed consent was obtained from all the participants following which an adequate pre-surgical preparation consisting of detailed case history, blood tests wherever indicated and radiographic examination. Baseline blood pressure, pulse rate and SPO2 was recorded in a tabular form. Local infiltration anesthetic technique was used for achieving anesthesia at the rate of 1 ml per minute at which blood pressure and SPO2 were also recorded. Simple extraction of the teeth was started 5 minutes following administration of local anesthesia at which point intraoperatively the blood pressure, pulse and SPO2 was recorded. Postoperatively the blood pressure, pulse and SPO2 was recorded. Following the procedure standard post-operative instructions were given to the patients along with the antibiotics (when indicated) and analgesics. All extractions and administration of local anesthesia was performed by the same surgeon while the reading of the monitor was recorded in the pro-forma chart by the assistant. The statistical tests used for the analysis were independent sample t test (comparing means of different groups), Repeated measures ANOVA (for comparison between the groups) and Tukey HSD Post-hoc Test for significant results in ANOVA. p < 0.05 is considered as level of significance.
RESULTS
The sample consisted of 42 males and 58 females between ages of 40 to 70, participated in the study. A mean age of 45.96 years in group A, 51.38 in group B, 48.76 in group C and 45.6 in group D. There was no statistically significant difference between age and gender (p > 0.05).
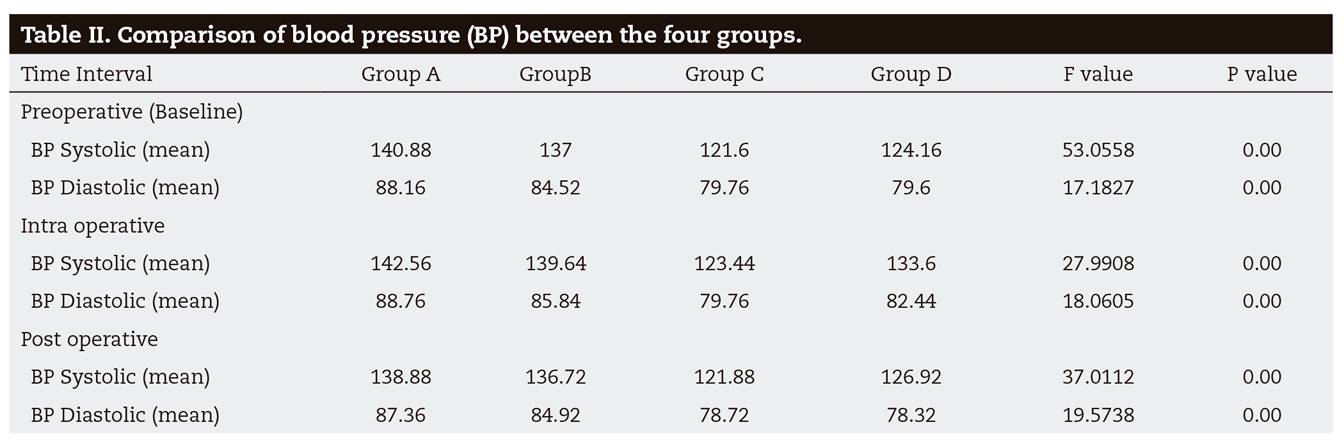
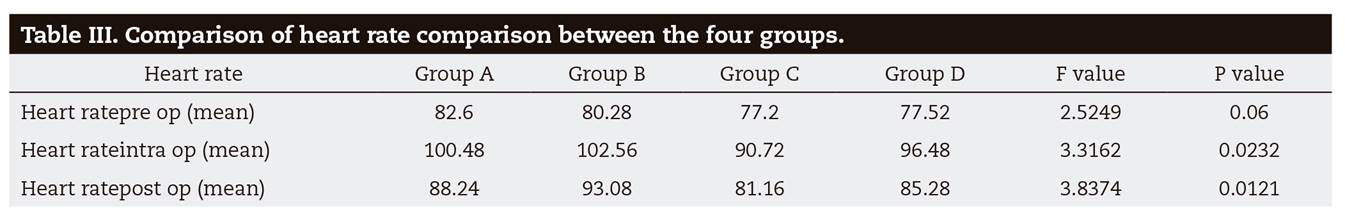
The blood pressure between the groups is given in Table 2 were slightly higher in intra-operative period but reduced even lower than the baseline post-operatively. In group B, a slight increase in heart rate 102.56 bpm and blood pressure 139.64 mm/Hg during intra operative period. Group C and Group D also followed the same trend of increase in heart rate and blood pressure intra-operatively. Regardless of addition of vasoconstrictor, there was a mild increase in systolic and diastolic pressure after administration of anesthetic in all groups. The hypertensive patients had preoperative systolic and diastolic pressure on a higher side than normotensive patients. Heart rate increased in all groups after administration of local anesthetic. The highest values were recorded intraoperatively in group B (Table 3). The SPO2 remained almost unchanged in all four groups during measurement.
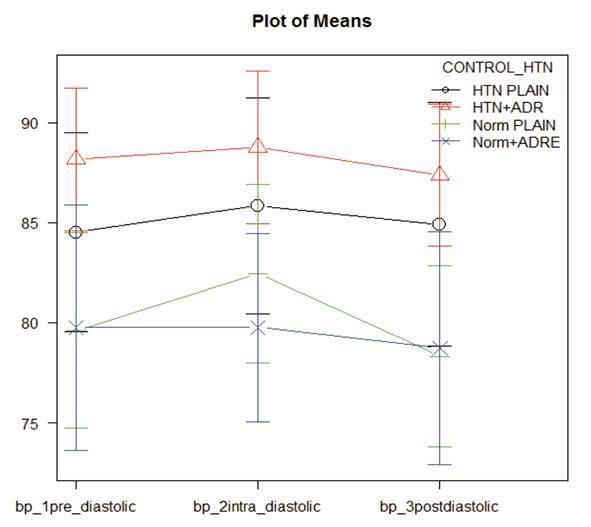
Further comparison between the parameters of all the groups revealed that blood pressure values were significantly higher in groups A and B. There was a statistical difference between hypertensive and normotensive patients irrespective of addition of epinephrine in hypertensive patients in their systolic blood pressure (p = 0.00). Comparison of change in the values after injection of anesthetic are explained by plot of means in Figure 1 and Figure 2. Heart rate values increased intraoperatively in all the groups with a significant difference between Group B vs. Group C intra and post operatively (Figure 3). There was a statistically significant difference between group A (98.91) and group B (97.92) in postoperative SPO2 with comparison of changes illustrated in Figure 4 (p = 0.04).

Figure 1. The trends in the fluctuations of mean blood pressure over time in each group are demonstratedby the slopes of the graph.

Figure 3. The trends in the fluctuations of heart rateover time in each group are demonstrated by theslopes of the graph.
DISCUSSION
Epinephrine is the principal vasoconstrictor being used in local anesthetic solution. The localized vasodilator effects of lignocaine in subcutaneous and submucosal vessels are counteracted by epinephrine which causes vasoconstriction in the surrounding tissues. This vasoconstriction of tissues decreases the bleeding at surgical site and increases efficacy of anesthesia whilereducing the plasma concentration of anesthetic agent being used and therefore decreased systemic toxicity9. Furthermore, bleeding control can be very useful as it improves visibility and access at surgical site1. Many clinicians do not use epinephrine in hypertensive patients and patients having cardiac complications. The systemic absorption of epinephrine and its adverse cardiac effects thereafter limits its use in such patients10,11. Factors responsible for such a hyper dynamic cardiovascular response may include pain at the injection site, intravascular injection, psychogenic stress, drug interaction, or systemic absorption of the epinephrine12 previous investigations have revealed that the inclusion of vasoconstrictor causes the arterial plasma epinephrine concentration to double but meantime was also associated with cardiovascular stability in young healthy patients. Many investigators have concluded that local anesthetic solutions containing epinephrine are usually well tolerated by patients with mild and moderate degrees of cardiovascular disease13,14,15,16. Anxiety, stress and pain during dental treatment results in release of endogenous catecholamines which can result in unacceptable cardiovascular effects17, On the contrary, some studies show that rapid absorption of exogenous epinephrine result in this increase rather than the endogenous release of catecholamines18,19. Blood pressure is affected in the same way by vasoconstrictors as well as by other factors such as stress and anxiety20. So, hypertensive patients constitute an important risk group.
Patients that were considered hypertensive in this study were those who were previously diagnosed by a physician and have their blood pressure presently well controlled with antihypertensive medication at the time of this study. As per the ASA (American Society of Anesthesiologist) physical status classification, this group of patients belonged to class II. In our study mean age of 45.96 years in group A, 51.38 in group B, 48.76 in group C and 45.6 in group D was found. There was no statistically significant difference between age and gender (p > 0.05).
Both systolic and diastolic blood pressure increased slightly after administration of anesthetic in all four group regardless of addition of vasoconstrictor and decreased after the surgical procedure to levels even lower than those recorded at baseline. Since the increase was also noticed in patients who were given plain anesthetic, it can be attributed to the release of endogenous catecholamines due to the pain, anxiety and stress of the procedure. Our study results were in accordance to the results reported by Nichols21. In another study, a steady but insignificant increase in systolic blood pressure was observed in hypertensive subjects after administration of anesthesia in both lignocaine epinephrine and plain lignocaine groups3.
Gungormus and Buyukkurt in their study found out that no significant change is seen in the blood pressure of hypertensive patients following administration of epinephrine-containing 2 % articaine22. Matsumura et al demonstrated that catecholamine present in local anesthetic solution caused an increase in blood pressure and pulse rate23. The hypertensive patients in this study failed to respond to a great extent to lignocaine-epinephrine than plain lignocaine injection.
On comparing intraoperative systolic blood pressure, there was a statistically significant results between groups A and C, A and D, B and C, B and D and C and D. We concur that there is a significant difference between hypertensive and normotensive patients irrespective of addition of epinephrine in hypertensive patients in their systolic blood pressure. Also, there is significant difference in normotensive patients who received anesthetic with epinephrine. The mean intraoperative systolic blood pressure was more in normotensive patients receiving plain local anesthetic as compared with patients administered local anesthetic with epinephrine. This may be attributed to reduced action of local anesthetic leading to reduced pain control and due to the vasodilating action of systemically absorbed local anesthetic leading directly or indirectly through release of endogenous catecholamines to the circulation. Post-operative systolic and diastolic pressure followed the same trend as their intraoperative measurement. However, Significant difference in systolic pressure between hypertensive groups and normotensives groups was observed. But there is no significant difference between groups C and D, indicating that addition of epinephrine has no effect on diastolic blood pressure of normotensive patients. Based on this finding, it may be said that it is beneficial to use local anesthesia with vasoconstrictor for patients with controlled hypertension, provided all precautions to prevent inadvertent intravascular injection are undertaken by the care provider. The observed increase can further be attributed to factors such as psychological and physical stress, including that from painful stimuli, and patient anxiety since increased levels were observed in these groups. Other studies have shown slight variation from these results. Ogunlewe et al found no changes in the blood pressure and pulse rate response following injection of local anesthetic with epinephrine in hypertensive patients24. With Gungormus and Buyukkurt and Meyer reporting similar results22,25.
Heart rate increased in all groups after administration of local anesthetic. The highest values were recorded intraoperatively in group B (hypertensive patients administered with plain local anesthetic). In all groups the heart rate returned back close to baseline reading postoperatively. In analysis there was a significant difference between group B and group C. But it is of less relevance as there was no statistical difference between groups A and group B and between group C and group D. But from the plot of mean heart rate we concur that both preoperative and intraoperative heart rates were higher in hypertensive patients as compared with normotensive patients. Also, the increase in heart rate cannot be attributed to the addition of epinephrine or hypertension as it increases almost equally in all four groups. The study conducted by Tolas et al., observed a significant increase in circulating epinephrine concentration, almost doubling plasma epinephrine concentration after injecting local anesthetic with 1;100000 epinephrine while no significant increase was noted in subjects who received injections of plain local anesthetic although the hemodynamic variables were stable26. They concluded that epinephrine in conjunction with local anesthesia was associated with cardiovascular stability in young healthy patients and the increased plasma epinephrine results from the rapid absorption of exogenous epinephrine. The study conducted by Baguena et al. in Spanish population found significant changes in heart rate and blood pressure due to anxiety and fear related issues20. Alemany-Martínez et al. reported changes in heart rate were affected by pain, individual factors such as age, gender, hypertension, previous experience with dental treatments, and psychological response27. In his study, males showed higher blood pressure values than females, while the latter showed higher pulse rate values and anxiety levels. In another study pulse rate remained stable or decreased during local analgesia and peaked during exodontia and then decreased 10 minutes after treatment. Also this study shows a transient period of bradycardia immediately after injection of local anesthesia which contradicts the results of our study in which there is a steady increase in heart rate following local anesthesia administration in all the groups. Yokobayashi et al found that administration of local analgesic lowers the pulse rate and infiltration was more significant than block analgesia in this regard28. The results of our study were in agreement with the study conducted by Abraham-Inpijn et al who reported tachycardia > 120 beats/min with a maximum value of 154 beats/min during treatment29. In a study which evaluated changes in heart rate during third molar surgery, the lowest heart rates were recorded in the waiting room, in the dental chair, during anaesthesia, when applying surgical drapes, during suturing, and at the end of the procedure. The highest values were obtained during the time-out procedure, incision, and alveolotomy which is similar to our study30).
The SPO2 remained almost unchanged in all four groups during measurement. There was a statistically significant difference between group A and group B in postoperative SPO2. But there was no significance in preoperative and intraoperative SPO2 between the groups. From this data, we concur that there may be a correlation of SPO2 between hypertensive patients administered with epinephrine. The SPO2 have increased considerably postoperatively in patients administered local anesthetic with epinephrine than all other groups, whereas it has remained almost constant for hypertensive and normotensive patients administered with plain local anesthetic. Similar results were obtained in a study by Silvestre et al who did not observe any significant differences in oxygen saturation but had also remained insignificant in postoperative period16 (Table 4). Some studies have shown transient hypoxia after administration of local anesthesia31.
However, further studies with larger sample size are warranted to substantiate our results. Also, we acknowledge the potential for adverse cardiovascular effects by adrenergic stimulation in high-risk patients when a vasoconstrictor is used. That is the reason we have included only stage I hypertensive patients in Group A and B. Patients with higher blood pressure than stage I were excluded from our study. The type of vasoconstrictor combined with the local anesthetic and the total dose injected will be important clinically.
CONCLUSION
The use of epinephrine in local anesthetics have no significant role in altering the blood pressure and heart rate of stage I hypertensive as well as normotensive patients. The Systolic blood pressure increases in normotensive patients administered with plain local anesthetics than when local anesthetics is given with epinephrine. Addition of epinephrine has an effect on post-operative SPO2 in hypertensive patients. Oxygen saturation increases in patients administered local anesthetic with epinephrine.