Introduction
Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy (FAP) TTR V30M, or Transthyretin (TTR) Amyloid Polyneuropathy, is a progressive sensorimotor and autonomic neuropathy of adulthood onset (Adams, 2008). FAP is transmitted as an autosomal dominant trait and is caused by mutations in the TTR gene (18q12.1). Death occurs within a mean interval of 10.8 years after the onset of inaugural symptoms and may occur suddenly or may be secondary to infections or cachexia (Coelho et al., 2012). In addition to liver transplant, delaying the development of symptoms, there is a drug for adult patients with symptomatic polyneuropathy, Tafamidis, to delay neurologic impairment (Coelho et al., 2012). Subjects at-risk for FAP usually have knowledge about the disease through family members who are ill or who have died from the same disease. Being a disease which tends to manifest itself late, many at-risk subjects want to know their genetic status before the disease manifests itself. This knowledge about the subjects' genetic status may and must be provided in the context of genetic counseling. Austin, Semaka, and Hadjipavlou (2014) have conceptualized genetic counseling as a highly circumscribed form of psychotherapy, in which effective communication of genetic information is a central therapeutic goal. Genetic counseling is a clinical practice which implies that the genetic counselor has the following skills: genetics expertise and analysis skills; interpersonal, psychosocial, and counseling skills; education; and professional development and practice skills (Wicklund & Trepanier, 2014). In the genetic counseling process, the predictive and presymptomatic types of testing (PST) are used to detect gene mutations associated with disorders that appear after birth, often later in life (Nance, 2017). Usually, it takes about a year and during that period it is possible to assess the psychological impact of knowledge about the genetic status. However, at the end of the PST process, the access to subjects who were at-risk and who have come to know their genetic status is more complicated and therefore the long-term psychological impact is more difficult to assess.
Some studies have investigated the PST psychosocial impact in a middle and long-term period of time (Almqvist, Brinkman, Wiggins, Hayden, & The Canadian Collaborative Study of Predictive Testing, 2003; Decruyenaere et al., 2003; Decruyenaere et al., 2004; Gargiulo et al., 2009; Gonzalez et al., 2012; Tibben, Timman, Bannink, & Duivenvoorden, 1997; Timman, Roos, Maat, & Tibben, 2004). Those studies have mostly found no evidence of negative psychological impact in the middle and long-term. However, there is always a minority of at-risk subjects who present values which are indicative of negative psychological impacts and the aim of this study is to study and analyze the profile of those subjects.
Method
Objective of the Study
This study addresses the profile of persons whose long-term psychological impacts of PST for FAP is negative, i.e., the values of psychopathology, anxiety, and depression are higher than the normative values of the instruments' authors.
Participants
The sample consisted of 177 subjects, aged over 20 years, that were 50% at-risk for FAP, and performed the PST at least three years ago (Table 1). The sample consists mostly of females who are married or in unmarried unions, with a mean age of 34.55 years, employed, carrier, and having performed the PST for at least 6.65 years on average (6.65 years after performing PST).
Instrumentation
The instruments used in this study were a sociodemographic questionnaire, the Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI; Derogatis & Melisaratos, 1983; Portuguese version: Canavarro, 1999, 2007), the Zung Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS; Zung, 1971; Portuguese version: Ponciano, Vaz Serra & Relvas, 1982a 1982b), and the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI; Beck, Ward, Mendelson, Mock, & Erbaugh, 1961; Portuguese version: Vaz Serra & Pio Abreu, 1973a, 1973b). The chosen questionnaires are part of the protocol of the National Genetic Counseling Program for late-onset neurological diseases (LOND), and all of them are standardized for the Portuguese population.
The BSI assesses psychopathological symptoms through nine dimensions of symptoms and three global indices, being the latter summary reviews of emotional disturbance. The nine primary dimensions are: somatization, obsession-compulsion, interpersonal sensitivity, depression, anxiety, hostility, phobic anxiety, paranoid ideation, and psychoticism. The three global indices are the Global Severity Index (GSI), that provides the mean of all the scale values, the Positive Symptoms Total Index (PSTI), that is a count of the number of items endorsed at a level higher than zero, and the Positive Symptoms Distress Index (PSDI), that is the sum of all item values divided by the positive total symptoms. Canavarro (2007) has established for the Portuguese population normative values, either for the general population or for the population expressing emotional disturbances. According to Canavarro (2007), the cutoff point is 1.7 for PSTI.
The SAS assesses anxiety clinical symptomatology and is composed by 20 items, rated on a four-point Likert scale, ranging from 1 - rarely or never - to 4 - most or all of the time. The construct was evaluated based on the description of the anxiety's most common symptoms and signals for four anxiety dimensions (or subscales): cognitive (items 1to 5) for a maximum of 20 points, motor (items 6 to 9) for a maximum of 16 points, vegetative (items 10 to 18) for a maximum of 36 points, and central nervous system (CNS) (items 19 and 20) for a maximum value of 8 points. The score ranges between 20 and 80 and the cutoff point is 40.
The BDI identifies depression symptoms such as sadness, pessimism, sense of failure, dissatisfaction, guilt, expectation of punishment, disappointment with himself, self-criticism, suicidal ideation, tearfulness, irritability, social withdrawal, indecisiveness, body image distortion, loss of energy, changes in appetite, insomnia, fatigue, weight loss, health concerns, and loss of libido (Beck, Steer, & Brown, 1996). The BDI is a self-response inventory consisting of 21 items, designed to measure the severity of depressive symptoms. Each item has 4, 5, or 6 statements, sorted according symptoms' severity, which may be none, mild, moderate, or severe. Beck et al. (1996) have suggested that the value of 12 is the cutoff point above which the difference between normal and depressed population is set.
Table 2 Comparison of BSI Scales and Indices between the General Portuguese Population, Population with Emotional Disturbances and the Present Study
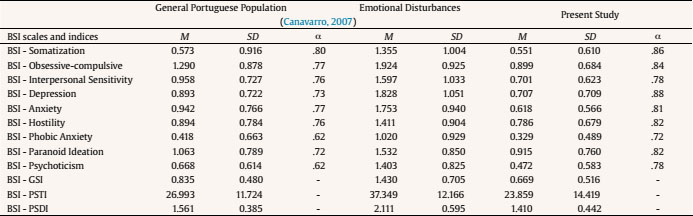
Note. M = mean; SD = standard deviation; α = Cronbach's alpha; GSI = general severity index; PSTI = positive symptoms total index; PSDI = positive symptom distress index.
Procedures
All subjects being questioned attended genetic counseling consultations in the Center for Preventive and Predictive Genetics (CGPP), Institute for Molecular and Cell Biology (IBMC), to know their genetic status for FAP. The only inclusion criteria in this study was that participants had completed the one-year PST protocol in CGPP service (National Protocol) at least three years ago before participating in the study, either carriers or non-carriers. Participants were contacted by mail, one time only, to answer the sociodemographic questionnaire and the BSI, SAS, and BDI. A six-month time frame was set to receive the participants' responses by mail. Of the 500 participants contacted, 203 answered, and only 177 questionnaires were used because the remaining ones were not properly filled out. The guarantee of the data confidentiality was made clear. The informed consent to voluntary collaborate in the research was additionally obtained. All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000.
Data Analysis
Quantitative data were analysed using the SPSS IBM software (version 24.0, 2016). Descriptive statistical and inferential analysis were carried out. Parameters such as mean and standard deviation, are presented. Mean comparison by ANOVA, Pearson correlations, and Cronbach's alpha coefficient values (α) are also included in the analysis.
Results
Table 2 presents the normative means of BSI scales and indices (Canavarro, 2007) for the general Portuguese population and for the Portuguese population with emotional disturbances, as well as for this study's population, i.e., subjects who took the PST at least 3 years ago. When comparing the normative values of the general population of the Portuguese version of the BSI (Canavarro, 2007) with the values of the present study, it is possible to observe that the present sample has lower values than those of the general population in all of the BSI scales and indices. α values of that sample are all higher - in some cases, significantly higher - than those found by the author of the Portuguese version (Table 2). Of the 177 subjects in the sample, 137 (77%) present a PSTI value below the cutoff value proposed by the author (1.7) (Canavarro, 2007) and 40 subjects (23%) a value equal or higher than 1.7.
In Table 3, the profile of subjects with a PSTI value at or above the cutoff point proposed by Canavarro (2007), i.e., 1.7, as well as the profile of subjects whose PSTI is less than 1.7, are presented. The profile of the subjects in the sample whose PSTI is higher than 1.7 has the following characteristics: mainly women, with a mean age of 37.95 years, married or in an unmarried union, employed, carriers, having performed the PST for at least 6.52 years, on average. Only the profession variable presents significant differences in the distribution of the subjects by the different profiles.
Table 3 Sociodemographic Characterization of the Sample (N = 177) regarding PSTI

Note. M = mean; SD = standard deviation.
1χ2(7, N = 177) = 15.003, p = .036.
A comparison between the BSI scales and indices mean values in relation to the independent variables of this study was carried out. Only statistically significant results are presented. The analysis of variance showed that the values of somatization, F(1, 175) = 4.989, p = .027, η2 = .028; depression, F(1, 175) = 3.940, p = .049, η2 = .022; and phobic anxiety, F(1, 175) = 5.043, p = .026, η2 = .028, are significantly higher in women (respectively, M = 0.64, SD = 0.69; M = 0.80, SD = 0.75; M = 0.40, SD = 0.55) than in men (respectively, M = 0.43, SD = 0.48; M = 0.58, SD = 0.63; M = 0.23, SD = 0.38). Table 4 presents results considered statistically significant, regarding marital status. It is possible to observe that divorced or separated subjects present higher values of BSI obsessive-compulsive, depression, phobic anxiety, and paranoid ideation scales, and GSI and PSTI indices, the latter being in divorced or separated subjects, higher than the cutoff point of 1.7. Post hoc analyses using Tukey's HSD indicated that, regarding obsession-compulsion, depression, and PSTI, significant differences occur between the divorced – married and divorced – singles, with the divorced subjects always presenting higher values. In relation to paranoid ideation and GSI, statistically significant differences are found between divorced and single subjects, divorce values being higher. Finally, in relation to phobic anxiety, significant differences occur between single and married subjects, with married subjects presenting higher values.
Table 4 Comparison of BSI Scales and Indices regarding Marital Status

Note. M = mean; SD = standard deviation; F = Snedecor's F distribution or Fisher-Snedecor distribution; df = degrees of freedom; p = p-value; GSI = general severity ndex; PSTI = positive symptoms total Index; η2 = eta squared; 1,2 results of post hoc analyses Tukey's HSD.
Table 5 Comparison of SAS Scales and Total SAS between the General Portuguese Population and the Present Study
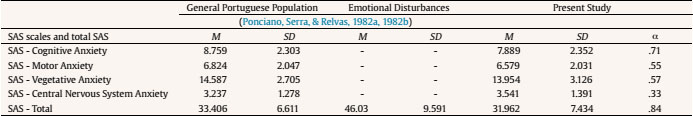
Note. M = mean; SD = standard deviation; α = Cronbach's alpha.
There are also statistically significant differences in relation to PSTI, F(3, 171) = 3.261, p = .023, η2 = .054, with respect to the profession, with the students clearly presenting a significantly lower value for PSTI (pensioner M = 1.44, SD = 0.47; unemployed M = 1.66, SD = 0.53; student M = 1.17, SD = 0.31; employed M = 1.40, SD = 0.42). Post hoc analyses using Tukey's HSD indicated that significant differences occur between the unemployed and the students.
In Table 5, it is possible to observe the normative means of the SAS scales and total SAS (Ponciano et al., 1982a, 1982b) for the general Portuguese population and to the population in the present study, i.e., subjects who took the PST at least 3 years ago. When comparing the normative values of the general population of SAS Portuguese version (Ponciano et al., 1982a, 1982b) with the values of the present study, it is possible to verify that the sample's study has lower SAS values than those of the general Portuguese population in all SAS scales and total SAS, except regarding CNS anxiety SAS scale. Alpha values for the sample's study are high for SAS cognitive anxiety and total SAS, moderate for SAS motor and vegetative anxiety, and low for CNS SAS. Ponciano et al. (1982a, 1982b) argue that the cuttoff point is set to the value 40. However, the value of 37 already suggests a probability that the subject may be anxious in a pathological form. Of the 177 subjects in the sample, whose profile is presented in Table 6, 148 (83.6%) present less than or equal to 39 and 29 subjects (16.4%) present equal to or greater than 40 (cutoff point). Subjects' profile whose cutoff point is greater than or equal to 40 is mainly female, with a mean age of 35.45 years, married or in an unmarried union, employed, carrier, and having performed the PST for at least 6.66 years, on average.
Table 6 Characterization of the Sample (N = 177) regarding SAS Cutoff Point values

Note. M = mean; SD = standard deviation.
A comparison was made between SAS scales and total SAS for the variables included in the present study. An analysis of variance showed that the values of vegetative anxiety, F(1, 175) = 9.133, p = .003, η2 = .049, and total anxiety, F(1, 175) = 5.365, p = .022, η2 = .030, are significantly higher in women (respectively, M = 14.55, SD = 3.30; M = 33.06, SD = 7.82) than in men (respectively, M = 13.15, SD = 2.69; M = 30.47, SD = 7.43).
In Table 7, the normative means of the BDI scales and total BDI for the general Portuguese population and for the population of the present study, i.e., subjects who performed the PST at least three years ago, are presented. The study's sample presents mean values which are indicative of absence of depression (6.233); α values of the same sample are high. Vaz-Serra and Abreu (1973a, 1973b) consider different levels of depression, as shown in Table 8. Most of the sample presents no depression and only 7.9% of the sample presents mild depression. However, 16 subjects (9%) present moderate to severe depression. The profiles of subjects with moderate and severe depression, mild depression, and absence of depression (Vaz-Serra & Abreu, 1973b) are presented in Table 8. The profile of subjects with moderate and severe depression has the following characteristics: mainly women, with a mean age of 42.31 years, married or in an unmarried union, employed, carrier, and having performed the PST for at least 6.75 years, on average.
Table 7 Comparison of BDI Scales and Total BDI between the General Portuguese Population and the Present Study
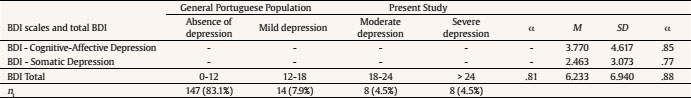
Note. M = mean; SD = standard deviation; α = Cronbach's alpha; ni = absolute frequency.
Table 8 Sociodemographic Characterization of the Sample (N = 177) regarding BDI Cutoff Point Values
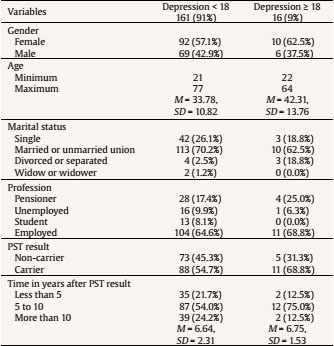
Note. M = mean; SD = standard deviation.
A comparison was made between BDI scales and total BDI for the variables included in the present study. The analysis of variance showed that the values of cognitive-affective depression, F(1, 175) = 3.744, p = .012, η2 = .061, and total depression, F(1, 175) = 2.940, p = .035, η2 = .049, are significantly higher in divorced (respectively, M = 9.29, SD = 7.11; M = 13.71, SD = 11.65) than in single (respectively, M = 3.75, SD = 4.66; M = 5.69, SD = 7.46.823), married or unmarried union (respectively, M = 3.49, SD = 4.30; M = 6.01, SD = 6.53), and widow or widower (respectively, M = 2.00, SD = 2.83; M = 6.00, SD = 4.24). Post hoc analyses using Tukey's HSD indicated that the significant differences occur between divorced-single and divorced-married. There are also statistically significant differences in relation to somatic and/or performance depression, F(3, 171) = 3.622, p = .014, η2 = .059, with respect to the profession, where the students clearly present lower values than the others (pensioner M = 3.87, SD = 4.06; unemployed M = 2.71, SD = 2.93; student M = 1.07, SD = 1.48; employed M = 2.46, SD = 3.07). Post hoc analyses using Tukey's HSD indicated that the significant differences occur between pensioners and students.
The correlations between the BSI, SAS and BDI scales, indices, and total BDI are all positive and significant at level .01.
Discussion
Considering that the main objective of this study is to know the profile of subjects whose long-term psychological impact of PST for FAP is negative, the profile of the sample including all subjects was determined, comparing it with the profile of subjects whose psychological impact was negative, i.e., presenting very high levels of psychopathology (BSI), anxiety (SAS), and depression (BDI). Thus, it can be stated that the sample of this study is mainly feminine, married, or living an unmarried union, with a mean age of 34.55 years, employed, carrier, and having performed the PST for about 6.65 years on average. It was also found that the most part of the sample does not present clinically significant psychopathology values; 3% of the sample presents PSTI values equal to or greater than 1.7. The profile of these subjects has the following characteristics: female, with a mean age of 37.95 years, married or in unmarried unions, employed, carrier, and having performed the PST for at least 6.52 years, on average. Moreover, 16% of the sample presents anxiety values greater than or equal to 40. The profile of these subjects has the following characteristics: female, with a mean age of 35.45 years, married or in unmarried unions, employed, carrier, and having performed the PST for at least 6.66 years, on average. Finally, 9% of the sample reveals moderate and severe depression values. The profile of these subjects has the following characteristics: female, with a mean age of 42.31 years, married or in unmarried unions, employed, carrier, and having performed the PST for at least 6.75 years, on average. These subjects, with clinically significant BSI, SAS, and BDI values, present an overlapping profile, except regarding age, because the clinically depressed subjects have higher mean ages. This profile also overlaps the profile of the total sample, except regarding age, as the mean age of the total sample is lower than that of subjects with high values in the BSI, SAS, and BDI.
The percentage of subjects with a long-term negative impact of the PST for FAP obtained in this study does not allow the authors to agree with other authors who claim the absence of negative psychological impact of the PST in the long-term (Almqvist et al. 2003; Decruyenaere et al. 2003; Decruyenaere et al., 2004; Gargiulo et al, 2009; Gonzalez et al., 2012; Timman et al., 2004). In fact, obtained data of 22.6% (BSI), 16.4% (SAS), and 9% (BDI) of subjects presenting negative psychological impact, after having performed the PST for more than 3 years, cannot be ignored.
Limitations of this study include the impossibility of controlling other variables that could contribute to the results obtained in the target subjects, namely traumatic life events. In addition, the lack of pre- and post-test scores and the lack of a control group make it difficult to conclude that the PST is the reason for increased symptomatology in a subset of the study's participants. Another limitation is related to the time periods considered, middle- and long term, i.e., more than 3 years after the PST, which may not be the most adequate for this sample. However, these periods were based in time periods considered by other authors (Lêdo, Leite, & Sequeiros, 2013; Lêdo, Leite, & Sequeiros, 2014; Lêdo, Leite, Souto, Dinis, & Sequeiros, 2016a, 2016b, in press; Lêdo, Paneque, Rocha, Leite, & Sequeiros, 2013).
Conclusion
Having investigated the profile of at-risk subjects whose long-term PST for FAP TTR V30M is negative, we found that married women or living in unmarried unions, aged between 30 and 45 years, employed, carriers, and having performed the PST test for 6-7 years are a group inspiring higher concern and requiring a more active role with respect to the psychological impacts of the PST for FAP. The role of the clinical and health psychologist with these patients is critical in the adjustment to the presymptomatic test result as well as in adherence to the available treatments conducive to a better quality of life in carriers.















