Introduction
In the context of health care organization, it is essential to guarantee people’s access to the services. In Brazil, health services are available in care networks that aim to offer comprehensive care to the patient1. Services that involve greater technological density such as hospital services tend to be concentrated2. Thus, the hospital setting is an important alternative that must be adapted to the peculiarities of the region where it is inserted and articulated with other care points2.
In the context of hospital care there are pharmaceutical services that correspond to a set of management and care activities that aim for access and Rational Use of Medicines and health products3,4. These services are performed by the Hospital Pharmacy (HP), which requires that qualified human resources (HR) perform care, management and advisory functions5 in an adequate infrastructure, in addition to logistical planning from the perspective of efficiency and security6-9. These aspects are essential for controlling hospital costs, since the costs associated with the use of medicines and health products in this context correspond to a large proportion of the expenditure10-13.
As important as understanding what pharmaceutical services are performed in the hospital context is understanding that they present structure and processes that influence the obtained results, and that they should be continuously evaluated according to standardized criteria and norms to support decision-making3,7,14.
Currently, data regarding evaluation of hospital pharmaceutical services are scarce, and when disclosed they suggest low adequacy of services in relation to established standards and/or focus on some specific pharmaceutical service3,7,14,15. In this context, the objective of this study was to evaluate the pharmaceutical services in public hospital pharmacies under management of the Health Department of Federal District (Secretaria de Saúde do Distrito Federal, SES-DF) (Brazil).
Methods
A cross-sectional evaluative study was carried out in three stages involving hospitals under SES-DF management, which is responsible for health care actions of the Federal District, where Brasilia, the capital city of Brazil is located.
For data collection, the instrument validated in executing the Diagnostic Project of the Hospital Pharmacy in Brazil15 designed according to current Brazilian sanitary legislation was implemented and applied to the hospital director and the person in charge of the HP. A pilot test was carried out to verify the adequacy of the questionnaire and visits were made to the hospitals by the main researcher between May and November 2016.
The first stage referred to the general characterization of the hospitals and their pharmacies. Hospitals were characterized according to the type of care (general or specialized), size (small: up to 50 beds; medium: 51-150 beds; large: 151-500 beds; and extra: more than 500 beds)16, active beds, hospital procedures performed (of medium and high complexity) and hospital activities according to information from the Brazilian health information system17 regarding data collection. The HPs were characterized according to their area, operation and HR.
Hospitals were classified into different complexity Hierarchical Strata (HS) using the K-means non-hierarchical clustering method18, which seeks to find clusters in data in order to create partitions so that observations within the same cluster are similar to each other and different across clusters. Four strata were considered based on the reference of four scoring algorithms regarding compliance of pharmaceutical services by hospital complexity proposed by Messeder19 based on a classification elaborated by the Ministry of Health of Brazil, in which HS1 and HS4 are respectively the most and least complex strata.
The next stage corresponded to normative evaluation of HPs through the logic model proposed by the Brazilian Diagnostic Project15 which considered ten components related to hospital pharmaceutical services (programming (quantity of medication to order), acquisition, storage, distribution, management, selection, information, pharmacotechnical component, pharmacotherapy follow-up and teaching and research (T&R)), proposing specific weights for each one according to their influence for carrying out activities15,19. Sixty-one validated indicators related to the components were subsequently calculated19.
The third step corresponded to an evaluation of HP by HS by applying scoring algorithms based on identifying aspects of the components that were executed by the evaluated HPs. The scores for each HP were determined according to the presentation of mandatory, non-obligatory and undesirable characteristics by the HP19.
These characteristics varied for each HS, as well as the mandatory components: the T&R component was only required for HS1, while pharmacotherapy follow-up and pharmacotechnical component were not mandatory for HS4. If the HP had the mandatory characteristics for non-mandatory components within each HS, the components were then considered in the score, and the component weights for final score were rearranged19.
The points of each HP within the HS were obtained by the score sum of the indicators weighted by component and compared to an ideal score that corresponded to the maximum points that could be obtained for each HS (HS1 = 884.3 points, HS2 = 830.8 points, HS3 = 624.9 points, HS4 = 470.0 points)20. The results were expressed as the compliance approximation percentage of the services in relation to the ideal (outcome variable) in which HP could have regular, average or good compliance if it obtained a percentage from 0 to 33.3%, from 33.4 to 66.6% or from 66.7 to 100%, respectively20. This percentage was calculated for each hospital (overall approximation percentage) and for each component of the logic model.
The percentages were analyzed for their normality, compared by HS using Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and correlated to influencing variables through linear regression analysis. The analyses were performed using the SAS/STAT program at a significance level of 5%.
The research was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Health Sciences of the University of Brasília (Brazil), and by the Research Ethics Committee of SES-DF.
Results
General characterization of the hospitals and the HP
Of the 15 hospitals, 13 (86.7%) were general and two were specialized hospitals. The overall hospital characterization and the evaluated HPs are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Overall characterization of the hospitals and the evaluated HPs

a:Specialized Hospitals.
Fri: Friday; H: Hospital; h: hours; HL: Hospital Level; Hld.: holiday; Mon: Monday; WL: workload; Wkd: weekend.
High complexity procedures were performed on a smaller scale and hospitals with a more complex HS had a higher proportion of care units.
All HPs had pharmacists and worked with medications and health products, and one of them was run by an administrative technician. The areas referred to as more and less adequate to the service were the administrative area (n =7, 46.7%) and the storage area (n =2, 13.3%), respectively.
Normative evaluation of hospital pharmacies (HP)
The evaluated services were performed in greater proportion by the HS1 and HS2 hospitals, which presented an average of nine activities on components opposed to the performance activities of seven components on average by HS3 and HS4 hospitals. The highest and the lowest means of the evaluated indicators corresponded to the management and selection component, respectively (Table 2.1, Table 2.2, Table 2.3 ).
Table 2.(cont.) Results regarding structure and process indicators among the evaluated hospitals

a:Quantity of medication to order. b: A central storage location. c: Medication doses provided per patient by a 24 hours period. d: Medications requested by nursing to main pharmacy and stocked on the nursing unit; the nursing is responsible for all aspects of preparation and administration of medications. e: Combined individual prescription collective distribution system.
CM: Chemotherapeutic Medications; HP: Hospital Pharmacy; IV: Intravenous; PTC: Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee.
SES-DF has a single Medication List for the hospital care level. Such items, as well as health products, are purchased by the HP through monthly requests on a defined date from a single Storage and Distribution Center. The items distributed by this center are acquired through a centralized purchasing process. However, all the evaluated hospitals made emergency purchases of items through a legally regulated program21.
Of the 3958 active beds available in the hospitals, 1872 (47.3%) were served by individualized distribution system (medication doses provided per patient by a 24 hours period).
Evaluation by hierarchical strata (HS)
Of the total HPs, four (26.7%) presented good compliance with the mandatory services according to their HS, and three of these belonged to the lesser complexity HS. Only storage and management components showed good compliance in the services provided (Table 3).
Table 3. Adequacy percentages (%) of the services provided by HP according to a presentation of mandatory items provided in each component of the logic model used as a methodological basis

a:Non-mandatory components depend on the HS to which the hospital belongs: the percentages in italics refer to non-mandatory component for the HS in question.
Ac: Acquisition; H: Hospital; HS: Hierarchical strata; HP: Hospital Pharmacy; P: Programming (quantity of medication to order); PhF: pharmacotherapy follow-up; St: Storage; T&R: Teaching and research.
The overall approximation percentages presented normal distribution and the means according to the HS corresponded to 43.9%, 57.5%, 53.3% and 85.1% for HS1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively. The approximation percen tage of HS4 was higher than the percentage of the other HS (p < 0.01), which in turn presented no statistical significant differences between them.
Table 4 presents the influences on the compliance approximation percentage of services and associated statistical significance resulting from the linear regression analysis.
Table 4. Linear regression analysis with reference of the estimated parameters analyzed on the outcome variable and associated statistical significance
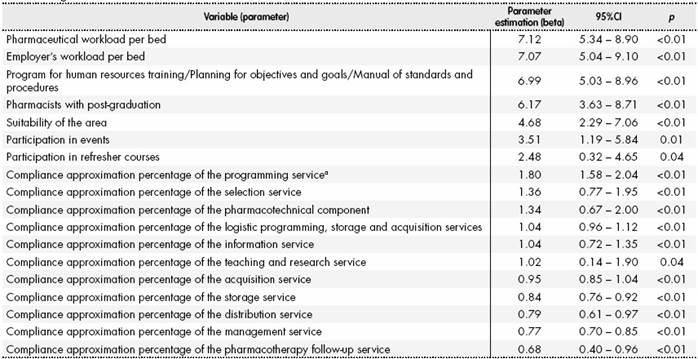
a:Quantity of medication to order. 95%CI: 95% Confidence Interval.
The variables related to the professional workload per bed and the existence of a program/schedule for HR qualification, planning goals and targets, and a manual of norms and procedures in HPs were the parameters that most influenced the outcome variable: the proportional increase of 1% in relation to these variables referred to an increase of 7.12%, 7.01% and 6.99% of the compliance approximation percentage of the services, respectively (p < 0.01) (Table 4).
Discussion
In recent years, changes in the focus of the hospital pharmaceutical services have been observed, which have become strategic for care activities7,22. At the same time, guaranteeing access to medications and health products in the hospital context via management services is a requirement in this context5.
The evaluated services are considered essential for performing related activities in the context of any HP. The absence of mandatory services according to the HS shows potential problems related to achieving the proposed objectives in a timely manner with quality and safety4,9,15,20.
Only four HPs presented good compliance with the activities with three of them belonging to the less complex HS. Nonetheless, the overall mean of the approximation percentages was higher than that reported by Silva et al. (2013) in a study involving 20 HPs of state hospitals in Rio de Janeiro (Brazil), in which none of the HPs had good performance in the evaluated activities4.
Management was the service that presented the best performance, being superior to the evaluation study in Rio de Janeiro4 and to the results presented in the HP diagnostic project in Brazil15. Management anticipates greater systematization of actions, thereby seeking their qualification and maximizing the available resources8,12,14,22. However, the absence of observed planning objectives and goals or a program of HR training hinders this process, and its existence in HPs could positively influence (p < 0.01) the performance of the evaluated services, as shown in the in linear regression analysis.
The HP must have the appropriate number of professionals to perform activities without occupational overload5. However, the number of beds observed per pharmacist was higher than that recommended by the Brazilian Society of Hospital Pharmacies5, and it was higher than that found by Silva et al. (2013)4 and by Pedersen, Schneider & Scheckelhoff (2011) in 562 North American HPs14. Only one HP had a pharmacist during the entire period of operation, in disagreement with Brazilian legislation related5,23.
The pharmacists and non-pharmacists workload per hospital bed were positively related to the compliance approximation percentage of the services, which suggests that the amount of HR is one of the factors that may justify HP performance in relation to the mandatory activities according to the HS that they belong to.
In order to meet management and care demands, there are increasing demands on professional qualification in addition to the amount of HR available5,6. Professional qualification was observed from the point of view of HR participation in events, refresher and post-graduation courses, and its positive influence on services was evidenced in in linear regression analysis, corroborating what was presented by Rutter et al.6 and by Pedersen, Schneider & Scheckelhoff14 in an evaluation study in a hospital in Singapore (2012).
The suitability of HP services requires that its actions are integrated, beginning with selection of medication and the health products that will be made available in the hospital scope24. However, the performance of selection activities was poor and below that presented by Durán-García et al. (2011)25 in a review study on such activities in North American and European hospitals, and by Santana et al. (2013) in a study with ten public hospitals in Sergipe (Brazil)26. The SES-DF has a central Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee which develops a single Medication List for hospitals. However, this does not impair local selection activities, given the particularities of each hospital2. The importance of this component is evident when considering its influence on compliance of pharmaceutical services in linear regression analysis.
Only four HPs showed good compliance with programming, storage and acquisition activities, three of them belonging to the less complex HS. Such services are essential for the control of hospital costs and for access to therapy with minimum inventory disruptions3,8,10,11,13,22,27.
Computerized systems enable rapid data availability, which is essential to meet the objectives of stock management(3-5,7,15,22). However, the amount of easily accessible data did not translate into improved overall stock control performance, since despite all HPs using a computerized system, only five presented the virtual register corresponded to the physical count of the medicines. These results were similar to those observed in other Brazilian studies4,26, and added to the fact that programming was one of the components that presented the greatest influence on the overall fulfillment of the services, it evidences a need for re-adapting this service, which must look for to minimize associated costs without interfering in meeting the demands7,10,11,26.
Thus, there is a need to reorient activities aiming to save space, simplify tasks and optimize HR8,11,14. In this context, it is essential to have coherent management activities to plan actions. The absence of items from the management component may have influenced the compliance percentage with logistics services, which can favor inventory disruption and negatively impact patient safety10,11.
Another important aspect concerns the centralization of acquisitions, which is frequent in the public health scope in Brazil and recommended considering cost reduction4,26; this reduces the possibility of local management regarding medication qualification, health products and/or technical qualification of the suppliers4.
The possibility of making urgent purchases corresponds to an interesting tool to favor decentralized acquisition activities. However, there must be real characterization of urgency and compliance with established legal criteria, such as the minimum specifications of what will be acquired and price monitoring to support decision making and to allow transparency of activities16, which was not observed in the evaluated HPs, or in other Brazilian studies4,15.
In the hospital context we must consider the need to meet the demands of the care units in adequate quantity and quality and in a timely manner8,11, which requires modernizing technical resources, adequate infrastructure and HR qualification, aiming toward distribution service efficiency and patient safety8,9.
Distribution systems that enable greater HP involvement, like individual prescription and unit distribution systems can reduce the access time to medications and reduce the number of errors14. Even though nine HPs showed good compliance with the predicted activities, the rate of active beds with at least medication doses provided per patient by a 24 hours period was low, which may negatively impact on HR availability for care activities and patient safety3,8,12,14,22.
Another service that presented low adequacy percentage was pharmacotechnical component. Despite the influence of this component in fulfilling the pharmaceutical services evidenced by the linear regression analysis, none of the HPs showed good adequacy percentage. Centralizing the services of this component in more complex hospitals or its outsourcing, as observed in this study, has increased over the years12,14 due to the complexity related to them and demands related to structuring and HR5,28.
Among pharmacotherapy follow-up, T&R and care information activities, the parameters that presented the best performance were those of the T&R component, similar to what was observed in a Brazilian study that evaluated pharmaceutical services of a university hospital in São Paulo (Brazil) (2007)7. Only two HPs showed good compliance with these activities, and also showed good overall compliance with the other evaluated activities. This aspect is important, since good compliance with pharmaceutical services is the basis for better HR training, and related to adequate care standards4,6.
The majority of HPs showed good compliance with pharmacotherapy follow-up activities. This result may be associated to the existence of a nucleus of clinical pharmacy in each hospital, with legally defined attributions that involve medication therapy monitoring in the hospital setting. These aspects were addressed in training courses, and are potentially associated with the observed positive results. However, pharmacotherapy follow-up activities fall short of what is required in the hospital context and performed to a lesser extent when compared to studies in other countries6,14. The mean of the evaluated indicators in comparison to other components refers to the idea that the focus of the pharmaceutical services still lies in logistics, similar to that evidenced in other Brazilian studies4,7,26.
No HP formally developed information activity. This aspect was also evidenced in the aforementioned Brazilian studies7,15,26, and it is related to a need for better training and qualification of the involved professionals5,6. This formalization is essential for better communication between HP and other professionals within the hospital environment7,29.
In addition to the specific aspects related to pharmaceutical services, it is essential to have adequate infrastructure compatible with the needs5,16 for performing pharmaceutical services, since its infrastructure is related to its functionality30. The positive influence of area adequacy on service performance according to the linear regression refers to this correlation.
This study presented important results and methodological aspects from an evaluative point of view since it considered the specifications of the pharmaceutical services, which were required in different proportions considering the complexity of the hospitals where they were performed.
Despite the fact that there are other international tools for hospital classification and the methodological aspects used are not worldwide validated (it is regionally limited), it was applied to maintain the internal validity considering that the studies which supported this research used the same methodological basis. Although this study presents intrinsic limitations of a cross-sectional study and geographical limitations, it should be emphasized that there are no recent studies in Brazil involving this subject and that the methodology applied, including hospital classification, was comprehensive and detailed, especially in comparison to the international methodologies of evaluation of the hospital pharmaceutical service found in the literature.
Contribution to scientific literature
This study presents recent data about hospital pharmacies in a Brazilian region through the application of a methodology that considered specificities related to the pharmaceutical services from the managerial to the care perspective according to the complexity of the hospitals where they were performed. It corresponded a detailed and comprehensive evaluation methodology in comparison to the international methodologies of evaluation in this context and the complementary analysis on the influence of managerial, structural and service-specific variables should guide actions and support decision-making process that seek to increase management capacity and the quality of provided service.
















