My SciELO
Services on Demand
Journal
Article
Indicators
-
 Cited by SciELO
Cited by SciELO -
 Access statistics
Access statistics
Related links
-
 Cited by Google
Cited by Google -
 Similars in
SciELO
Similars in
SciELO -
 Similars in Google
Similars in Google
Share
Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas
Print version ISSN 1130-0108
Rev. esp. enferm. dig. vol.109 n.4 Madrid Apr. 2017
https://dx.doi.org/10.17235/reed.2017.4532/2016
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Hemobilia related to cystic artery pseudoaneurysm as a cause of acute pancreatitis
Pancreatitis aguda por hemobilia secundaria a pseudoaneurisma de la arteria cística
Key words: Hemobilia. Pseudoaneurysm. Cystic. Pancreatitis
Palabras clave: Hemobilia. Pseudoaneurima. Cística. Pancreatitis.
Dear Editor,
Hemobilia is a rare cause of upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB). It is commonly iatrogenic, and is more rarely caused by tumors, lithiasis, and inflammatory or vascular disease. We describe a case of cystic artery pseudoaneurysm, which caused acute pancreatitis as an unusual complication.
Case report
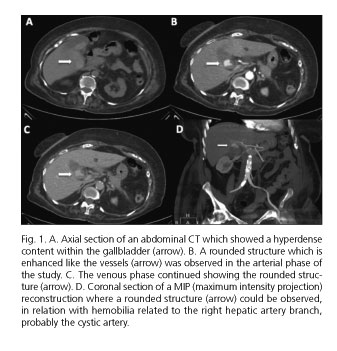
An 85-year-old woman with a history of gallstones presented with abdominal pain located in the right upper quadrant radiating to the back, vomiting and hematochezia. Laboratory findings showed leukocytosis (14,300, neutrophils 84.5%), hemoglobin 7 g/dl, elevation of reactive C protein 179 mg/l, amylase 648 U/l, lipase 1,417 U/l and cholestatic pattern. A gallbladder wall thickening with gallstones and an inflammatory process in the pancreatic tail was observed on an abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan. As UGIB and anemia continued an angio-CT was performed, showing a lobed contour structure within the gallbladder which was hyperdense in the arterial phase, did not change its morphology in the venous study, and was compatible with a cystic artery pseudoaneurysm (Fig. 1). The final diagnosis was acute pancreatitis by hemobilia secondary to a cystic artery pseudoaneurysm bleed. Bleeding point embolization was performed with a successful recovery of the patient.
Discussion
Hemobilia is a rare cause of UGIB and is commonly iatrogenic. Tumors, gallstones and vascular or inflammatory diseases may also cause hemobilia (1,2). Hemobilia classically presents with the Quincke triad (abdominal pain, obstructive jaundice and UGIB) (1,3,4). If bile duct obstruction by hemobilia occurs, it may cause pancreatitis. Gold standard treatment is selective transarterial embolization (3,5). In conclusion, we would like to emphasize that acute biliary symptoms combined with UGIB should strongly suggest the possibility of hemobilia, which involves high mortality rates without specific treatment.
Patricia Lozano-Cruz1, Percy Arenas2 and Ignacio Moral3
Departments of 1Internal Medicine, 2Radiology, and 3Digestive Diseases.
Hospital Universitario Príncipe de Asturias.
Alcalá de Henares, Madrid. Spain
References
1. Arroja B, Canhoto M, Barata P, et al. Hemobilia por pseudoaneurisma de una rama de la arteria hepática derecha. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2010;102(6):386-7. [ Links ]
2. Feinman M, Haut E. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Surg Clin North Am 2014;94(1):43-53. DOI: 10.1016/j.suc.2013.10.004. [ Links ]
3. Marynissen T, Maleux G, Heye S, et al. Transcatheter arterial embolization for iatrogenic hemobilia is a safe and effective procedure: Case series and review of the literature. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;24(8):905-9. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e328354ae1b. [ Links ]
4. Huang CW, Hsu PI, Chan HH. Acute pancreatitis and cholangitis caused by hemobilia secondary to hepatocellular carcinoma: A case report. J Intern Med Taiwan 2013;24:500-4. [ Links ]
5. Lorente-Hence JM, Diéguez-Rascón F, Núñez G, et al. Tratamiento endovascular de hemobilia iatrogénica. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2012;104(2):102-3. DOI: 10.4321/S1130-01082012000200015. [ Links ]











 text in
text in