INTRODUCTION
It is estimated that 30-40 % of cancer patients present pain at the moment of diagnosis, reaching 70-80 % as the disease progresses 1,2. Even when background cancer pain is adequately managed, brief episodes of acute pain, called breakthrough pain, can severely impact the quality of life of the patient. Breakthrough cancer pain (BTcP) has been defined as "a transient exacerbation of pain that occurs either spontaneously, or in relation to a specific predictable or unpredictable trigger, despite relatively stable and adequately controlled background pain" 3,4. Despite recent major progress in the awareness and treatment of BTcP, it has been estimated that the prevalence of BTcP can reach up to 95 % depending on the type of cancer and the diagnostic criteria, and about 60-90 % of cancer patients eventually die with pain 5,6,7. BTcP can have negative effects on the patient's physical func- tions and mood, which can lead to anxiety depression and sleep disorders 2. If not managed adequately, it is also associated with greater use of health services and social services 8).
The recommendations for the treatment of BTcP have been described in numerous studies and guide- lines 4,9,10,11,12. BTcP should be treated with a powerful analgesic with a rapid onset of action (≤ 10 minutes) and a short duration of effect (≤ 2 hours), with mini- mal side effects and easy to administer (comfortable, non-invasive and self-administered) 10. Generally, it is recommended that the management of patients with BTcP should include close monitoring of the patient's state from the very early stages of treatment (< 72 hours from start), during dose titration, and dynamically in subsequent stages of the disease. It was also emphasized that treatment should be individualized to fit each patient's specific needs, and recorded in his/ her medical history 10.
Studies aimed at determining the awareness and knowledge of the guidelines for the treatment of BTcP by practicing oncologists show that, despite general agreement on the guidelines' recommendations, com- pliance is limited and additional efforts are required to enhance its implementation 8,13,14,15,16. Success in the management of BTcP episodes will depend on their ade- quate identification and evaluation, as well as a correct adherence to treatment 17. Some of the reasons for not taking the medication in patients with treatment for BTcP include the lack of perceived efficacy and fears about adverse effects, overdose and addiction 18,19. However, adherence to treatment can be optimized through patient education, improved management pat- terns and better communication between doctors and patients 20. Although many studies have evaluated the adherence to treatment for chronic pain in cancer patients, there are no studies on the adherence to opioid treatment directed at BTcP episodes.
The main objective of this study was to evaluate the perception of Spanish oncologists on adherence to opi- oid treatment for BTcP. Our study also examined how oncologists assess adherence and what interventions for improvement are usually carried out in their usual clinical practice. The analysis of these data will help in the design or improvement of strategies for cancer pain management which ultimately will increase the quality of life of the patient.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This observational, multicentric study was carried out in 84 hospitals throughout Spain from September to November of 2017. Data was collected with an online questionnaire in which practicing oncologists actively involved in pain management responded to questions relative to their perception of treatment adherence and its management in current clinical practice. All the par- ticipating oncologists reported on pain management in patients with a diagnosis of cancer and currently with episodes of BTcP. The participant oncologists were chosen to be representative of all regions of Spain. The survey questions were developed by a Scientific Commit- tee comprised of members from Fundación ECO (Foun- dation for Excellence and Quality in Oncology), which is composed of expert oncologists. Survey questions were developed for the study by consensus among the members of the Scientific Committee, and were not formally validated.
This study was carried out following the ethical prin- ciples established in the current revised version of the Declaration of Helsinki (Ethical Principles for Medical Research in Humans, Seoul 2008) and Good Clinical Practice standards (ICH harmonized tripartite guide- line: Guideline for Good Clinical Practice, 1996). The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Commission for Clinical Studies of the Puerta del Hierro Hospital (Madrid, Spain).
Outcome variables
The main variable was the physician's perception of the degree of adherence by their patients of their opi- oid-based BTcP treatment.
Secondary variables were: a) the physician's percep- tion of the adherence to the opioid-based treatment of background oncologic pain; b) the opioid treatment prescribed to patients with BTcP; c) the clinical conse- quences of therapeutic non-adherence, and the phar- macologic and non-pharmacologic factors involved in non-adherence; d) determination of how the oncologists evaluate adherence; e) the actions and strategies fol- lowed to improve therapeutic adherence in current clin- ical practice by the participant oncologists; and f), the differences in perception of adherence, type of opioid used, and possible prescription of preventive measures to manage adverse reactions, as a function of the years of practice and specialty of the participating physician.
Study design and data collection
All the data used in this study was collected by means of an online questionnaire which included questions on the demographic information of each of the participat- ing oncologists and 25 questions related to their per- ception of adherence of the opioid treatment of cancer treatment and their current clinical practice. Of the 25 questions related to the perception of adherence, 20 questions were closed, 2 questions were open, and 3 were questions were to be responded according to a verbal rating scale (VRS). The VRS was used to mea- sure a) the patients perceived efficacy of the opioids used to treat BTcP, b) the perceived concern of the patients about possible adverse effects of the opioids used to treat BTcP, and c) the patients concern about the possibility of addiction caused by the opioids. The questionnaire was designed as simple questions that reflect perceptions about the use of analgesics for the treatment of pain. We did not include questions about quality of life as they would not only reflect pain but also other aspects of the cancer treatment.
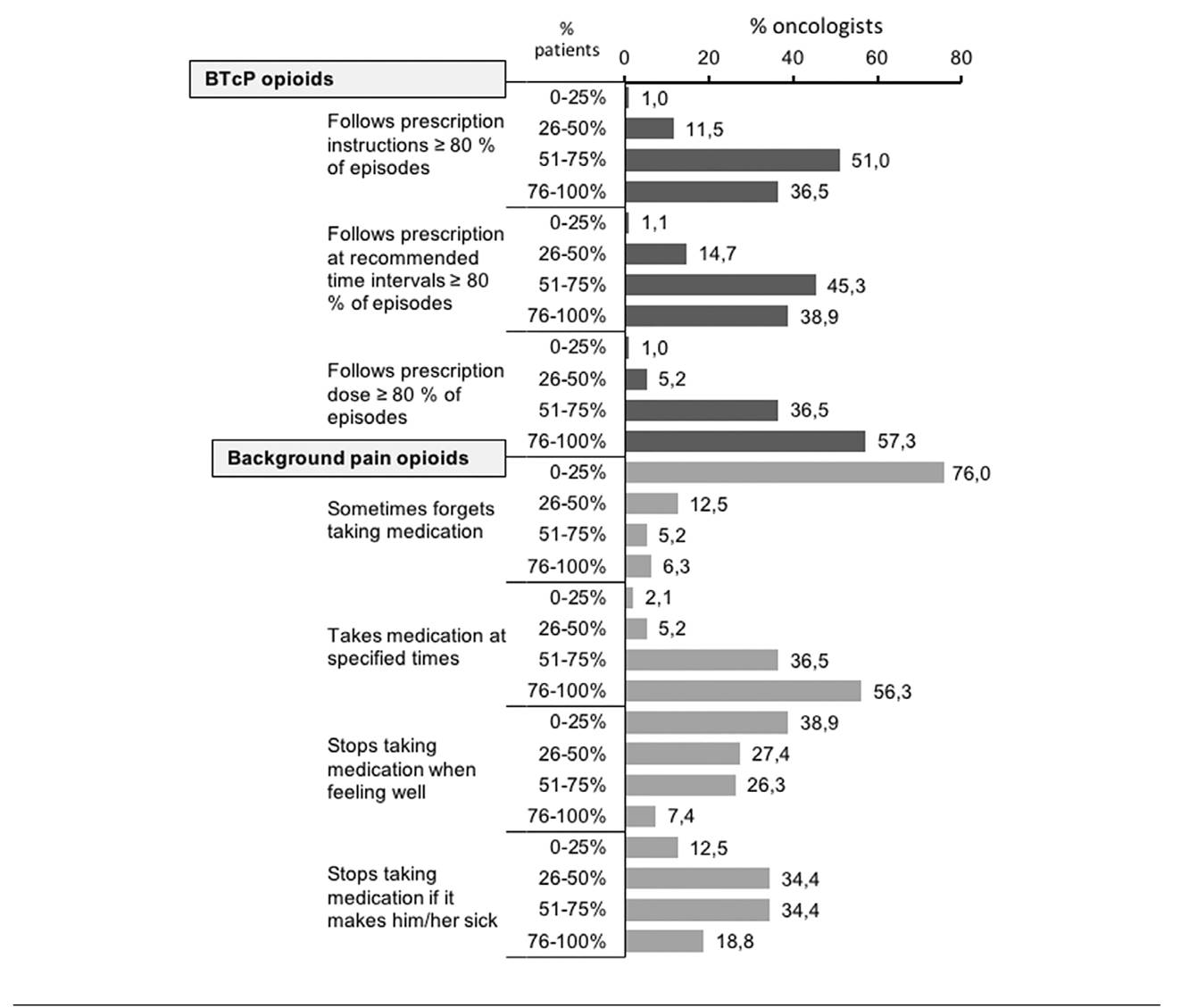
Each participating physician recorded the percent- age of patients that followed the prescription of BTcP treatment and took the opioids at the doses and rec- ommended intervals. Compliant patients were defined as those that follow the prescription in at least 80 % of BTcP episodes.
The physician also recorded the percentage of patients that follow the prescription for the treatment of background oncologic pain, including patients that sometimes forget to take the prescribed medication, take the medication at the prescribed times, fail to take the medication when they feel well or fail to take the medication if it makes them feel unwell.
Statistical analysis
An analysis of descriptive statistics was presented for all the variables. The continuous variables were sum- marized by N, mean and standard deviation (SD). The categorical variables were described by N and percent- age of each category. All the tables, figures or graphs were calculated from the number of valid cases (N), and this number is the one that was considered for the calculation of percentages or other statistical con- siderations.
All statistical analyzes were performed using the sta- tistical package SAS(c) (Statistical Analysis System) for Windows version 9.2 or later.
RESULTS
This study analyzed the perception of adherence to opioid treatments for BTcP of 97 oncologists working in 84 public and private Spanish hospitals (response rate = 70.29 %; 138 oncologists initially approached for the study). Their demographic data is shown in Table 1. Most of the participants were women (60.8 %) aged 30-45 years and with 5-15 years of experience in their profession. Oncologists included specialists in all areas of cancer treatment.
Opioid treatments
The preferred use of opioids for the treatment of cancer-related background pain and of BTcP is shown in Table 2. For background pain, most oncologists report- ed using fentanyl as a first choice, morphine as sec- ond choice and oxycodone as third choice. For BTcP, oncologists mostly prescribed sublingual fentanyl as a first choice, nasal fentanyl as a second choice, and oral fentanyl or fast-acting morphine as third choice.
In general tolerance for the specific opioid treatment for BTcP was high, as 59.8 % of the oncologists report- ed good tolerance for > 76 % of the patients. Medica- tion to prevent opioid-dependent adverse effects was prescribed by 69.1 % of the oncologists, and the rest (29.9 %) reported doing it sometimes. Opioid dose titra- tion to the minimum necessary was also done by most oncologists (74.2 %) but 21.6 % reported doing it only sometimes and 4.1 % reported never doing it. When BTCP episodes persisted, 95.9 % of the oncologists considered dose adjustments of the BTCP treatment.
Adherence to the opioid treatment
The physicians reported that adherence to therapy was evaluated by a direct interview with the patient (96.8 %) or a specific questionnaire (1.1 %). Only 2.1 % of the oncologists reported that adherence was not measured in their current clinical practice.
The adherence to the treatment for opioids for BTcP or background treatments is shown in Figure 1. Most oncologists (87.5 %) perceived that > 50 % patients followed prescription instructions and took the correct dose of medication at recommended time intervals. However, many oncologists (51.0 %) perceived that a significant fraction of the patients (25-50 %), did not adhere to the treatment. The oncologists reported high adherence for background pain opioids, although most consider that their patients stop taking medication if it makes them feel unwell or if they feel better.
Lack of adherence to opioid treatments
Most oncologists (89.6 %) considered that therapeu- tic non-adherence significantly worsened the progres- sion of their patients with respect to BTcP, with loss of quality of life as main consequence (87.5 %) and dete- rioration of family and social relations and prognosis as secondary consequences (Table 3).
The main non-pharmacological factors that hindered therapeutic adherence in the patients were, according to the oncologists, the self-perceived feeling that they do not need being treated (35.8 %), the lack of family support (31.6 %), and the lack of disease awareness (26.3 %) (Table 3). Conversely, the main pharmacological factors that hindered adherence were perceived inefficacy of the treatment (37.5 %), concern about potential adverse effects (32.3 %), and potential addic- tion to the opioids (10.4 %), among others (Table 3).
Adequacy of the treatment
On a scale of 0-10 (10 = highly effective on a verbal rating scale), the physicians reported that their patients perceived that the efficacy of the opioids used to treat BTcP was (mean ± SD) 7.51 ± 0.77. Additionally, on a scale of 0-10 (10 = highly concerned), the oncologists reported that the concern of their patients about pos- sible adverse effects of the opioids used to treat BTcP was 6.69 ± 1.94. Finally, asked about the possibility of addiction caused by the opioids, the physicians reported that their patients' concern, on a scale of 0-10 (10 = highly concerned), was 6.0.
Interventions to improve adherence
Most oncologists (79.2 %) indicated that their patients should receive more information on the med- ications prescribed to manage their pain. When asked about the interventions required to improve adherence to opioid treatment, the oncologists reported several possi- ble options: treatment of adverse effects (88.7 %), edu- cation about pain management to patients and relatives (85.6 %), written prescription instructions (85.6 %), and simplification of drug regimens (84.6 %) (Table 3).
Most oncologists (> 60 %) reported that the nurs- es are also involved in the education to patients and relatives, as well as in tasks related to support and guidance of patients.
DISCUSSION
This study evaluated various aspects of management of BTcP and the perception of therapeutic adherence by oncol- ogists working in Spanish hospitals. Our study revealed that, although adherence to the opioid-based treatments for background pain and to BTcP is generally high, several issues require further attention and improvement.
One of the findings of our study was that there is still a significant fraction of oncologists that do not prescribe preventive treatment of characteristic opi- oid-related adverse reactions (nausea, vomiting, consti- pation) when administering opioids for BTcP. This pre- ventive treatment is advised in all current guidelines 3,4,10,21,22. Also recommended in the guides is dose titration, which our study finds that almost 25 % of the participating oncologists do not do or do only occasionally. However, titration can be done rapidly and safely with current formulations of fentanyl (sublingual or nasal) which the oncologists prefer as first choice for the treatment of BTcP 12. Adequate titration of dose could help reduce side effects and reassure the patient that the treatment is effective and individualized for his/her condition.
The pharmacologic profile of fentanyl is the most adequate for the treatment BTcP, but 5.1 % of the oncologists use fast-acting morphine as a first choice. The percentage of Spanish oncologists choosing mor- phine increased to 25 % when asked for second or third choice of drug for BTcP. However, fast acting mor- phine, because of it hydrophilic nature, has analgesic effects (slow onset of analgesia and prolonged duration of effect) that correlate poorly with typical BTcP epi- sodes 4,23. Current European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) guidelines indicate that transmucosal fentanyl formulations have a role in unpredictable and rapid-onset BTcP 21. It is possible that some patients could stop taking opioids if they feel that the treatment is not effective against their BTcP. Most studies show that transmucosal formulations of fentanyl provided the strongest and fastest pain relief as compared to oral morphine for BTcP 24.
BTcP treatment should be reassessed regularly so that adjustments can be introduced as the disease pro- gresses. This reassessment should not only take into account the analgesia, but also changes in quality of life of the patient, side effects, and patient's satisfaction 12. In this regard, our study showed that the oncol- ogists perceived that patients were generally satisfied with the treatment, although to some extent concerned about side effects or addiction. Characteristic fears of the patients were adverse effects associated with the treatment or the possibility of addiction, as it has been described in other studies 18,19. It is also possible that disease prognosis could influence the adherence to the treatment. In patients with better prognosis per- haps the use and type of BTcP medication should be adapted to the expected length of treatment, therefore limiting the potential adverse effects of longer expo- sures, such as the possibility of addiction.
Communication skills can also aid the physician improve adherence and critically influence the patient's approach to opioid therapy 19. For example, providing both written and verbal information about pain manage- ment plans have been shown to be important 25. A large majority of oncologists emphasized the need for written instructions on BTcP management and better education to patients, stressing the deficiencies in the current process. In our study, although most oncolo- gists advocated giving their patients more information, it was not specified who or when should provide this information. Our study showed that nurses have a sig- nificant role in education of patients and relatives, but it is uncertain if they are ready to perform this role or the effectiveness of their participation. In fact, a study of nurses' practices across 12 European countries (but not including Spain) showed that they are often unpre- pared to deal with BTcP 26. Even if this study was focused on oncologic BTcP exclusively from perspective of oncologists, if should be of interest in future studies to include other professionals involved in Pain Units in Spanish hospitals, thus reflecting their multidisciplinary nature.
One of the limitations of our study was that the oncol- ogist could be biased in his quantitative response of the adherence if he did not keep detailed records of the number of patients with BTcP treated and interviewed on this issue. Also, the details of the interaction with the patient were not specified or standardized. As it is common with self-reported data, it could also be sub- ject to bias by the 'Hawthorne effect', by which oncol- ogists could have modified their behavior in response to their awareness of being observed 27. However, the strengths of the study include a high number of representative oncologists of all regions of Spain and also that the study was designed to provide insights on the current, real world, practices in Spain.
CONCLUSIONS
Oncologists perceived that adherence to BTcP treatment by their patients could be strengthened by improved treatment of adverse effects, better educa- tion about pain management to patients and relatives, providing written prescription instructions, and simplifi- cation of drug regimens to improve adherence.