Mi SciELO
Servicios Personalizados
Revista
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Accesos
Accesos
Links relacionados
-
 Citado por Google
Citado por Google -
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO -
 Similares en Google
Similares en Google
Compartir
Enfermería Global
versión On-line ISSN 1695-6141
Enferm. glob. vol.17 no.51 Murcia jul. 2018 Epub 01-Jul-2018
https://dx.doi.org/10.6018/eglobal.17.3.305911
Reviews
Theory of rational action and its characteristics in nursing research
1 Enfermero/a. Alumno/a de Doctorado en Enfermería. Programa de Posgraduación en Enfermería de la Universidad Federal da Paraíba. João Pessoa-PB-Brasil. mailson725@gmail.com
2 Enfermera. Alumna de Doctorado en Enfermería. Docente del Curso de Enfermería de la Universidad Federal de Campina Grande. Campina Grande-PB-Brasil
3 Doctora en Enfermería. Docente de la Escuela Técnica de Salud y del Programa de Posgraduación en Enfermería de la Universidad Federal da Paraíba. João Pessoa-PB-Brasil.
Objective
To identify the scientific production related to the use of Rational Action Theory in nursing research.
Method
This is a bibliometric study, carried out with 22 articles published in the period 2006-2016, selected in the CINAHL and Scopus databases.
Results
The year with the highest number of publications (18.2%) was 2006. The United States of America stood out in the largest amount of research (36.3%), and the International Journal of Nursing Studies had the highest impact factor, 3,561. The results demonstrate hegemony of publications in international journals, demonstrating the global use of the theoretical model in different contexts.
Conclusions
It is expected to use this theoretical reference in the scientific production of the area, as well as in the diffusion of its applicability in predicting intentions and behavior in the context of health, being able to be an adjuvant in the promotion of health promotion, and therapeutic adherence related to chronic diseases.
Keywords: Social Theory; Behavior; Attitude; Social Norms; Nursing; Bibliometry
INTRODUCTIÓN
Theoretical models have contributed as references for structuring care, adapted to the needs/specificities of people in diverse social and environmental contexts. The theoretical-methodological references offer support for the construction of knowledge and professional practice, since they help in the development of the triad, theory, research, and practice, presenting the complexity and multiplicity of the phenomena present in the health area, with the purpose of describing, explaining, predicting or prescribing human behavior1.
This study focuses on the Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA), originating in social psychology and presented in 1975 by Ajzen and Fishbein, American teachers and researchers. This theoretical model is based on the human being as a rational species, which uses the available information systematically, implicitly or explicitly, whether complete, true or not, to form the behavioral intention. In this way, human behavior is under personal control and the individual could change his behavior by reasoning about what causes him to act in a certain way2)(3.
TRA has been applied to predict the behavior of the individual in a given situation, as well as to identify the factors that determine it. The behavioral intention of the individual is a function of two basic determinants: one of a personal nature (attitude) and one of social influence (subjective norm). The TRA model uses five constructs in predicting behavior: behavioral beliefs, attitude, normative beliefs, subjective norm, and behavioral intention2)(3)(4.
Attitude is a function of what the individual believes will happen in performing the behavior (behavioral beliefs) and of the positive or negative evaluations he makes about the consequences of performing that behavior. The subjective norm corresponds to the perception that the individual possesses through social pressures on him to perform or not determined behavior (normative beliefs), as well as the motivation to respond to such pressures2)(5)(4. Behavioral intentions are direct predictors of behavior 4.
Since TRA is a theoretical reference whose focus is to understand and predict human behavior, its application can take place in several areas of knowledge, including health. In the meantime, nursing is a field of knowledge in which the knowledge generated reverts to the care of people. Therefore, the profession needs to conduct research that reveals factors and causes of certain behaviors to elaborate intervention strategies subsidized by consistent theoretical models that favor therapeutic adherence in health.
A challenge for nursing care is the attempt to modify unhealthy behaviors for the individual to experience health free of damages related to chronic diseases. Thus, the relevance of the study is based on the importance of knowing how Nursing can use theoretical-methodological references of other areas of knowledge, enriching its corpus of knowledge, with the purpose of encouraging the development of care-oriented care technologies health, disease prevention and reduction of illness.
Considering the relevance of theoretical-methodological models for the direction of Nursing care in the area of teaching, research and care, as well as the need to understand health behavior in its different contexts, this research has as a guided question: What are the characteristics of the productions in Nursing that used the Theory of Rational Action as a theoretical-methodological reference? Thus, the objective was to identify the scientific production related to the use of Rational Action Theory in nursing research.
METHODS
This is a descriptive study, of the bibliometric type with a quantitative approach. Bibliometrics is a method used in several areas of knowledge, with the purpose of grouping and synthesizing research results on a delimited topic or a guiding question, in a systematic and orderly way, which contributes to the construction and improvement of knowledge of the area investigated6.
A search was made in the electronic databases CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing & Allied Health Literature) and Scopus, in January 2017. The own name of the theory, Theory of Reasoned Action, and the controlled descriptor of the medical vocabulary Medical Subject Heading (MeSH), Nursing was used as a descriptor to obtain studies developed in the field of Nursing with interposition of the boolean operator AND. Thus, it was sought to remove the largest number of studies that did not fit the subject matter investigated. It was decided to establish limits regarding the year of publication of the investigations, adopting temporal cut of 2006-2016 to identify the literature of the last decade.
The inclusion criteria were articles from primary studies using TRA as a theoretical-methodological reference, published in English, Spanish or Portuguese within the established time frame. Case reports, review articles, book chapters, monographs, dissertations or theses, news newspaper articles, editorials and non-scientific texts were excluded.
The studies were read in full by pairs to fulfill the data collection instrument. The information collected underwent a double spreadsheet process of the Microsoft Excel® program to identify inconsistencies and minimize the risk of errors. After that, the data passed through the judgment of three doctoral students of the Graduate Program in Nursing, obtaining unanimity regarding the results obtained, enabling a better quality of the review.
Articles that did not use the Theory of Rational Action in data analysis were excluded. After the careful reading and refinement of the search, there were 22 articles selected that composed the sample (Figure 1).

Figure 1 Flowchart of the selection process of scientific productions in the nursing area. João Pessoa, PB, Brazil, 2017.
After the reading, the bibliometric data were inserted in a synoptic table elaborated by the authors, containing the following items: database, title of the publication, title of the authors, year, journal, language, Qualis/Capes/Brazil, objectives, methodological outline and the area of study interest. The study data were analyzed through descriptive statistics. The obtained results are presented by absolute and relative frequencies, shown in the table, figures, and conceptual map. The map was developed through the free Cmap Tools program, version 6.01.01.
RESULTS
Considering the bibliometric indicators quantified in the 22 articles selected, there were 15 (68.2%) available in CINAHL and seven (31.8%) in Scopus. Regarding the language, all studies were presented in the English.
Among the countries that used TRA in studies in the Nursing area, there was a higher prevalence of production in the United States, eight (36.4%), followed by Israel five (22.7%) and Taiwan four (18.2%). There was only one (4.5%) study in Australia, Brazil, Scotland, Spain, and Ireland.
All the studies were linked to higher education institutions, with the first author with the following academic qualifications: 12 (54.6%) doctors, two (9%) masters, and one (4.6%) specialist; seven (31.8%) studies did not specify the titration of the authors, hindering to classify them.
The distribution of studies per year revealed that 2006 concentrated the largest number of publications (Figure 2).
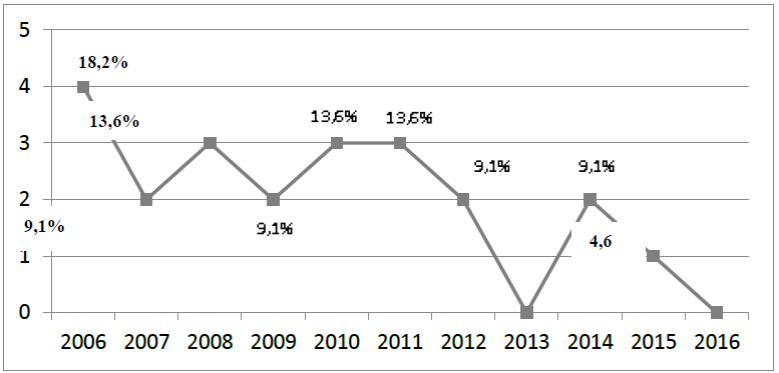
Figure 2 Distribution of studies on TRA and Nursing, regarding the year of publication, from 2006 to 2016. João Pessoa, PB, Brazil, 2017
Regarding the distribution of scientific journals, it was verified that all there articles were international, especially the International Journal of Nursing Practice. The other journals presented only one study. As for Qualis/Capes/Brazil, more than half of the journals presented this stratification, being classified in Stratum A1. The greatest impact factor was attributed to the International Journal of Nursing Studies (Table 1).
Table 1 Distribution of journals with publications of Nursing studies with the use of TRA, according to Qualis/Capes/Brazil and Impact factor. João Pessoa, PB, Brazil, 2017.

* Journal not presenting Qualis/CAPES/Brazil
Source: Data of the research, 2017
Regarding the methodological approaches used in the investigations, those with a quantitative approach prevailed with 19 articles (86.3%). The qualitative was applied in two (9.1%) and the hybrid in one (4.6%) production. Regarding the objectives, 13 (59%) were descriptive, four (18.2%) were correlational studies, three (13.6%) were quasi-experimental and two (9.2%) were methodological studies. Regarding the procedures for data collection, it was verified that in 18 (82%) surveys there were questionnaires used. Regarding the collection technique, four (18.2%) studies conducted interviews, two (9.1%) used online research technologies and one (4.5%) followed the observation technique.
Regarding the level of health care, nine (41%) works were performed in primary care, two (9%) in the secondary and seven (32%) in the tertiary. In four (18%) studies, it was not possible to identify the level of care. Next, the characteristics of the productions with the applicability of TRA in the Nursing area, the practice scenario and the target audience of the investigations can be observed (Figure 3).
DISCUSSION
The study identified 22 articles disseminating the application of TRA in scientific research in the field of Nursing over 10 years. It was noted that the largest number of publications was concentrated in 20067-10. Of them, the only study conducted in Brazil was conducted by Pinto et al.10, whose objective was to identify the normative beliefs and attitudes that contribute to the formation of the behavioral intention of the nurse in performing the hemodynamic study through the pulmonary artery catheter.
Although studies in the Nursing area use other references or theoretical transdisciplinary models, it is important to reflect on the need to include the descriptor "nursing" in productions developed by researchers in this area. This strategy can increase the chances of identifying a greater number of publications with the theme, which strengthens the category and provokes greater visibility and recognition as a profession and science based on methodological rigor.
The publications of international publications were responsible for the dissemination of articles, especially the International Journal of Nursing Practice, accounting for 9.1% of all journals. It is a journal responsible for the publication of original works that seek to advance and understand the international development of nursing and midwifery as an academic discipline and sub-area, not excluding other areas of interest11.
The publications selected in this journal described the application of TRA in nursing care to adult12 and elderly13 patients, both studies conducted in Israel and by the same team of researchers. As for Qualis/CAPES/Brazil, the journal presents the classification stratum A1, considered the best classification of the system.
The Qualis/CAPES/Brazil System expresses the result of a set of procedures used by the Coordination of Improvement of Higher Level Personnel - CAPES, for stratification of the quality of the productions from the Stricto Sensu Brazilian Postgraduate Programs. The intellectual productions of researchers, teachers, students, and professionals are evaluated, as well as helping to identify the articles with greater scientific rigor. The evaluation criteria adopt the classification into seven quality indicative layers ranging from A1 to A2, B1 to B5, and C, with A1 and C being the highest and lowest weight attributes, respectively14.
When observing the Qualis/CAPES of the selected journals, it is verified that the vehicles that present this classification are in the stratum of higher quality, considering the attributes of greater weight (A1). This classification points towards studies of greater scientific rigor, as well as of greater visibility in the productions of the Graduate Programs of Brazil.
As regards the impact factor (IF), it was found that the International Journal of Nursing Studies presented the largest of the journals investigated with 3,561. The iF is one of the existing bibliometric instruments and aims to measure the authors' scientific output, the quality of the publications and presumptively classify the scientific journals included in the Journal Citations Reports (JCR) of the Institute for Scientific Information (ISI)15.
The IF of a scientific journal consists of the average citation equation of the scientific articles published in a given journal indexed in a database, that is, the visibility of the journal is proportional to the number of citations of a particular article. Probably the study serves as a scientific reference to other research in the same area15.
The International Journal of Nursing Studies has been featured in the international health community since 1963, with editorial studies aimed at evaluating and understanding complex interventions and health policies through methodological work that introduces or elaborates analytical techniques, measures and research methods16.
From the descriptors used, it is seen that the USA was the country that produced the most articles in nursing, with reference to TRA, corresponding to 36.4%, with the greater representativeness of the origin and headquarters of the published journals. It can be inferred that this derives from the origin of TRA since it had been developed by American psychologists and professors. Also, it is highlighted the hegemony of the English language in the publications researched, which shows the importance of this language in the dissemination of the knowledge produced.
Regarding the authors' qualifications, doctors predominated, which allows adding reliability and relevance to the study of phenomena in the area of health and nursing, in face of the degree of scientific support, constituting the last level of academic titling and maturity. The originality of a study determines the advance in scientific knowledge by unpublished publication of research results that improve understanding about a given event and context.
Regarding the characteristics of the use of TRA in the selected studies, the following aspects of analysis were observed: health care level, health subareas, research scenario, the approach used, objectives and procedure/instrument of data collection.
It was verified that the level of primary assistance preponderated to the others. The following topics were highlighted in the research listed: smoking prevention17, maternal and child care18, attention to antidepressant behaviors against unplanned pregnancy19, sexual health education20)(21)(22, decision to restrict the mobility of elderly people due to the risk of falls13, maltreatment23 and elderly people care strategies24. Regarding the prevalent themes, it was highlighted the education in sexual health and care for the elderly person.
Regarding the use of TRA in nursing studies, the approaches referred to behavioral intention in sexual health22, HIV infection among men who have sex with men21, and behavior of nurses on sex education directed at school adolescents20.
The subareas of health care that predominated in the studies were: women's health22)(25)(26, in which the following subjects were addressed: behavioral intention in sexual health22, psychometric measures to evaluate subjective attitudes and norms regarding use of oral contraceptives25 and health care for pregnant HIV-positive women26; and health of the elderly person13)(23)(24. In this subarea, the central themes were: nursing care given to the elderly person13)(23 and the relationship between senility and dementia in long-term care institutions24.
In the mental health area19)(27)(28, the studies emphasized the behavioral intention of antidepressive therapeutic adoption among adolescent mothers19, online education for nurses to encourage cessation of smoking among people with mental suffering27 and intention of nurses in the creation of therapeutic groups in psychiatric settings28. The importance of the use of TRA in these studies is emphasized since the understanding of behavioral intentions related to contexts of social vulnerability in psychiatry and chemical dependence points to strategies for behavior change.
The hospital area was highlighted in most studies7)(10)(12)(25)(28)(29)(30, with emphasis on the intensive care unit sector8)(9)(10. In these studies, the focus was on obtaining information about nurses' behavioral beliefs and intentions in performing certain procedures/actions, such as: adherence to hand hygiene as a tool to control hospital infection8, an open visit policy as a strategy for humanization of health care in nursing9 and the accomplishment of the hemodynamic study by nurses10.
The aforementioned studies are relevant to nursing because they focus on implementing actions with lesser and greater complexity in the hospital routine. The scientific evidence can allow the modification of weakened beliefs, constituting as progress to the category, improving the functioning of the service and raising the quality of care offered to the patient.
Eleven studies involved nurses as research subjects, where it was sought to evaluate: beliefs and attitudes9)(10)(27, attitudes25)(29, behavioral intentions13)(23)(28)(30)(31) and behavior20. This makes clear the range of options that researchers can use from the theoretical model, either fragmented or in its entirety. The results are based on constructs that reflect reliability and scientific consistency related to TRA.
Regarding the methodological aspects of the researches, a prevalence of descriptive studies7)(10)(13)(17)(18)(19)(20)(21)(22)(23)(24)(28)(31)(32) was observed, with a quantitative approach 8)(9)(12)(18)(19)(20)(21)(22)(25)(26)(28)(29)(31)(32, using questionnaires8)(9)(12)(13)(17)(19)(20)(21)(23)(25)(26)(28)(29)(31)(32. Regarding the elaboration of the instruments, the majority used psychometrics using Likert scales7)(9)(12)(13)(17)(19)(20)(22)(23)(27)(28)(29)(31)(32.
Quantitative research has its roots in positivist thinking, emphasizing deductive reasoning, the rules of logic, and the measurable attributes of human experience33. Thus, the descriptive study aims to understand the variables of the model, from the application of quantitative questionnaires that allow better operationalization and greater generalization of the results obtained.
Regarding the statistical tests used, the most notable were: Pearson test 9)(12)(21)(22)(27)(28, Spearman's coefficient 30, Student's t-test 9)(21)(30, Paired t-test 27, Kruskal Wallis 25, Mann Whitney 25, Chi-Square 18, Regression tests 18)(19)(20)(21)(28 and Analysis of variance 26. Wilks Lambda 25) and Cronbach's Alpha 9)(12)(18)(19)(20)(25)(26)(27)(28)(29)(31) were used to evaluate the reliability of the instruments. In this context, the methodological robustness and the statistical rigor used in the analysis of the results are mentioned, attesting the reliability of the constructs proposed by the TRA.
CONCLUSIONS
From the bibliometric indicators analyzed, a hegemony of publications in international journals was identified, demonstrating the global use of the theoretical model in several contexts. It is expected that the results found favor the use of this theoretical reference in the scientific productions of the Nursing area, as well as in the diffusion of its applicability in predicting the intentions and the behavior in the health context, constituting as an adjuvant strategy in favor of the promotion health, disease prevention and treatment adherence related to chronic diseases.
REFERENCIAS
1. Lins GAI, Armendaris MK, Pinho DLM, Kamada I, Cristine Alves Jesus CAC, Reis PED. Theory of human becoming in nursing ecology: applying meleis' evaluation method. Text Context Nursing [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2017 Fev 9]; 22(4): 1179-86. Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/tce/v22n4/en_37.pdf [ Links ]
2. Moraes MW, Gallani MCBJ, Meneghini P. Beliefs that influence adolescents in organ donations. Rev Enferm USP [Internet]. 2006 [cited 2017 Mar 1]; 40(4):484-92. Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/reeusp/v40n4/v40n4a05.pdf [ Links ]
3. Oliveira SHS, Abreu MSN, Barroso MGT, Vieira NFC. Portuguese adolescent´s beliefes in relation to the use of the condom. Rev Eletr Enf [Internet]. 2009 [cited 2017 Fev 5]; 11(4):912-22. Available from: https://www.fen.ufg.br/revista/v11/n4/pdf/v11n4a17.pdf [ Links ]
4. Fishbein M, Ajzen I. Predicting and changing behavior: the reasoned action approach. New York: Routledge; 2015. 518 p. [ Links ]
5. Cunha BGF, Dias MR. Persuasive communications and regular blood donation: an experimental study. Cad. Saúde Pública [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2017 Mar 2]; 24(6):1407-1418. Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/csp/v24n6/21.pdf [ Links ]
6. Medeiros KKAS, Costa GMC, Coura AS, Celino SDM, Araújo AKF. Associações entre o Qualis/CAPES e aspectos bibliométricos da produção científica da enfermagem gerontogeriátrica. Rev Rene [Internet]. 2012 [ cited 2017 Mar 20];13(4):958-68. Available from: http://www.periodicos.ufc.br/index.php/rene/article/view/4069/3184 [ Links ]
7. Schofield I, Knussen C, Tolson D. A mixed method study to comparate use and experience of hospital care and a nurse-led acute respiratory assesment service offering home care to people with na acute exarcebartion of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. International Journal of Nursing Studies [Internet]. 2006 [cited 2017 Jan 18]; 43: 465-76. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2005.07.002 [ Links ]
8. Creedon AS. Infection control: behavioural issues for healthcare workers. Clinical Governance: an international journal [Internet]. 2006 [cited 2017 Jan 11]; 11(4): 316-25. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/14777270610708850 [ Links ]
9. Marco L, Bermejillo I, Garayalde N, Sarrate I, Margall MA, Asiain MC. Intensive care nurses' beliefs and attitudes towards the effect of open visiting on patients, family and nurses. Nursing in Critical Care [Internet]. 2006 [cited 2017 Jan 14]; 11(1): 33-41. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16471296 [ Links ]
10. Pinto CJM, Colombo RCR, Gallani MCBJ. Nurses' attitudinal and normative beliefs concerning hemodynamic assessement by pulmonary artery catheterization. Rev latino-am Enfermagem [Internet]. 2006 [cited Jan 6]; 14(6):915-22. Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/rlae/v14n6/v14n6a13.pdf [ Links ]
11. International Journal of Nursing Practice [Internet]. [ cited 2017 Mar 02]. Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/10.1111/(ISSN)1440-172X [ Links ]
12. Natan MB, Beyil V, Neta O. Nurses' perception of the quality of care they provide to hospitalized drugs addicts: testing the Theory of Reasoned Action. International Journal of Nursing Practice [Internet]. 2009 [cited 2017 Jan 9]; 15: 566-73. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19958412 [ Links ]
13. Natan MB, Akrish O, Zaltkina B, Noy RHN. Physically restrainig elder residents of long-term care facilities from a nurses' perspective. International Journal of Nursing [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2017 Jan 19]; 16: 499-507. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20854348 [ Links ]
14. Erdmann AL, Marziale MHP, PedreiraMLG, Lana FCF, Pagliuca LMF, Padilha MI, Fernandes JD. Evaluation of scientific periodicals and the brazilian production of nursing articles. Rev Latino-am Enfermagem [Internet]. 2009 [cited 2017 Fev 15]; 17(3):403-9. Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/rlae/v17n3/19.pdf [ Links ]
15. Ruiz MA, Greco OT, Braile DM. Journal impact factor: this editorial, academic and scientific influence. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc [Internet]. 2009 [cited 2017 Mar 18]; 24(3): 273-278. Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/rbccv/v24n3/en_v24n3a04.pdf [ Links ]
16. International Journal of Nursing Studies [Internet]. [cited 2017 Mar 10]. Available from: http://www.journalofnursingstudies.com [ Links ]
17. Heath J, Crowell NA. Factors influencing intentions to integrate tobacco education among advanced practice nursing faculty. Journal of Professional Nursing [Internet]. 2007 [cited 2017 Mar 1]; 23(4): 189-200. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17675113 [ Links ]
18. Chen MJ, Tang CH, Jeng HM, Chiu AWH. The maternal and child healthcare needs of new immigrants in Taipei. Journal of Nursing Research [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2017 Jan 28]; 16(4): 307-18. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19061177 [ Links ]
19. Logsdon MC, Usui W, Pinto-Foltz M, Rakestraw VL. Intention to seek depression treatment in adolescent mother and a comparison group of adolescent girls. Archives of Psychiatric Nursing [Internet]. 2009 [cited 2017 Jan 24]; 23(1):41-49. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apnu.2008.02.013 [ Links ]
20. Mullan B, Westwood J. The application of the theory of reasoned action to school nurses' behaviour. Journal of research in Nursing [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2017 Jan 13]; 15(3):261-71. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1177/1744987109104674 [ Links ]
21. Natan MB, Zeltzer I, Melnikov K. Disclosure of HIV infection among Israeli men who have sex with men. J Transcultural Nurs [Internet]. 2011 [ cited 2017 Fev 4]; 22(1):40-45. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1177/1043659610387146 [ Links ]
22. Pai HC, Lee S, Yen WJ. The effect of sexual self-concept on sexual health behavioural intentions: a test of moderating mechanisms in early acolescent girls. J Adv Nurs [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2017 Jan 12]; 68(1): 47-55. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21627681 [ Links ]
23. Natan MB, Lowenstein A. Psycho-social factors affecting elders' maltreatment in long-term care facilities. Int Nurs Rev [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2017 Jan 17]; 57: 113-20. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20487483 [ Links ]
24. Corcoran MA. Caregiving styles: a cognitive and behavioral typology associated with dementia family caregiving. Gerontologist [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2017 Jan 10]; 51(4):463-72. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/geront/gnr002 [ Links ]
25. Tyer-Viola LA. Obstetric nurses' attitudes and nursing care intentions regardings care of HIV-positive pregnant women. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nursin [Intenet]. 2007 [ cited 2017 Jan 12]; 36(5):398-409. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6909.2007.00172.x [ Links ]
26. Lee J, Carvallo M, Lee T. Psychometric properties of a measudre assessing attitudes and norms as determinants of intention to use oral contraceptives. Asian Nurs Res [Internet]. 2015 [ cited 2017 Jan 11]; 9: 138-145. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.anr.2015.04.003 [ Links ]
27. Amole J, Heath J, Joshua TV, McLear B. Online tobacco cessation education to optimize Standards of practice for psychiatric mental health nurses. Nurs Clin North Am [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2017 Jan 15]; 47:71-79. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22289399 [ Links ]
28. Drori T, Guetta H, Natan MB, Polakevich Y. Nurse intention to implement creative group activities among psychiatric patients. Perspect Psychiatr Care [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2017 Jan 6]; 50: 264-270. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24405010 [ Links ]
29. Bu X, Wu YB. Development and psychometric evaluation of the instrument: attitude toward patient advocacy. Res Nurs Health [Internet]. 2008 [ cited 2017 Jan 8]; 31:63-75. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18163382 [ Links ]
30. Vincent CVH, Wilkie DJ, Wang E. Pediatric nurses' beliefs and pain management practices: na intervention pilot. West J Nurs Res [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2017 Jan 9]; 33(6):825-845. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1177/0193945910391681 [ Links ]
31. Hung SY, Tsai JCA, Chuang CC. Investigating primary health care nurses1 intention to use information technology: an empirical study in Taiwan. Decision Suppport Systems [Internet]. 2014 [ cited 2017 Jan 7]; 57: 331-342. Available from: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2013.09.016 [ Links ]
32. Tung FC, Chang SC. A new hybrid model for exploring the adoption of online nursing courses. Nurse Educ Today [Internet]. 2008 [ cited 2017 Jan 20]; 28: 293-300. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2007.06.003 [ Links ]
33. Lacerda MR, Costenaro RGS. Metodologias da pesquisa para a enfermagem e saúde: da teoria à pratica. Porto Alegre: Moriá, 2015. 511p. [ Links ]
Received: October 09, 2017; Accepted: November 10, 2017











 texto en
texto en 



