My SciELO
Services on Demand
Journal
Article
Indicators
-
 Cited by SciELO
Cited by SciELO -
 Access statistics
Access statistics
Related links
-
 Cited by Google
Cited by Google -
 Similars in
SciELO
Similars in
SciELO -
 Similars in Google
Similars in Google
Share
Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas
Print version ISSN 1130-0108
Rev. esp. enferm. dig. vol.109 n.2 Madrid Feb. 2017
https://dx.doi.org/10.17235/reed.2017.4482/2016
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Acute psychotic episode secondary to Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment
Brote psicótico agudo secundario a tratamiento erradicador de Helicobacter pylori
Key words: Antibiomania. Helicobacter pylori. Psychosis. Clarithromycin.
Palabras clave: Antibiomanía. Helicobacter pylori. Psicosis. Claritromicina.
Dear Editor,
The side effects of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) eradication treatment are few, usually in the form of gastrointestinal or allergic complaints (1). However, occasionally, some antibiotics such as clarithromycin, included in the classic eradication regimen, may result in reversible psychosis, a condition called "antibiomania" or "Hoigne syndrome" (2).
Case report
We report the case of a 57-year-old male with no history of psychiatric disorders or substance abuse, who was admitted for mild upper GI bleeding from a Forrest IIC duodenal ulcer. H. pylori eradication with pantoprazole, amoxicillin and clarithromycin was prescribed.
At 24 hours after admission he presented with self-limited withdrawal. At 36 hours he also had mistrust and self-reference ideas involving his caregivers ("They want to kill me", "What am I doing here?"), and threw himself out of the window in his room in an attempt to escape from hospital, suffering multiple non-severe contusions. Brain CT and EEG were normal.
The Psychiatry Department substituted levofloxacin for clarithromycin, and added olanzapine, which resulted in complete remission at 48 hours. The sudden onset of the episode, characteristics and clinical improvement following clarithromycin discontinuation supported a diagnosis of acute psychotic episode secondary to clarithromycin.
Discussion
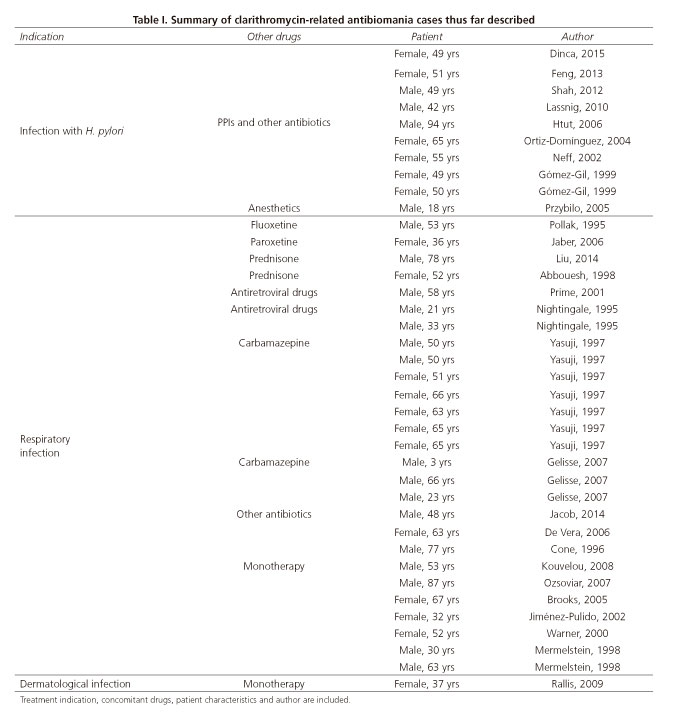
Antibiomania is a syndrome characterized by confusion, insomnia, mania and/or hallucinations that develops at 24-72 hours after antibiotic therapy onset, and subsides within 72 hours after antibiotic discontinuation (1). Its pathophysiology remains unknown and is likely multifactorial (3); cases have been described with clarithromycin both as monotherapy (3) and in combination with other drugs (4,5) (Table I). Awareness is crucial regarding this complication, which is uncommon but potentially serious.
Rubén Fernández-Martos, Aurora Burgos-García and Consuelo Froilán-Torres
Department of Digestive Diseases. Hospital Universitario La Paz. Madrid, Spain
References
1. Shah M, Subhani M, Rizvonb K, et al. Transient psychotic episode induced by Helicobacter pylori triple therapy treatment. Case Rep Gastroenterol 2012;6:381-6 DOI: 10.1159/000339713. [ Links ]
2. Hoigné R, Schock K. Anaphylactic shock and acute nonallergic reactions following procaine-penicillin. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 1959;89:1350-6. [ Links ]
3. Kouvelou E, Pourzitaki C, Aroni F, et al. Acute psychosis induced by clarithromycin in a healthy adult? J Clin Psychopharmacol 2008;28(5):579-80. DOI: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e318185a357. [ Links ]
4. Dinca EB, Skinner A, Dinca RV, et al. The dangers of gastritis: A case of clarithromycin-associated brief psychotic episode. J Nerv Ment Dis 2015;203(2):149-51. DOI: 10.1097/NMD.0000000000000251. [ Links ]
5. Rallis E, Moussatou V, Saltos L. Clarithromycin-induced Hoigne syndrome in a patient treated for rosacea. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2009;23(9):1093-4. DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2008.03085.x. [ Links ]











 text in
text in