Introduction
The success of methadone treatment programs has traditionally been measured with variables such as retention, a decrease in criminal behaviors or abstinence from non-prescribed drugs. It is more difficult to find studies which consider assessing the patients themselves (Amato et al., 2005; Hedrich et al., 2012), something that is unacceptable in any other clinical area. Thus, number of studies that explore the impact on individuals' quality of life (De Maeyer et al., 2011) and their satisfaction and agreement with the treatment received (Vanderplasschen, Naert, Vander Laenen, & De Maeyer, 2015) have proliferated in recent years. These patient-centered variables are of crucial relevance when it comes to designing programs to handle the needs of this population (De Maeyer, Vanderplasschen, & Broekaert, 2010; Laudet, 2011).
Quality of life means “an individual’s perceptions of their position in life, in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live, and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards and concerns”. Assessing it makes the person's subjectivity an indicator of the results of professional interventions and improving it is ultimately the aim of all medical, psychotherapeutic and social-relational treatments (Skevington, Sartorius, Amir & THE WHOQOL Group, 2004).
One of the problems with estimating quality of life among this population is the large number of instruments used, with up to 15 having been identified (De Maeyer et al., 2010). Some authors advocate the use of instruments specifically designed for the target population (Rojas, Lozano, Foresti, Zolfaghari, & Zubaran, 2015). Yet, even though this would enable comparisons between the various treatments, it would prevent comparisons between the results with those obtained among the reference population. This is possible, however, when instruments of general use are utilized.
The World Health Organization has proposed an instrument that is capable of measuring quality of life in a reliable and valid way in a wide range of countries and cultures: the World Health Organization Quality-of-Life (WHOQOL). The most complete version consists of 100 items that refer to four health-related domains: physical, psychological, social and environmental (Power, Bullinger, & Harper, 1999). The shorter 26-item version, known as WHOQOL-BREF (The WHOQOL Group, 1998), has been more frequently used in clinical studies. The psychometric qualities of this version have been studied for a large number of pathological conditions (Skevington, & McCrate, 2012) and in cross-cultural studies (Skevington, Lotfy, & O'Connell, 2004). It has also been applied to various clinical areas such as neurology (Den Oudsten, Lucas-Carrasco, Green, & The WHOQOL-Dis Group, 2011; (Lucas-Carrasco, Skevington, Gómez-Benito, Rejas, & March, 2011), in addition to non-clinical populations (Espinoza, Osorio, Torrejón, Lucas-Carrasco, & Bunout, 2011).
The WHOQOL-BREF has proven to be an instrument that is sensitive to the changes caused by treatment, with methadone (Feelemyer, Des Jarlais, Arasteh, Phillips, & Hagan, 2014) and without (Sánchez-Hervás, Tomás-Gradolí, Molina Bou, del Olmo Gurrea, & Morales Gallús, 2002). In general, the findings show that people improve their quality of life when they stop using non-prescribed opiates and undergo treatment with methadone (Padaiga, Subata, & Vanagas, 2007). However, when the results are compared between samples of people who are addicted to opiates and control samples, the scores have been systematically lower for the former and even more so with concurrent psychopathological diagnoses (Bizzarri et al., 2005).
Some studies have explored certain psychometric properties of the WHOQOL-BREF among populations with addictive conducts, such as the reliability or convergent validity with similar tests (Barros da Silva Lima, Fleck, Pechansky, De Boni, & Sukop, 2005), yet hardly any studies have been found on the construct validity that also reflect significant inconsistencies in the structure (Fu et al., 2013). The few papers available that explore the theoretical suitability of four domains to the data available have shown some inconsistencies in psychiatric population samples (Trompenaars, Masthoff, van Heck, Hodiamont, & de Vries, 2005) and in varied-source clinical and non-clinical samples (Skevington et al., 2004; Urzúa & Caqueo-Urízar, 2013), including samples recruited from methadone treatment programs (Chang, Wang, Tang, Cheng, & Lin, 2014). One study with the Spanish version among a student population in Spanish-speaking countries also found significant structural deficiencies in the test (Benitez-Borrego, Guàrdia-Olmos, & Urzúa-Morales, 2014). The purpose of this research is to study various psychometric characteristics of the WHOQOL-BREF test among a sample of people under treatment with methadone. Specifically, it will explore the reliability on an item level and scale level, and the construct validity. Additionally, the relationship between the test and several different variables such as sex, age, highest education level, etc. will be explored.
Method
Participants
The sample obtained was comprised of 523 subjects being treated with methadone. Of these, 458 were receiving treatment at centers of the Madrid Institute of Addictions network (n = 1898; confidence interval of 4% for p = .05) and 65 in public centers in Extremadura (n = 100; CI = 7% for p = .5). The inclusion criterion was receiving methadone prescribed for heroin addiction for at least 3 months through the corresponding service. The exclusion criteria were: a current diagnosis of dependence on a substance other than heroin, recent alcohol consumption, any type of brain damage, acute psychotic symptoms, difficulties understanding Spanish or any other difficulty that would compromise answering the test properly. All of the participants received information on the purpose of the assessment and signed an informed consent document, allowing for the anonymous use of the results. Table 1 outlines the sample descriptions.
Instruments
The Spanish version of the WHOQOL-BREF (The WHOQOL Group, 1998), adapted by Lucas-Carrasco (1998, 2012), a self-report comprised of 26 items which are answered on a Likert-type scale of 5 options (scored between 1 and 5). Items 1 and 2 ask about quality of life and overall health and the remaining 24 are grouped into 4 domains: physical health, psychological health, social relations and the environment. Higher scores meant higher levels of self-perceived quality of life. Permission for use was requested from the World Health Organization webpage (www.who.int/substance_abuse/research_tools/whoqolbref/en/) and authorization was received to use the version provided by the Andalusian Health Service (Servicio Andaluz de Salud, 2010).
Procedure
Patients were asked to collaborate upon arriving at a center to receive their daily or weekly dose of methadone. If they had no time at that moment, they were offered a scheduled appointment to do so over the following days. Once they agreed to participate, the assessments were done in a room that had been prepared for this purpose. The evaluator would read the questions and the patient would mark the answers on data sheets with the various response types. The evaluators attended three training sessions prior to the start of the assessment period in addition to receiving ongoing guidance in order to resolve any questions that arose. The self-report tests were a part of a larger set, the general protocol for which has already been published (Pedrero-Pérez, & MethaQoL Group, 2017). The study was authorized by the institution's Research Committee and positive reports were issued by two Ethics Commissions.
Data analysis
The syntax provided by the University of Washington (http://depts.washington.edu/seaqol/docs/Wq_bref.txt) was used to transform the scores meaning the scales were offered in a range of 0 to 100. This syntax was also modified to obtain a score of between 4 and 20, as presented in the validation of the Spanish version (Lucas Carrasco, 1998). A confirmatory factor analysis was first done based on the theoretically established questionnaire components. Given the Likert-type response system, the unweighted least squares method was used. The indicators provided by the AMOS 18 program were used to study the adequacy of the theoretical model to the data. Two methods were developed to estimate the most adequate number of factors to be retained: an optimized parallel analysis and a MAP, using the program FACTOR 10.3.01 (Lorenzo-Seva, & Ferrando, 2013). The structural relationships between the four domains were explored with path analysis, using the maximum likelihood method after guaranteeing the multivariate normal distribution of the data and applying the adequacy indicators provided by the AMOS 18 program. The internal consistency of the items was studied using the discrimination coefficient (corrected item-total correlation) and of the scales, using McDonald's omega (() as a more adequate measure than Cronbach's α (Dunn, Baguley, & Brunsden, 2014). Pearson's r was used for the bivariate correlations and the Bonferroni correction was applied for multiple correlations. An ANCOVA was done to compare scores and control variables with an interaction effect using Wilk's Lambda. The size of the effect was calculated using the omega-squared (( 2 ).
Results
The model that resulted from the confirmatory factor analysis is shown in Figure 1. The adjustment indicators were satisfactory in all cases, χ 2 = 664.6, RMR = .07, GFI = .97, AGFI = .97, PGFI = .80, NFI = .95, PNFI = .85, RFI = .95, with the adjustment of the theoretically proposed dimensions to the data obtained in the sample present assumable. However, it would be better to adjust the data to a uni-factor solution as found when doing an optimized parallel analysis based on the matrix of polychoric correlations and also a MAP. Table 2 shows the descriptions and discriminating power of each item and the internal consistency of each scale, ( = .89 for the whole test.
Table 2: Descriptions, correlation of each item of WHOQOL-BREF to the scale following exclusion, and internal consistency of each scale.
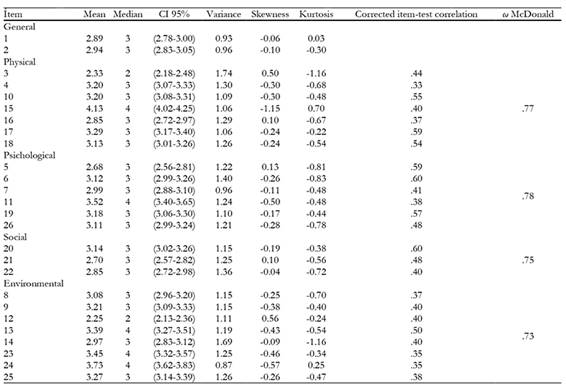
Figure 2 shows the structural relationships between the four WHOQOL-BREF domains. The multivariate normal distribution of the data was first checked, Mardia= 3.75, p > .05, and then path analysis was done using the maximum likelihood method. The model shown is the one that reflected the best adjustment indicators, CMIN/DF= 1.85, GFI = .99, AGFI = .98, NFI = .99, RFI = .98, IFI = .99, TLI = .99, RMSEA = .04, meeting all of the maximum demand criteria, CMIN/DF < 2, RMSEA < .05, and absolute and incremental indicators > .95. Physical health was observed as showing the greatest predictive power for the rest of the domains; it is direct in the case of psychological health and environment and indirect in the case of social relationships.

Figure 2 Structural relationship among the four domains of WHOQOL-BREF (regression weights and variances of exogenous variables).
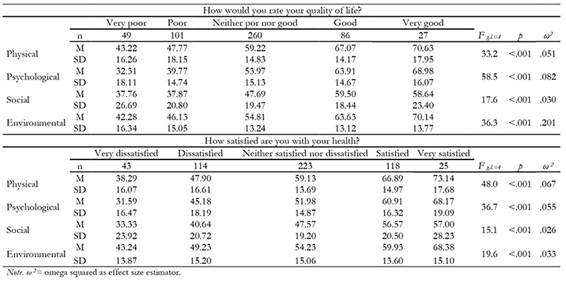
The general question “How would you rate your quality of life?” is predicted at a rate of 34% of its variance based on the scores obtained for psychological health, R 2 = .30, ( = 0.35, t(df = 3) = 7.0, p < .001, environmental health, R 2 = .03, (= 0.20, t(df = 3) = 4.3, p < .001, and physical health, R 2 = .01, ( = 0.13, t(df = 3) = 2.9, p <.01. The second general question “How satisfied are you with your health?” is predicted (31% of the variance) based on physical health, R 2 = .27, ( = 0.37, t(df = 3) = 7.9, p < .001, and psychological health, R 2 = .04, ( = 0.25, t(df = 3) = 5.4, p < .001. Both reflected correlation between each other of r = .47 (mutual coefficient of determination r 2 = .22). Table 3 shows the scores obtained for each group according to the answers to the question “How would you rate your quality of life?”. There are significant differences in all cases between the scores obtained for each domain and a graduation of scores appears in almost all of the cases as per the general estimate following the post hoc (Bonferroni) tests (except in certain cases where the answers 1 or 2, or 4 or 5 appear as equivalents). An identical analysis and results are found for the second general question “How satisfied are you with your health?”.
Table 4 presents the average scores obtained from the sample in this study and those obtained from the study validating the Spanish version of the WHOQOL-BREF (Lucas-Carrasco, 1998). No significant differences were found due to sex in any of the domains explored by the WHOQOL. However, age, λ = .977, p <.05, and education level, λ = .953, p < .001, showed an interaction effect. Age showed negative correlation with social health, r = -.12, p < .01, and environmental health, r = -.09, p < .05, in the complete sample yet only in males, r = -.13, p < .01 and r = -.11, p < .05 respectively, when the sample was divided into sexes and the educational level was controlled. It did not affect the correlation in females. However, the highest educational level showed positive correlation with psychological health, r = .15, p < .01, and environmental health, r = .18, p < .001. These correlations were especially significant among females: with age controlled, the education level strongly correlated with environmental health, r = .37, p < .001, psychological health, r = .35, p < .001, and physical health, r = .23, p < .05; in the males, however, education level only showed significant correlation with environmental health, r = .13, p < .01. When controlling these variables together, differences did arise between males and females in psychological health, p < .01, ω 2 = .008, social health, p < .05, ω 2 = .006, and environmental health, p < .001, ω 2 = .015.
Discussion
The results obtained in this study support the suitability of the four-dimensional or four-domain structure of the data obtained with the sample used. The adequacy indicators are sufficient in all cases to support this statement. Nonetheless, other analyses completed suggest that this division into dimensions is artificial and that a uni-factor structure would be more suitable. The structural analysis shows how perceived health decisively influences the other perceived types of health either directly or indirectly through a self-perception of psychological health. At the base of this matter lies the controversy regarding whether quality of life is a one-dimensional or multi-dimensional construct and, as a result, whether it must be explored through simple items (such as the first: “How would you rate your quality of life?”) or through various items which explore diverse aspects of the subject's perception. Most authors advocate a variety of items, arguing that a single question requires the subject to make an excessively quick assessment while answering many different items can get the subject to consider aspects that would have been ignored in an overall response (Fayers & Machin, 2007). The same can be said of the second question “How satisfied are you with your health?”: meta-analysis studies find a powerful predictive capacity in the answer to this question or other similar ones of a general nature on health and even death-related results, the likelihood of which doubles in people who state they are in poor health (DeSalvo, Bloser, Reynolds, He, & Muntner, 2006). The data from this study seem to indicate that the general questions would be sufficient as they already classify the subjects on the different levels later provided by the rest of the items with a continuous gradient and a great effect size. However, the limits must be considered as far as the patients' accessibility or greater availability, which would make it possible to explore the different domains separately, thus supplying information of interest in a view to designing interventions.
Considering the test as a whole, the WHOQOL-BREF is a reliable test with sufficient internal consistency both when exploring on an item level as well as a domain level in the sample studied: all of the items show adequate discriminatory power (r it > .30) and all of the scales, a ω > .70. A similar study on more than 500 subjects undergoing treatment with methadone found poor suitability of the four dimensions to the data obtained with unacceptable adequacy indicators (Fu et al., 2013) although methods were used that are not optimal for the nature of the data when estimating the structure and internal consistency (maximum likelihood and alpha coefficient, respectively).
At attempt was made to compare the scores obtained in the sample from this study with those obtained in the validation study for the Spanish population (Lucas Carrasco, 2012). The reason is to determine the distance between patients undergoing treatment and the values considered normal for the reference population. However, the comparison can only be apparent given that, surprisingly, this study does not provide standard deviations but rather only the average scores of the groups studied using a score of between 4 and 24 points, which is different from what was used by the authors of the test. Furthermore, very small samples (healthy population n = 101) were used, the origin and method for the recruitment of which are not reported. Thus, the score for the sample studied in this study is apparently resembles the one obtained for people diagnosed with schizophrenia yet much less so to those obtained from patients with physical problems, both below those obtained from healthy people. The lack of information concerning the standard deviation prevents establishing confidence intervals for each average to prove that such apparent differences are real.
When the age and education level variables are controlled, females score less on quality of life than males, as is often the case in these types of studies (Pedrero-Pérez, & Díaz-Olalla, 2016). However, and although significant, these differences do not reflect a large effect size which indicates their lack of clinical relevance. What they do reveal is the differential impact of some variables on the quality of life of males and females: a higher education level seems to be an important protection factor for females which leads to better quality of life levels when controlling other variables.
As a result, the WHOQOL-BREF proves to be an adequate instrument for measuring quality of life as perceived by subjects undergoing treatment with methadone both as far as its psychometric properties (reliability and construct validity) as well as its applicability to this population. Methadone programs must primarily consider the assessments made by the patients themselves given that their main objective is to improve their quality of life in a stable and persistent manner. This issue, which would seem rather obvious, has been repeatedly forgotten in research in favor of indicators such as the level of consumption of non-prescribed substances or criminal activity. There is no doubt that these indicators are of enormous interest and must continue to be explored, but the primary question is considering the patient's own perspective as occurs in any other area of health.