INTRODUCTION
Osteoporosis is a skeletal disease occurring due to the normal aging process and characterized by progressive loss of bone mass and disorders in its microstructure, which cause brittleness and make the bone susceptible to fractures 1. This loss of bone mass occurs from an imbalance in bone remodeling, where bone resorption overcomes bone formation 2. Bone health is influenced by several factors. Some of these factors cannot be modified, such as age, sex, ethnicity and genetics, while other can be modified, such as hormonal factors, smoking, physical activity and dietary patterns 3.
The Brazilian population has undergone a nutritional transition process characterized by a high saturated fat diet followed by a reduction in physical activity levels 4. Intake of dietary fats produces deleterious effects on bone mineralization, as a diet with high saturated fats can interfere with the absorption of intestinal calcium, due to insoluble calcium soaps formed by free fatty acids, contributing to a lower absorption of this mineral 4,5.
Osteoporosis is a major public health problem; it is necessary to create therapeutic strategies that act positively on bone health, such as regular physical exercise and ingestion of some foods and nutrients, contributing to the formation, and reducing or preventing their loss 6. Physical activity causes changes in bone structure and geometry due to the mechanical load that is applied during activity. Thus, it stimulates osteogenic responses and helps to prevent or slow down bone mass loss, as it occurs in osteoporosis 7.
Studies have shown that resveratrol is potentially beneficial for bone health. It is a polyphenol naturally synthesized by vines to protect plants against fungal infection 6. It is present in red wine and in a wide variety of foods of plant origin such as grapes, walnuts and blackberries 8. In vitro studies show that resveratrol can promote osteoblasts activity and formation and antagonize the effects of osteoclasts, which are the cells responsible for bone resorption. This is due to resveratrol's ability to inhibit the transcription activity of NF-kB, which acts directly on osteoclast genesis. In addition, it has osteogenic and osteoinductive effects through increased levels of osteocalcin and alkaline phosphatase 6.
Thus, the objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of red grape juice, red wine and resveratrol consumption on bone parameters in adult female Wistar rats submitted to a high-fat diet and physical training.
METHOD
The present study was performed with 50 adult female, Norvergicus Wistar Albinus rats (90 days of age), initially weighing around 230 g, from the Laboratory of Experimental Nutrition. Animals were individually housed in cages in a controlled environment. All experimental procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee and complied with the regulations for the use of laboratory animals.
During the experiment, animals were kept in individual polypropylene cages in an environment with constant temperature (22 °C ± 2 °C) and adequate lighting (light and dark cycle every 12 hours).
Animals were divided in five groups, with food and water offered in free demand and followed for 60 days. The rations used in the experiment were prepared according to the American Institute of Nutrition (AIN) 93M recommendations 9 for Rattus norvegicus and manipulated at the Laboratory of Experimental Nutrition (Table I). Rats were distributed in five different groups: a) control group (CG), receiving a balanced diet based on casein (AIN 93M); b) high-gat group (HFG), receiving a high-fat casein-based diet (20%), when the usual fat content is 4-8%; c) resveratrol group (RG), receiving a high-fat casein-based diet (20%), and 15 ml of a resveratrol solution 4% (diluted in distilled water) per day; d) grape juice group (GJG), receiving high-fat casein-based diet (20%) and 15 ml of whole grape juice per day; and e) red wine group (RWG), receiving high-fat casein-based diet (20%) and 10 ml of red wine per day. Both whole grape juice (Aurora Tinto Integral(r)) and red wine (Góes Tempos(r)) were purchased at the local market; the resveratrol solution was prepared every day and dispensed to the animals (Table II).
Table I Composition of the control and high-fat diets used in the experiment
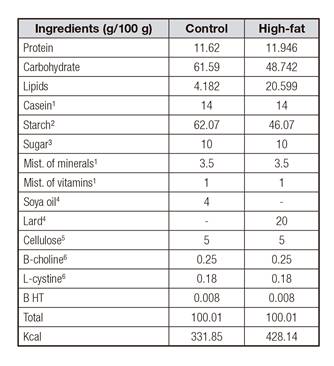
Balanced diet according to the recommendations of the AIN 93 M (9). 1M. Cassab Comércio e Indústria Ltda. 2Maisena - Unilever Bestfoods Brasil Ltda. 3União. 4Liza Cargill Agricultura Ltda. 5Macrocel - Blanver Ltda. 6Comércio e Indústria Farmos Ltd.
Table II Nutritional composition of the grape juice and red wine used in the experiment
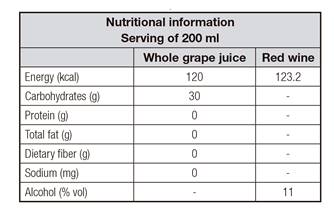
Nutritional composition of the grape juice and red wine that were offered to animals during the 60 days of experiment.
Animals groups were submitted to adaptation on a treadmill for small animals with six bays and activated by a 12V motor; the adaptation period started two weeks before the beginning of the experiment. During the adaptation period, the animals were placed on the treadmill three days a week on alternate days and each training day was increased one minute, starting with three minutes and increasing one minute a day until eight minutes. Speeds varied as follows: 0.3 m/min, 0.4 m/min, 0.6 m/min, 0.8 m/min and 0.9 m/min. At the beginning of the experiment, when the animals completed 90 days of life, the five groups of animals executed the running protocol at a speed of 10 m/min for the slip of the canvas, which consequently induced movement of the animal under study. The training session had a ten minute duration and was carried out for 60 days, five days a week until the end of the experiment 10.
Food intake and body weights were monitored weekly. The amount of ration, grape juice, red wine and resveratrol solution were quantified to obtain daily intake. For body mass gain analysis, animals were weighed twice a week in a digital scale (Filizola(r)), with 3 kg capacity and 0.05 g accuracy.
After 60 days of treatment, animals were anesthetized with Thiopentax(r) (thiopental sodium, 0.1 mg/100 g) and euthanized by exsanguination. Right femurs were collected, cleaned of soft tissues and stored at -80 °C for further analysis. Bone dimensions: distance between epiphyses and diaphysis midpoint thickness were evaluated using a tachymeter, with a reading capacity of 0.01 mm, and then femurs were weighed (g). Femur bone mineral densities (BMD, g/cm2) and bone mineral content (BMC, g) were determined by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) sing Lunar DXA equipment 200368 GE instrument and software encore 2008 version 12.20 (GE Healthcare, Madison, Wisconsin). The evaluation was blind, since the DXA technician did not know the experimental protocol 11.
Results were expressed through descriptive statistics as mean and standard deviation. The data were evaluated for their normality using the Kolgomorov-Smirnov test. The ANOVA one way test was used for the comparison between groups, and the Newman-Keuls' was used as post-test. A p < 0.05 was considered as significant. Graph Pad Prism software version 5.00, 2007 (San Diego, CA) was used for these analyses.
RESULTS
At the end of the experiment, there were no significant differences in the final weights of each group (Fig. 1).
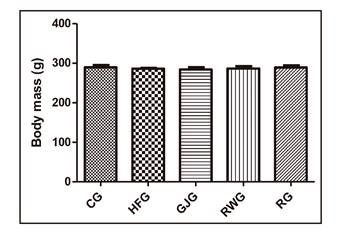
Figure 1 Body mass of animals after 60 days of experiment. CG: Control group, fed with control diet; HFG: High-fat group, fed with high-fat ration; GJG: Grape juice group, fed with high-fat ration and receiving whole grape juice; RWG: Red wine group, fed with high-fat ration and receiving red wine; RG: Resveratrol group, fed with high-fat ration and receiving 4% solution of resveratrol. Results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. *Univariate analysis of variance, followed by the Newman-Keuls test post.
Differences in energy consumption between groups were observed. The RWG and RG groups consumed more energy when compared to the other groups, but there were significant differences among them (Fig. 2).
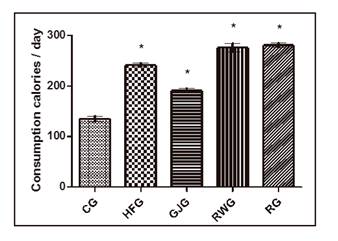
Figure 2 Daily energy intake (kcal) (ration + experimental drinks) of the groups during the 60 days of experiment. CG: Control group, fed with control diet; HFG: High-fat group, fed with high-fat ration; GJG: Grape juice group, fed with high-fat ration and receiving whole grape juice; RWG: Red wine group, fed with high-fat ration and receiving red wine; RG: Resveratrol group, fed with high-fat ration and receiving 4% (RG) solution of resveratrol. *Considered significant values (p < 0.05, univariate analysis of variance, followed by the Newman-Keuls test post).
At the end of the 60 day experiment, the distance between the epiphyses was significantly higher in the RWG when compared to CG, HFG and GJG (p < 0.05). The mean point of the diaphysis width was significantly higher in RWG and RG when compared to CG, HFG and GJG (p < 0.0001). However, no significant difference was found between RWG and RG.
DXA analysis showed significantly higher bone mineral density in RWG and RG when compared to CG, HFG and GJG (p < 0.0001). Nevertheless, no significant difference was found between RWG and RG. Regarding bone mineral content, it was significantly higher in RWG when compared to CG, HFG and GJG (p < 0.05). There were no significant differences between RWG and RG (Table III).
Table III Bone parameters of the femur of female Wistar rats submitted to physical training after 60 days of experiment

CG: Control group, fed with control diet; HFG: High-fat group, fed with high-fat ration; GJG: Grape juice group, fed with high-fat ration and receiving whole grape juice; RWG: Red wine group, fed with high-fat ration and receiving red wine; RG: Resveratrol group, fed with high-fat ration and receiving 4% solution of resveratrol; BMD: Bone mineral density; BMC: Bone mineral content. Results expressed as mean ± standard deviation. *Considered significant values (p < 0.05, univariate analysis of variance, followed by the Newman-Keuls test post).
DISCUSSION
The groups receiving only high-fat ration and high-fat ration associated with polyphenol-rich beverages presented higher energy consumption when compared to the control group. However, the higher energy consumption did not influence the final weight of the animals receiving a high-fat diet. Physical exercise associated with polyphenol-rich beverages may have contributed to maintenance and control of body mass 12.
Distance between epiphyses, femoral mass and BMC were greater only in the group receiving red wine, while BMD and midpoint of the diaphysis width were higher in both wine and resveratrol solution groups. Among the positive effects of resveratrol on bone mass, it stimulates early osteoprogenitor cells in bone marrow due to the osteoblastic line effect on bone formation, besides inhibiting signaling pathways for osteoclast differentiation 13. As cortical bone microarchitecture is considered to be one of the main determinants of bone resistance, it might be suggested an ability of these beverages to increase bone resistance 14.
Studies have shown that resveratrol has both osteogenic and osteoinductive effects. Resveratrol acts by activating Sirtuin 1 (Sirt 1), a NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase, which leads to NK-1B deacetylation induced by RANKL, inhibiting its transcriptional activation 15. This process inhibits osteoclasts differentiation by preventing bone loss. In vitro studies have shown that resveratrol increases the activity of alkaline phosphatase (a biomarker for osteoblastic differentiation), indicating its ability to stimulate osteoblasts differentiation, cells responsible for bone formation 16.
Resveratrol has been characterized as a phytoestrogen based on its ability to bind to and activate estrogen receptor 17. Alcohol, in moderate amounts, induces estrogen production in a postmenopausal woman, explaining alcohol protection against bone loss. Estrogen plays an important role in bone maintenance. In adult women, estrogen slows down bone remodeling, maintaining the proper balance between bone formation and resorption. The effects of estrogen deficiency are related to an improvement in the activity of cells responsible for bone resorption, osteoclasts, leading to an increase in fracture risk 18.
In addition, acute ingestion of small amounts of alcohol induces secretion of calcitonin, a molecule which protects bone tissue 18. Red wine, in addition to resveratrol effects, also has benefits associated with its alcohol content. Therefore, this may justify a better red wine result against the bone parameters compared to resveratrol.
The minor results of grape juice when compared to red wine and the resveratrol solution can be explained by its bioavailability. Absorption and bioavailability of resveratrol vary among individuals, but they are independent of diet or amount of lipids in the diet. However, grape juice has a lower amount of free resveratrol, suggesting a lower bioavailability of resveratrol compared to the pure compound.
Cao et al. (2010) and Chen et al. (2010) showed lower bone mass associated with increased bone resorption and decreased bone formation. However, in this study, it was observed that even animals receiving only high-fat diet did not present inferior bone parameters, compared to the animals in the control group. This can be explained by the beneficial effects mechanical load exerts on bone tissue during physical activity.














