Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is the leading cause of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end stage renal disease (ESRD) in developed countries.1 In diabetic patients, early detection of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is of critical importance.
Albuminuria was widely accepted as the earliest marker of DKD progression and was traditionally used as a screening test for DKD.1 Since 1980s, renal disease in diabetes has been classified in stages defined by increased albuminuria/proteinuria levels (normo-micro-macro). Classically, the development of macroalbuminuria or overt proteinuria marked the initiation of faster glomerular filtration ratio (GFR) declining.2
However, several studies have criticized this definition in the last decades. They described progressive declining of GFR without significant albuminuria in subjects with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, i.e. a non-albuminuric DKD (NA-DKD).3,4 Although declining GFR can occur without albuminuria, the development of advanced CKD stages seems to be strongly dependent on the progression to albuminuria greater than 300 mg/dL.5 The majority of the studies found that the rising in albuminuria is accompanied by GFR decline.3-5 These findings suggested that decreased GFR could be, for some group of diabetics, an early marker of DKD.
In the last few years, the traditional concept of the natural history of DKD has changed. This evidence has led the American Diabetes Association (ADA) to recommend the screening of DKD based on the albumin excretion ratio (AER) and estimated GFR (eGFR).2
In addition, albuminuria as a marker of glomerular lesion progression has some limitations because of its intra-patient variability and possibility of spontaneous regression (in over 50% of patients with lower levels of albuminuria),6 in contrast with GFR that has low variability and infrequent improvement.
Growing evidence has shown that there is a continuous relationship between the level of albuminuria and the decline of GFR and cardiovascular (CV) risk. It should be noted that the levels of urinary AER, even within normal ranges, are positively correlated with the declining of GFR and cardiovascular risk.7-10
The prevalence and which patients develop NA-DKD are not completely defined.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the prevalence and the demographic and clinical characteristics of type 2 diabetic patients with NA-DKD.
Subjects and methods
Study design
This was an observational, 1-year retrospective, single-centre study of a cohort of type 2 diabetic patients followed in an outpatient department.
Population
From the 731 patients followed in a diabetes outpatient department of our Hospital between 09/2012 and 09/2013, 457 patients were haphazardly selected. Inclusion criteria for this study were type 2 DM, age greater than 18 years old and the patient had to be followed at the outpatient department for at least 3 months.
From the 457 diabetic patients evaluated, patients with type 1 diabetes (n = 20), secondary diabetes (n = 25), other probable causes for CKD (n = 17), need for renal replacement therapy (n = 6) and insufficient information in the clinical process (n = 48) were excluded from the analysis. In order to exclude other probable causes for kidney disease all patients with an active urinary sediment and nephrotic proteinuria (n = 7), were excluded (Fig. 1). In order to standardize the population, patients with eGFR higher than or equal to 75 mL/min (n = 188) were also excluded from the analysis.
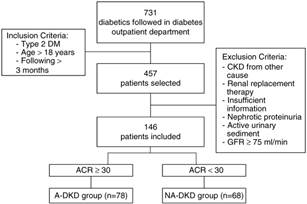
Fig. 1 Flow-chart of study. (DM Diabetes mellitus; CKD Chronic Kidney Disease; GFR Glomerular filtration rate; ACR Urine Albumin/Creatinine Ratio; A-DKD Albuminuric Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD); NA-DKD Non-albuminuric DKD).
After the application of these exclusion criteria, 146 patients remained in the study. eGFR was determined using the standard Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration formula (CKD-EPI). The spot urine albumin/creatinine ratio (ACR) was used to determine the albuminuria range, and we considered albuminuria when ACR was greater than or equal to 30 mg/g. According to this definition, the patients with eGFR < 75 mL/min, were divided in two groups: NA-DKD - patients without albuminuria and albuminuric DKD (A-DKD) - patients with albuminuria (Fig. 1).
In NA-DKD patients the results of all previous ACR measurements available at clinical process were reviewed and patients that had albuminuria before the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor use were excluded, to eliminate any patient whose normoalbuminuric status was related to RAS inhibitor use.
Information concerning demografic data, including age, gender, date of diabetes diagnosis, use of antidiabetic and hypotensive medications was collected from the clinical process. Details of physical examination such as weight, height (for body mass index calculation - BMI) and blood pressure, and also results from the most recent blood tests and laboratory urinalysis were also assessed by clinical process analysis. Presence or absence of past history of diabetic retinopathy (diagnosed by fundoscopy) and neuropathy, arterial hypertension (systolic blood pressure >140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure >90 mmHg), coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease and peripheral vascular disease (diagnosed by Doppler ultrasound) was also recorded. Metabolic syndrome was defined according to the definition published by World Health Organization (WHO).
Statistical analysis
Variables are expressed as frequencies for categorical variables, mean values with SD for continuous variables and median values with interquartile ranges for ordinal variables.
Comparison between groups was performed using T-test for normally distributed variables, Wilcoxon test for non-normally distributed variables and χ 2 test for categorical variables. Spearman correlation was also used for univariable analyis.
Logistic regression analysis was used for multivariable analysis.
Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS system 21.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL). For all comparisons, a p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Of the studied population (n = 146), 57.5% were male; mean age was 73.1 ± 9.5 years and with a median time of diabetes diagnosis of 16 years. Mean glicated haemoglobin (HbA1c) was 6.9 ± 1.1% and 26.9% were treated with insulin. Mean GFR was 50.4 ± 15.6 mL/min, mean albuminuria was 189.4 ± 477.8 mg/g and mean haemoglobin was 12.4 ± 1.6 g/dL.
Almost 80% of the patients had hypertension, 32.9% had coronary heart disease, 6.8% had cerebrovascular disease, 15.8% had diabetic retinopathy and 9.6% had peripheral artery disease (Table 1).
Table 1 Clinical and biochemical parameters of the studied population.
| Variable | Patients (n = 146) |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 73.1 (9.5) |
| Male gender | 84.0 (57.5%) |
| Duration of diabetes, years, median | 16.0 (11-27) |
| Hypertension | 116.0 (79.5%) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 28.5 (5.0) |
| Metabolic syndrome | 77.0 (52.7%) |
| Haemoglobin, g/dL | 12.4 (1.6) |
| Glicated haemoglobin, % | 6.9 (1.1) |
| GFR, mL/min | 50.4 (15.6) |
| Albuminuria, mg/g | 189.4 (477.8) |
| Coronary heart disease | 48.0 (32.9%) |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 10.0 (6.8%) |
| Diabetic neuropathy, % | 25.0 (17.1%) |
| Peripheral artery disease, % | 14.0 (9.6%) |
| Diabetic retinopathy, % | 23.0 (15.8%) |
| Insulin | 61.0 (41.8%) |
| Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors | 101.0 (69.2%) |
Values are: mean (SD), median (interquartile range) or frequencies [n(%)].
Of the 146 patients with eGFR < 75 mL/min, 78 (53.4%) had also albuminuria (A-DKD group) and the remaining 68 patients (46.6%) had only decreased eGFR, without albuminuria (NA-DKD group).
The albuminuric phenotype was more frequent in males (65.4%) and the non-albuminuric phenotype was slightly more prevalent in females (51.5%) (p = 0.045).
Compared with patients with albuminuria, those without albuminuria were more likely to be older (75.1 vs. 71.0 years, p = 0.021). The duration of diabetes diagnosis was similar between groups.
NA-DKD patients also had a lower eGFR (45.8 vs. 48.8 mL/min, p = 0.004) and lower haemoglobin concentration (11.8 vs. 12.5 g/dL, p = 0.020) (Table 2).
Table 2 Clinical and laboratorial characteristics of patients with diabetic kidney disease.
| NA-DKD (n = 68) | A-DKD (n = 78) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 75.1 (8.5) | 71.0 (10.2) | 0.021 |
| Male gender, % | 48.5 | 65.4 | 0.045 |
| Duration of diabetes, years, median | 19.0 (10-30) | 16.0 (11-25) | ns |
| More than 15 years of diabetes, % | 38.2 | 44.9 | ns |
| Dyslipidemia, % | 52.9 | 67.9 | ns |
| Hypertension, % | 66.2 | 91.0 | 0.000 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 29.4 (5.5) | 27.6 (5.2) | ns |
| Body mass index higher than 25 kg/m2, % | 47.1 | 56.4 | ns |
| Metabolic syndrome, % | 50.0 | 55.1 | ns |
| Haemoglobin, g/dl | 11.8 (1.5) | 12.5 (1.7) | 0.020 |
| Glicated haemoglobin, % | 6.7 (0.8) | 7.0 (0.8) | ns |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 148.7 (28.0) | 162.2 (47.0) | ns |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 127.7 (54.5) | 140.9 (60.2) | ns |
| HDL, mg/dL | 47.8 (16.3) | 48.7 (15.9) | ns |
| LDL, mg/dL | 75.5 (19.9) | 85.6 (39.2) | ns |
| Uric Acid, mg/dL | 5.8 (1.4) | 6.2 (1.3) | 0.044 |
| GFR, mL/min | 45.8 (14.9) | 48.8 (14.4) | 0.004 |
| Albuminuria | 10.9 (7.8) | 202.6 (271.0) | 0.000 |
| Systolic pressure, mmHg | 131.1 (15.0) | 133.9 (14.6) | ns |
| Diastolic pressure, mmHg | 68.1 (10.2) | 73.2 (11.3) | ns |
| Pulse pressure, mmHg | 62.4 (17.2) | 62.3 (13.9) | ns |
GFR, glomerular filtration rate; NA-DKD, non-albuminuric diabetic kidney disease; A-DKD, albuminuric diabetic kidney disease; ns, not significant.
Values are: mean ± SD, median (interquartile range) or frequencies [n(%)].
NA-DKD group had lower hypertension prevalence than A-DKD (66.2 vs. 91.0%, p < 0.001), and in concordance with this was under fewer hypotensive drugs (median of 1 vs. 2 hypotensive drugs, p < 0.001) and was less frequently medicated with RAS inhibitors (58.8 vs. 78.2%, p = 0.013) (Tables 3 and 4). Nevertheless, the mean diastolic and systolic blood pressures measured in office were similar between groups.
Table 3 Distribution of target-organ damage of the patients with DKD.
| NA-DKD | A-DKD | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coronary heart disease (%) | 22.0 | 42.3 | 0.013 |
| Cerebrovascular disease (%) | 7.4 | 6.4 | ns |
| Diabetic neuropathy (%) | 17.6 | 16.7 | ns |
| Peripheral artery disease (%) | 13.2 | 6.4 | ns |
| Diabetic retinopathy (%) | 11.8 | 19.2 | ns |
NA-DKD, non-albuminuric diabetic kidney disease; A-DKD, albuminuric diabetic kidney disease; ns, not significant.
Table 4 Anti-diabetic and hypotensive medication in diabetic kidney disease patients.
| NA-DKD | A-DKD | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of oral antidiabetics (median) | 1.0 (1-2) | 2.0 (0-3) | 0.001 |
| Insulin (%) | 30.9 | 51.3 | 0.018 |
| Number of hypotensive drugs (median) | 1.0 (0-2) | 2.0 (1-3) | 0.000 |
| Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors (%) | 58.8 | 78.2 | 0.013 |
NA-DKD, non-albuminuric diabetic kidney disease; A-DKD, albuminuric diabetic kidney disease.
Patients with non-albuminuric phenotype took fewer oral antidiabetics (median of 1 vs. 2 oral antidiabetics, p = 0.001) and were less frequently treated with insulin (30.9 vs. 51.3%, p = 0.013), however the metabolic control of diabetes (evaluated by HbA1c) was similar between groups (Tables 3 and 4). Prevalence of metabolic syndrome was also similar in the two groups.
Patients with non-albuminuric phenotype had significantly lower prevalence of coronary heart disease (22.1 vs. 42.3, p = 0.013), while the prevalence of the other diabetes target-organ damage like retinopathy, neuropathy, cerebrovascular disease and peripheral artery disease was not different between groups (Table 3).
The multivariable analysis (logistic regression), adjusted to gender, age, GFR, hypertension and CAD prevalence, showed that developing NA-DKD was positively associated with age (OR 1.07, 95% CI 1.02-1.11, p = 0.005) and female gender (OR 3.11, 95% CI 1.35-7.17, p = 0.008) and negatively associated with GFR (OR 0.95, 95% CI 0.93-0.97, p < 0.001) but not with hypertension and CAD. This model was statically significant (p < 0.001), however it only explains 32% (R 2 = 0.32) of NA-DKD prevalence.
Spearman's correlation was run to determine the relationship between GFR and albuminuria. There was a negative correlation between these two variables (r s = −0.166, p = 0.036).
Discussion
Albuminuria has been used classically as the first sign of renal involvement in diabetic patients and it is also used to evaluate the progression of DKD.1,2 However, in the last few years growing evidence has shown that a significant proportion of diabetic patients has decreased GFR without albuminuria, the so called NA-DKD.3,4
In our patients approximately one half (46.6%) of all patients with DKD had just decreased GFR without albuminuria, which is in accordance with other authors that found a prevalence of 13-69.4% of NA-DKD.3,11-15
Using albuminuria as an early marker of DKD onset or progression requires a careful interpretation because in diabetic patients albuminuria has a great tendency to regress spontaneously to normal levels. Some authors4,16 found that approximately 18-51% of type 2 diabetic patients (followed during 2-10 years) initially albuminurics became non-albuminurics spontaneously during follow-up time. On the other hand, United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS)17 showed that some diabetic patients pass directly from a normoalbuminuric stage to renal insufficiency (0.1% per year).
Although, some authors, such as Pavkov and colleagues5, advocated that in DKD the declining of GFR may precede the onset of albuminuria, they still defend that the progression to CKD stage 5D is strongly dependent on the appearance of albuminuria (especially albuminuria greater than 300 mg/g). This finding is in accordance with our results of a significant negative correlation between albuminuria and decreased eGFR.
Given the large intra-patients albuminuria variability and the possibility of bypassing the classic stages of the natural history of diabetic nephropathy, trusting albuminuria to identify and evaluate the progression of DKD may delay the diagnosis of a significant proportion of patients. A new concept for the natural history of diabetic nephropathy assumes albuminuria and decreased GFR as complementary manifestations of DKD, but not obligatory or temporarily related manifestations.4,5,18
In comparison to albuminuria, GFR has some advantages as a marker of renal impairment: spontaneous regression is unlikely and it's reduction is usually progressive.
Non-albuminuric patients were older and were 3 times more frequently female, which is in accordance with other authors.12,19 Although, there is a nephron loosing related to age, older ages have been related not only with lower GFR but also with higher albuminuria.17,25
The female tendency for NA-DKD is a consistent finding in other studies,12,19 but the reasons for this association are still unknown.20 NDR25 and UKPDS17 studies in diabetic patients suggested that female gender is a risk factor for renal impairment (GFR ≤ 60 mL/min), while male gender is associated with the development of albuminuria.
It contrasts with the known faster decline of GFR in males with kidney diseases other than DKD, and male gender has been proposed as a protective factor in the development of reduced GFR in diabetic patients.17,20
Penno and colleagues21 showed that the majority of patients with type 2 DM with diabetic retinopathy and DKD had increased albuminuria (independently of decreased eGFR), which reinforces that retinopathy is a risk marker for albuminuria but not for decreased eGFR. According to our results, we found that NA-DKD patients had more advanced CKD with lower eGFR and lower haemoglobin. This association suggests that NA-DKD patients have histologic lesions closer to macroangiopathy and interstitial disease with reduced renal mass, than a glomerulopathy alone. Some authors22 demonstrated that diabetic patients with decreased eGFR had a higher intrarenal resistive index, and that there was no association between albuminuria range and this index, suggesting a role for intrarenal vascular disease in renal insufficiency in NA-DKD patients. Many authors have also assumed cholesterol emboli as a frequent cause of decreased GFR in diabetic patients.23
We also found that metabolic syndrome prevalence was not different between albuminuric and non-albuminuric patients, however we noted a tendency to higher prevalence of some metabolic syndrome criteria, such as hypertension, dyslipidaemia and hypertriglyceridaemia, in albuminuric group.
Nevertheless, the only study we found that analyzed the prevalence of this syndrome in NA-DKD,14 found it more frequent in non-albuminuric patients. Other studies,20,24,25 although not directed to the prevalence of metabolic syndrome, found contradictory results in respect to the prevalence of isolated metabolic syndrome traits.
It is unclear why some patients develop DKD with significant albuminuria, while others have impaired renal function associated with very low levels of albuminuria. Evidently, diabetic patients can develop renal disease other than diabetic nephropathy, as occurs in any individual, therefore a superimposed non-diabetic kidney disease could explain this phenotype. Some authors26 showed that more than 95% of renal diseases in type 1 diabetic patients were result of a diabetic glomerulosclerosis, unlike in type 2, which is a more heterogeneous group. Twelve to eighty-one percent of renal biopsies of type 2 diabetes patients presented a renal disease unrelated to diabetes.26,27 However, we must be aware of the selection criteria in these studies for doing renal biopsy in type 2 diabetes patients with renal injury - most of them had nephrotic proteinuria or hematuria, which suggests a superimposed non-DKD.
A frequent question is, if the development of NA-DKD can be due to hypertensive nephroangiosclerosis, the second main cause of CKD in developed countries and a frequent comorbidity in type 2 diabetic patients (79.5% of our diabetics had hypertension). However, in our study, hypertension prevalence was similar between groups and albuminuric patients took more hypotensive drugs and more renin-angiotensin system inhibitors making nephroangiosclerosis an unlikely cause for decreased GFR in NA-DKD group.
It has been also suggested that RAS inhibitors can mask albuminuria and can justify the non-albuminuric phenotype. Nevertheless, in our study we excluded any patient whose normo-albuminuric status was related to RAS inhibitor initiation.
In our patients the metabolic control of diabetes (evaluated by HbA1c) was not different between albuminuric and non-albuminuric patients. However, the UKPDS study17 shown that HbA1c is predictor for albuminuria, but not for decreased GFR in diabetic patients.
NEFRON 11 study28 found unexpectedly a similar frequency of nonalbuminuric renal impairment between general population and diabetic patients. These authors suggest that it is possible that NA-DKD is being increasingly identified due to the current recommendations of screening DKD by calculating GFR and measuring albuminuria.
Budhiraja et al.29 evaluated 10 biopsy specimen's obtained from type 2 diabetic patients who underwent nephrectomy for renal cancer and had decreased GFR without proteinuria and found changes consistent with diabetic glomerulosclerosis. They assumed that the absence of proteinuria in presence of advanced glomerular lesion could be due to reabsorption of proteinuria by relatively preserved tubules.
An Israeli work group30 performed a study in rats (experimental models of type 2 diabetes) and found strong evidence that NA-DKD occurred with histopathology findings consistent with diabetic nephropathy, suggesting that NA-DKD phenotype was really diabetic nephropathy and no other cause. They suggested that the development of one phenotype instead of another might be explained by genetic determinants. However, a recent biopsy study31 of 31 type 2 diabetic patients with decreased eGFR, explored the renal structural changes in albuminuric (n = 23) and normoalbuminuric (n = 8) patients, and found more heterogeneity of the renal lesions in non-albuminuric than in albuminuric subjects. They found that in non-albuminuric subjects just half had typical glomerulopathy (present in almost all A-DKD patients), frequent predominantly interstitial or vascular changes and the majority of them had some degree of arteriosclerosis. These results suggest the implication of diverse pathogenic factors such as age, blood pressure and intrarenal vascular disease.
Caromoni and colleagues32 evaluated 23 renal biopsies of patients with type 1 diabetics who had NA-DKD and also found glomerular changes consistent with a typical diabetic nephropathy. The scarce studies comparing renal biopsy findings in NA-DKD and A-DKD patients does not enable us to identify which histopathologic mechanism is behind of the non albuminuric phenotype.
Porrini et al.20 showed that NA-DKD patients had a rate of GFR decline of 3.5 mL/min/1.73 m2 (which means a 2-5 times faster decline than in the healthy population) and that A-DKD patients had an even higher decline of GFR. Perkins et al.33 found that also in type 1 diabetic patients the decline rate of eGFR was higher in albuminuric than in non-albuminuric subjects.
Rigalleau11 and Zeeuw34 found that NA-DKD patients had a lower risk of progression to CKD stage 5D (lower decline in GFR and lower increase in albuminuria). Remuzzi and Bertani35 postulated that albuminuria is not only a marker of severity of kidney disease but also albuminuria itself could damage the kidney.
Patients with NA-DKD presented lower all-cause mortality in several studies11,36 in comparison with albuminuric patients, suggesting that NA-DKD may have a better prognosis than A-DKD.
RIACE Study Group37 found a lower rate of cardiovascular events in NA-DKD, what could probably be, even partially, related to the fact that albuminuria is a cardiovascular risk marker.
The main limitation of our study, like the majority of NA-DKD studies, was the impossibility to confirm histologically with renal biopsy specimens if NA-DKD patients had glomerular lesions consistent with diabetic nephropathy or another cause for decreased GFR. Some questions still remain unanswered: why some patients develop NA-DKD; if the traditional medical approach used to prevent or delay the progression of DKD has the same efficacy in NA-DKD patients and if NA-DKD is a different phenotype of DKD or just an alternative pathway of DKD.
Conclusions
Early decreased GFR without albuminuria is increasingly recognized as a marker of DKD in a significant proportion of diabetic patients (46.6% in our study). Patients with NA-DKD seem to exhibit distinct clinical features from A-DKD, which could have therapeutic, screening and prognosis implications. The existence of these new phenotype or pathway in diabetic nephropathy suggests the necessity to review our understanding and classification of diabetic nephropathy as a 5 stage progressive process. However, albuminuria still has a strong prognostic importance and it is an important cardiovascular risk marker.














