Introduction
The increasing adoption of information and communication technologies by society in general and by the health sector in particular, together with the need to transform healthcare to make it more efficient and patient-centered, have in the last few years triggered a growing demand for certain services to be provided remotely. Such services include distance care and monitoring, patient education and counseling, and coordination between different clinical teams. All these services can be subsumed under the category of telemedicine1.
This demand for remote healthcare has long been recognized in the realm of hospital pharmacy practice. In this respect, the term telepharmacy was coined years ago to refer to the delivery of hospital pharmacy services from a distance2,3. Nonetheless, the literature proposes multiple definitions for the term, each with different variants and nuances4,5. In this regard, the Spanish Society of Hospital Pharmacists (SEFH) has recently published its position statement on telepharmacy, according to which telepharmacy is the provision of pharmaceutical care from a distance through information and communication technologies6.
At present, implementation of telepharmacy constitutes a significant challenge for pharmacists devoted mainly to their traditional hospital work, especially when it comes to providing pharmaceutical care to outpatients7,8. Although in Spain the so-called Strategic Outpatient Pharmaceutical Care Map (Mapa Estratégico para la Atención al Paciente Externo)9,10 provided for the gradual implementation of telepharmacy, the recent SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has accelerated the need to ensure an adequate standard of pharmaceutical care for patients treated by hospital pharmacy departments throughout the country.
A few days after the state of emergency was declared in Spain11, the country's healthcare authorities introduced exceptional norms for dispensing hospital-issued medications as well as a series of procedures aimed at ensuring the provision of all ordinary and extraordinary pharmacy services and protecting individuals, goods and places12 for as long as the healthcare emergency continued. According to that norm, pharmaceutical authorities of the different autonomous regions were exceptionally authorized to under-take the measures they saw fit to guarantee proper dispensation of hospital-issued medications.
The purpose of this study is to analyze the implementation and development of telepharmacy services in Spain during the COVID-19 pandemic, focusing specifically on one group of beneficiaries, namely hospital pharmacy outpatients.
Methods
A survey was prepared and posted on SEFH's website. An email was sent to all SEFH members inviting them to participate, specifying that only one response per hospital would be accepted. To access the survey,
SEFH members were required to introduce their membership number. To minimize data attrition and maximize the size of the sample, a reminder was sent 24 hours before the established deadline. The survey remained active for 96 hours. The study period lasted six weeks.
The survey contained 10 questions (Appendix 1. In the first section, respondents had to state their professional information (name of their hospital and autonomous region) and a few details about their hospital (number of beds and number of outpatients treated in 2019). The second section included questions relative to telepharmacy. Firstly, respondents had to state whether their hospital had been providing remote pharmaceutical care with distance dispensing of medications prior to the onset of the health crisis. After that, there were questions about the procedure followed to send the medication to the patients' homes.
The questions about drug deliveries were aimed at gauging the burden of work borne by hospital pharmacies during the pandemic, thereby allowing the extraction of activity indicators. Specifically, respondents were asked about the number of deliveries made to patients receiving remote pharmaceutical care through telepharmacy, and about the percentage that these patients represented of the total candidate patients.
Lastly, two questions were asked about the use of telepharmacy and the information shared with patients in connection with pharmacotherapeutic monitoring activities. One of them asked whether a teleconsultation had taken place prior to sending patients their medication, and the other asked whether telepharmacy activities were recorded in the department's appointments register.
Before proceeding to the analysis of the data, 10 duplicate records had to be removed.
A descriptive analysis was carried out based on the frequency distribution of the different outcome indicators used in the study for a confidence interval of 95%. Given that it was expected that the study population would be made up of all the hospital pharmacy departments in the Spanish National Health System, the sampling accuracy was calculated for a confidence interval of 95% and a response rate of 50%. The Epidat 3.1 (2006) statistical package was used both for calculating sampling accuracy and the confidence interval.
Results
A total of 39.3% (n = 185) of hospitals in the Spanish National Health Systems from all autonomous regions responded to the survey (Table 1). Of them, 184 (99.4%) were public or state-contracted hospitals belonging to the National Health System, and only one (0.6%) was a private hospital. Taking into account that the survey was answered by 185 hospital pharmacies, sampling accuracy was found to stand at 5.6%.
In 2019, the hospital pharmacy departments that completed the survey administered (onsite or remote) pharmaceutical care with remote dispensing to around 616,000 outpatients. Before the COVID-19 crisis, 83.2% (77.1-88.3%, CI: 95%) (n = 154) of hospital pharmacies did not engage in remote pharmaceutical care activities that included the shipping of medications.
Over the study period, 119,972 patients were reported to have received their medications through remote dispensing telepharmacy services, with a total of 134,142 shipments made. This meant that in 41 hospitals over 80% of outpatients received their medication through a telepharmacy procedure (Figure 1).
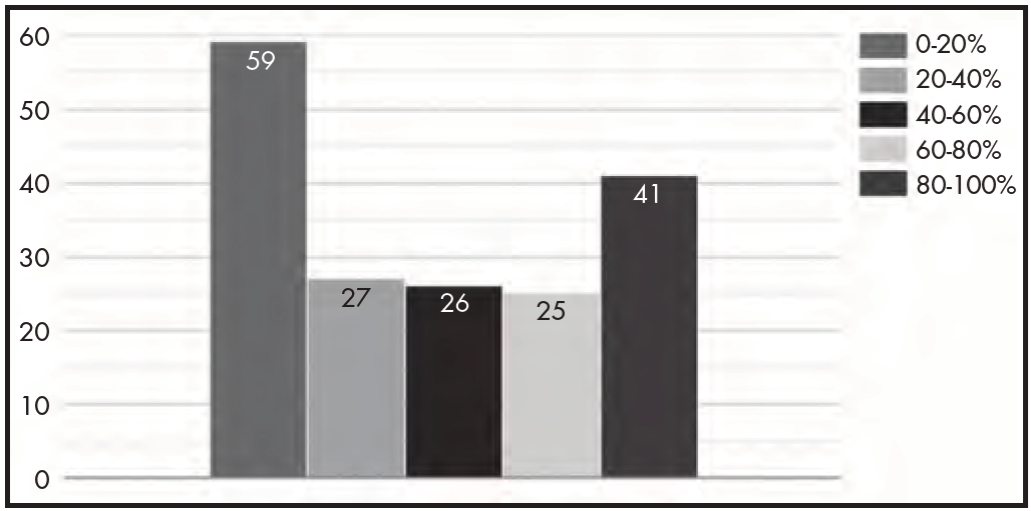
Figure 1. Percentage of outpatients who were dispensed their medication remotely by each of the hospitals.
A total of 87.6% (81.9-92.0%, CI: 95%) of hospital pharmacies conducted a teleconsultation with the patient prior to shipping their medications (Figure 2) and 59.6% (52.0-66.6%, CI: 95%) recorded telepharmacy activities in their appointments register.
The analysis found that 55.7% (48.2-63.1%, IC 95%) of hospital pharmacies did not use any selection criteria to decide which patients could be shipped their medications but rather shipped them to all the patients scheduled to pick up their medication from the hospital pharmacy in the program to spare them the risk of travelling. A total of 44.3% of hospitals had a procedure in place that included some selection criteria: 30.2% of hospitals selected patients according to their personal circumstances, 9.7% based on their condition; and 4.3% as a function of the nature of their medication or other criteria.
The most frequently used telepharmacy procedure was home dispensing and informed delivery of medications (87.0%) (81.3-91.5%, CI: 95%) (116,129 shipments), followed by coordination with primary care outpatient clinics (8,389 shipments), and coordination with pharmacies (7,512 shipments). Some hospital pharmacy departments used more than one procedure at a time (Figure 3).
The means used to deliver the medications to their addressees included courier companies (47.0%; 87 hospitals), the hospital's own transport services (38.4%; 71 hospitals), recourse to other private and/or volunteer entities (41.6%; 77 hospitals), use of a dedicated drug delivery company (14.0%; 26 hospital), and other solutions (7.0%; 13 hospitals).
Discussion
Restrictions on mobility and home confinement as a result of the state of emergency declared during the COVID-19 pandemic have turned telepharmacy into a valuable tool for hospital pharmacies to facilitate access to pharmaceutical care and, specifically, enable distance dispensation of hospital-issued medications. This survey afforded SEFH an understanding of the extent to which telepharmacy was implemented across Spain, including details on home dispensing of medications, the means used, and the procedures implemented.
A significant aspect to be underscored is the huge expansion of telepharmacy, including remote dispensing and delivery of medications, during the state of emergency in Spain. Estimations based on the answers provided by respondents to the survey (39.3% of the 471 public hospitals registered in the 2018 edition of the general hospital registry (Catálogo General de Hospitales) of Spain's Ministry of Health, Consumer Affairs and Social Welfare)13 indicate that around 300,000 outpatients received telepharmacy services in the country. Special mention should be made of the alacrity with which hospital pharmacies adapted to outpatients' clinical needs arising from the crisis. Indeed, a mere six weeks was enough for a high percentage of pharmaceutical care services to come to be provided through telepharmacy. It must be taken into consideration that, from the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic to the publication of Ministerial Order SND/293/2020 on 25 March, many hospital pharmacies extended their dispensation periods and postponed pharmacological consultations in compliance with the Law14.
It must be pointed out that most hospital pharmacies scheduled a pharmacological teleconsultation prior to dispensing medication. Different studies have revealed that remote consultations positively impact health outcomes, specifically regarding clinical management and adherence to treatment by chronic patients15. It was not however the purpose of the survey to look into the teleconsultation methods used; to evaluate the health outcomes achieved by patients; or the costs associated to telepharmacy, which are undoubtedly interesting areas for further investigation into the application of telepharmacy.
One of the most striking findings of the survey was the large number of patients benefiting from telepharmacy services, as recorded in hospital information systems. SEFH's position statement of telepharmacy6, published once the study period was over, identifies the electronic medical record as the most efficient information system for the delivery of telepharmacy services and states that, whenever possible, such records should be integrated with the healthcare information systems and the telemedicine systems already in place in the different hospitals. This underscores the sheer usefulness of telepharmacy as a professional support service where the pharmacist's physical presence is replaced by a relationship with the patient which, though virtual, abides by all the face-to-face procedures already in place in the hospital. For this relationship to work smoothly, hospital pharmacists were required to act as fast as possible to provide patients with all the information they needed before telepharmacy could be delivered to them. The pharmacotherapeutic expertise of specialist pharmacists together with the meticulous registration of pharmaceutical care interventions in the patients' electronic medical record have allowed them to make fast decisions in collaboration with the other members of the multidisciplinary team in charge of the patient before the medication was dispensed and shipped out to the patient.
Although there was no requirement for hospital pharmacies to use any single shipping method, most deliveries during this period were shipped to the patient's home. On most occasions, hospitals used courier companies for these deliveries, although in some cases other methods were used such as the hospital's own transport services, volunteers, postal services, or civil protection services. The profuse recourse to courier companies may have been motivated by the availability of the so-called solidarity fund (fondo solidario) instituted by SEFH on 1 April, which made it possible for hospital pharmacies to ship medications free of charge, a benefit that had up to then not been included in their service offering, or at least not to the extent that it eventually became necessary. In the future, hospital pharmacies will have to further develop telepharmacy as a complementary tool within a mixed pharmaceutical care model based on both an onsite and a distance component, which caters for the individual needs of patients in an increasingly humanized healthcare environment16,17.
The main limitation of this study lies in the fact that the survey was not validated prior to its administration and was specifically created to analyze a situation as exceptional as the COVID-19 pandemic. Nor does the study contribute any information on the degree of satisfaction of telepharmacy users; evaluate the procedures implemented; analyze their effect on treatment adherence; or consider any effectiveness or safety variables, as such aspects were not covered by the survey. Earlier telepharmacy experiences with specific populations such as HIV or hemophilic patients18,19 showed a very high level of satisfaction (9.7 ± 0.7 out of 10) with teleconsultations and home dispensing, regarding the shipping system used, the privacy and confidentiality it allowed, and the quality of care it provided. Future research work should focus on health outcomes, as well as on the economic effects of delivering pharmaceutical care through telepharmacy, without leaving aside other aspects such as patient satisfaction and the experience of care. The results of the survey show that hospital pharmacies in Spain have the capacity to embrace the implementation of efficient telepharmacy services in the near future, once the COVID-19 pandemic finally recedes. For that it will be necessary to develop a robust legal framework, adapted to the patients' needs and to the current challenges in the realm of public health6.
Telepharmacy-specific procedures will have to be developed that include a definition of the criteria to be applied to select potential beneficiaries of the service. Taking into consideration the high degree of satisfaction reported since its implementation16, telepharmacy could become a service that bolsters the quality and safety of the healthcare system with high rates of user approval. All these factors must be considered when planning and consolidating the delivery of remote pharmaceutical care through telepharmacy in the future.
In short, telepharmacy associated to the remote dispensing of medications has undergone a significant expansion during the COVID-19 pandemic in the outpatient care setting. This new tool has also made it possible to monitor patients from a pharmacotherapeutic point of view, evaluate treatment adherence and even reduce the infection rate by facilitating home confinement during the state of emergency.
Contribution to scientific literature
The study reports on the experience gained by hospital pharmacy departments in Spain in the areas of outpatient pharmaceutical care and remote dispensing and informed delivery of medication during the COVID-19 crisis. This is the first nationwide survey of a large sample of hospitals in the Spanish National Health System on the provision of telepharmacy.











 texto en
texto en 






