Parenting stress is a complex process that can be subsumed within the general stress model of Lazarus and Folkman (1984) and understood as the aversive psychological reaction that occurs when caregivers feel overwhelmed and perceive that they lack the skills required to cope with their parental role (Abidin, 1995; Deater-Deckard, 1998). Parenting stress is conceptually distinct from other life stressors that a parent might experience (e.g, negative life events, financial problems), although they are frequently related (Holly et al, 2019).
Parenting stress has been found to be associated with parenting processes across all developmental periods. Research suggests that parenting stress tends to show stability and to decrease over time as the child becomes older, particularly when its initial levels are not very high (Neece et al, 2012; Stone et al, 2016; Williford et al, 2007).
Research has also shown parenting stress as a normative process that can affect every parent. However, it may be more severe for parents of children with clinically significant emotional, behavioural, or health issues (Crnic et al, 2005; Deater-Deckard & Panneton, 2017; Holly et al, 2019), and particularly challenging for families where parenting demands converge with negative situational circumstances (e.g, low-income) or personal difficulties (e.g, parents mental health problems, children with subclinical behaviour problems; Barroso et al, 2018; Menon et al, 2020). Higher levels of parenting stress have been found to be associated to depression and psychological difficulties in parents (Schleider et al, 2015; Theule et al, 2010; Thomason et al, 2014), behaviour problems and self-regulation difficulties in children (Anthony et al, 2005; Mackler et al, 2015; Mäntymaa et al, 2012; Stone et al, 2016), and negative interactions between parents and children (Dubois-Comtois et al, 2013; Gerdes et al, 2007; Van Steijn et al, 2014). Finally, there is evidence that parents' and children's factors contribute to parenting stress in a complex transactional process. Both contribute to parenting stress and at the same time are affected by it, having consequences for the well-being of parents and children (Crnic & Rose, 2017).
Considering the negative effects of parenting stress, its reduction constitutes a common and relevant goal of preventive and rehabilitative parenting programmes (Chen & Chan, 2016; Reyno & McGrath, 2006; Van Steijn et al, 2014), so reliable and valid measures are necessary. One of the most commonly instruments used in both clinical and research contexts is the Parenting Stress Index (PSI; Abidin, 1983), a 120-item self-report measure. Given its length, an abbreviated 36-item version was developed – the Parenting Stress Index-Short Form (PSI-SF; Abidin, 1983) – consisting of three subscales of twelve items each: Parental Distress (PD), Parent-Child Dysfunctional Interaction (PCDI), and Difficult Child (DC). The Parental Distress (PD) subscale captures the level of distress resulting from personal factors such as depression or conflict with a partner and life restrictions due to a parent's perception of his or her child-rearing competence. The Parent-Child Dysfunctional Interaction (PCDI) subscale assesses the extent to which a parent feels that his/her child is not meeting expectations and that interactions with the child are not reinforcing. The Difficult Child (DC) subscale measures a parent's view of his/her child's temperament, defiance, non-compliance, and demandingness. A total score of parenting stress is calculated by summing scores from the three subscales.
The Parenting Stress Index-Short Form (PSI-SF) has been used to measure parenting stress in parents from clinical and high-risk populations (Barbot et al, 2014; Crum & Moreland, 2017; Mackler et al, 2015; Vallotton et al, 2016), and to measure treatment effectiveness (Battagliese et al, 2015; Reyno & McGrath, 2006). PSI-SF has been translated to and applied in different languages like Italian (Miragoli et al, 2018), Spanish (Pérez & Menéndez, 2014), Portuguese (Seabra-Santos et al, 2016), and Finnish (Mäntymaa et al, 2012).
Excluding the study carried out by Abidin (1995), twenty studies have been found in Web of Science and PsycInfo databases analysing the psychometric properties of PSI-SFSixteen of those studies examined factor structure, yielding mixed findings. Confirmatory factor analyses in two of these studies found that the original three-factor model offered an adequate fit (Çekiç & Hamamci, 2018; Lee et al, 2008). Three other studies considered the three-factor model as the best choice due to its clinical value although with suboptimal fit indices (Lee et al, 2016; Reitman et al, 2002; Touchèque et al, 2016). Another group of studies involving both exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses concluded that the three-factor model was appropriate but removed some items (Dardas & Ahmad, 2014; Deater-Deckard & Scarr, 1996; Kang et al, 2017; Luo et al, 2019) or proposed two-factor (Haskett et al, 2006) or five-factor (McKelvey et al, 2009; Whiteside-Mansell et al, 2007; Zaidman-Zait et al, 2011) models. Despite statistical analyses (confirmatory or exploratory factor analyses) and the amount of dimensions/factors proposed for the PSI-SF, all the studies reported moderate to high correlations between them, supporting the theoretical assumption that the relationship between PSI-SF's dimensions can be considered oblique.
Four studies have analysed factor structure or psychometric properties of the Spanish version of PSI-SFTwo of them used a sample of Spanish middle-class, married couples with infants aged between ten and thirty-nine-month old. Their findings suggested two different models for fathers and for mothers: whereas the original three-factor solution fitted the data for fathers (Díaz-Herrero et al, 2011), a two-factor model – labelled Childrearing Stress (CS), and Personal Distress (PD) – was proposed for mothers (Díaz-Herrero et al, 2010). A third study that administered PSI-SF's two-factor model proposed by Díaz-Herrero et al. (2010) to 109 Spanish at-risk mothers with one child aged below 12 years obtained satisfactory internal consistency and adequate discriminant validity indexes (Pérez-Padilla et al, 2015). Finally, an exploratory factor analysis of a fourth study carried out with a Chilean sample of 336 dyads consisting mostly of young, single mothers and their infants (age: M = 84.8 days, SD = 78 days) found that the PSI-SF shared the three-factor structure of the original, but proposed the elimination of two items (from the Parent-Child Dysfunctional Interaction and the Difficult Child subscales; Aracena et al, 2016).
As it has been seen, studies about the factor structure of the Parenting Stress Index-Short Form (PSI-SF) have not yielded consistent results. Several hypotheses can be proposed. First, differences may be linked to sample characteristics. For example, studies conducted with particular populations as younger, less educated, and poorer mothers of younger children (Aracena et al, 2016) or parents of children with autism spectrum disorders diagnosis (Zaidman-Zait et al, 2011) can yield different findings related to PSI-SF dimensions. Second, despite the possible effect of sample characteristics, differences between studies may be also linked to statistical analyses (e.g, confirmatory vs. exploratory factor analyses) used to explore PSI-SF dimensions.
Finally, studies analysing PSI-SF's convergent validity have found significant relationships between PSI-SF's total score and measures of family conflict, exposure to violence, and other negative life events; between the Parental Distress subscale and measures of depression or parental anxiety; and between the Difficult Child subscale and measures of child behaviour problems (Aracena et al, 2016; Barroso et al, 2016; Haskett et al, 2006; Lee et al, 2016; McKelvey et al, 2009; Pérez-Padilla et al, 2015; Reitman et al, 2002; Whiteside-Mansell et al, 2007; Zaidman-Zait et al, 2011).
The aim of the present study was to analyse the psychometric properties of the Spanish version of the Parenting Stress Index-Short Form (PSI-SF) with two groups of mothers with children aged 0 to 8 years old: mothers with significant problems to cope with their children's behaviour and mothers from the general population. The factor structure of PSI-SF Spanish version along with data on internal consistency and convergent validity were analysed as well as differences between groups.
Method
Participants
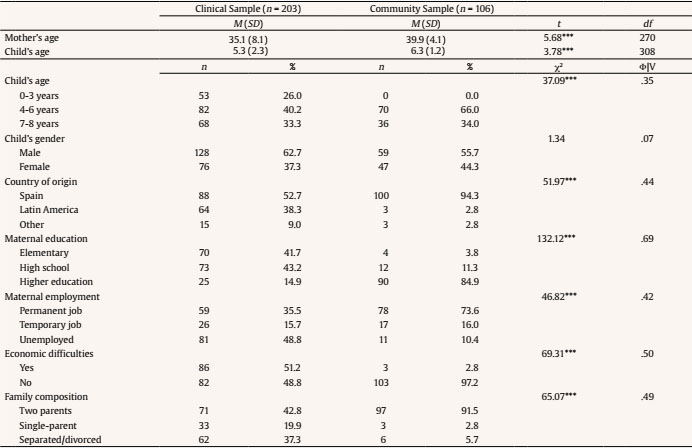
Two different samples of mothers of children aged under 8 years old participated in the study (N = 309). The first sample (clinical sample) consisted of 203 mothers with significant problems to cope with their children's behaviour recruited from family support and treatment programmes provided from Child Protection Services of the region of Gipuzkoa (Spain). The second (community sample) was a convenience sample consisting of 106 mothers from the general population of Gipuzkoa who were recruited via six schools that agreed to participate.
As can be seen in Table 1, there were sample differences in sociodemographic characteristics. Compared to the community sample, mothers and children from the clinical sample were younger and included higher percentages of single-parent or separated/divorced families, mothers from other countries, with lower educational levels, and economic problems.
Instruments
Parenting Stress Index/Short Form (PSI-SF; Abidin, 1995). PSI-SF is a 36-item, self-report measure of parenting stress. It includes three subscales: Parental Distress (PD; e.g, “I feel trapped by my responsibilities as a parent”, “I feel lonely and without friends”), Parent-Child Dysfunctional Interaction (PCDI; e.g, “Sometimes I feel my child doesn't like me and doesn't want to be close to me”, “When I do things for my child I get the feeling that my efforts are not appreciated” ), and Difficult Child (DC; e.g, “My child makes more demands on me than most children”, “My child gets upset easily over the smallest thing”). Each subscale consists of 12 items rated from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree), with subscales scores ranging from 12 to 60. A Total score is calculated by summing the three subscales scores, ranging from 36 to 180. Scores of 90 or above may indicate a clinical level of stress. Abidin (1995) reported Cronbach's alpha coefficients of .91 for PSI-SF total score, and .87, .80, and .85 for PD, PCDI, and DC subscales, respectively. Psychometric data obtained in the present study are presented in the Results section.
Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II; Beck et al, 1996). BDI-II is a 21-item, self-report measure of depressive symptomatology. This measure is appropriate for both psychiatric and normative populations. Responses are given using a four-point scale from 0 to 3 (0 = I do not feel like a failure, 1 = I have failed more than I should have, 2 = As I look back, I see a lot of failures, and 3 = I feel I am a total failure as a person), with scores ranging from 0 to 63 and higher scores indicating higher levels of depressive symptomatology. BDI-II has been shown to have adequate reliability (between .92 and .93 for internal consistency and r = .93 for test-retest reliability) as well as adequate construct validity (Beck et al, 1996). In the present study, internal consistency indices were satisfactory for both groups of mothers (Cronbach's alphas of .87 for the clinical sample, and .77 for the community sample).
Brief Child Abuse Potential Inventory (B-CAPI; Ondersma et al, 2005). B-CAPI is a self-report screening questionnaire composed by 34 items extracted from the Child Abuse Potential Inventory (CAP; Milner, 1986). Twenty-five items composed the Abuse scale that measures the risk of a parent to physically abuse their children (e.g, “I am often upset and do not know why”, “Sometimes I feel lonely”), and two Validity scales: a three-item Random Response scale and a six-item Lie scale. Responses are in a binary scale (agree-disagree), so scores range between 0 to a maximum of 25 in the Abuse scale. Ondersma et al. (2005) indicated good internal consistency for the Abuse scale (KR20 = .89). In the present study, KR20 for the Abuse scale was computed for the clinical sample (.83) and for the community sample (.83). The 34 items used in this study were pulled out from the Spanish version of the CAP Inventory (De Paúl et al, 1999).
Eyberg Child Behaviour Inventory (ECBI; Eyberg & Pincus, 1999). ECBI is a parent-rating scale covering 36 common child disruptive behaviours with two subscales. The Intensity subscale measures the frequency of a child's problem behaviour (e.g, “Acts defiant when told to do something”, “Refuses to go to bed on time”) on a seven-point scale, ranging from 1 to 7 with a minimum score of 36 and a maximum of 252. The Problem subscale measures the extent to which a parent finds their child's behaviour troublesome, which is rated on a binary scale (0 = No, 1 = Yes) with a range score from 0 to 36. Eyberg and Pincus (1999) reported high internal consistency for both Intensity and Problem subscales (α = .95 and KR20 = .94, respectively). In the present study, both Intensity and Problem subscales showed high internal consistency for clinical (α = .91 and KR20 = .88) and community samples (α = .88 and KR20 = .89).
Procedure
The research design was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of the Basque Country UPV/EHU (Spain). All participant mothers were informed of study goals and gave informed consent. Mothers in the clinical sample were informed by Child Protection Services caseworkers and completed the instruments at baseline and 6-months later in the presence of a trained clinical psychologist. Mothers in the community sample were informed by their children's school directors, collected the instruments from the school, completed them at home, and returned in a sealed envelope.
Data Analysis
Analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics Version 24.0, Mplus 7.11, and R Studio. Preliminary analyses were conducted to examine data characteristics. Multivariate normality was estimated by Mardia's multivariate skewness and kurtosis tests (Mardia, 1970).
Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was used to examine PSI-SF factor structure
using weighted least squares mean and variance adjusted (WLSMV) estimation method. This method is recommended in non-normally distributed data with severe floor or ceiling effects (Brown, 2015). When the WSLMV estimator is used, missing data are treated with pairwise deletion, which is acceptable when the amount of missing data is minimal (Kline, 2011). In the present study, less than 1% of responses per PSI-SF item in both samples were missing.
Multiple fit indices were examined: root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) values below .08 represent acceptable fit, comparative fit index (CFI) and Tucker-Lewis index (TLI) values between .90 and.95 represent reasonable model fit, and values above .95 represent excellent model fit (Brown, 2015).
Internal consistency was examined by computing Cronbach's alpha, McDonald's omega, and omega hierarchical coefficients for the PSI-SF as a whole and for the three subscales. Cronbach's alpha is less reliable in multidimensional measures and require equal factor loadings (Viladrich et al, 2017). Therefore, omega coefficients were also calculated using R Studio software.
Convergent validity was assessed by computing Spearman correlations between the Parental Distress subscale of the PSI-SF, and both the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II) and the Brief Child Abuse Potential Inventory (B-CAPI) scores, and between the Difficult Child subscale of the PSI-SF and the Eyberg Child Behaviour Inventory (ECBI) scores.
Measurement invariance (MI) between both samples and between subgroups of the clinical sample, child age, gender, and economic difficulties was intended to test. However, it was no possible to calculate MI because groups did not contained the same number of categories per item. For informative purposes, MANOVAs were conducted to test PSI-SF differences between clinical and community samples, and between subgroups in the clinical sample.
Differences between baseline and 6-months PSI-SF scores were analysed in the clinical sample with a repeated measures MANOVA.
Results
Preliminary Analysis
Analyses of item distribution of PSI-SF indicated violations of univariate normality in some items for both samples (see Table 3). Additionally, Mardia's multivariate skewness and kurtosis test was statistically significant (p < .01), suggesting a violation of multinormality in both samples.
PSI-SF Factor Structure and Reliability
Table 3. Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) Standardized Factor Loadings, Descriptive Statistics for Each Item, and Reliability Coefficients of PSI-SF for the Clinical and Community Samples

Note. S = skewness; K = kurtosis; SE = standardized errors; α = alpha; ω = omega; ωh = hierarchical omega; CI = confidence interval 95%.
*p < .05
Clinical sample. Three structural models of the PSI-SF were examined using confirmatory factor analysis (CFA): the original three-factor model proposed by Abidin (1995), the two-factor model proposed by Díaz-Herrero et al. (2010), and a one-factor model using PSI-SF total score. Goodness-of-fit indices for the three models tested are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2. Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) Model Fit Indexes for One, Two, and Three Factors of the PSI-SF for the Clinical and Community Samples

Note. χ2 = chi-square goodness of fit statistic; df = degrees of freedom; RMSEA = root-mean-square error of approximation; CFI = comparative fit index; TLI = Tucker Lewis index.
*p < .05
The three-factor model provided the best fit to the data with acceptable goodness of fit indices (RMSEA = .07, CFI = .91, TLI = .90). CFA items loadings, standardized errors, factor correlations, and reliability coefficients are presented in Table 3.
Items loadings and standard errors presented adequate estimates with loadings higher than .30 and standard errors between .03 and .09. Although two items loadings were lower to .30 (items 22 and 31) they were significant to their factors, so no further analyses were made.
As can be observed in Table 3, correlations between PSI-SF three factors ranged between .53 and .70. Following Brown (2015), the three dimensions showed adequate discriminant validity and were not overlapping. Furthermore, all reliability coefficients were adequate for the three-factor model.
Community sample. CFA analysis conducted for the community sample obtained similar findings than those for the clinical sample (see Table 2). The three-factor model provided the best fit to the data (RMSEA = .06, CFI = .92, TLI = .92). Factor loadings of the three-factor model were all above .30 with adequate standard errors between .04 and .12. Adequate correlations between the three factors were obtained, with values ranging between .34 and .77. Moreover, reliability coefficients showed adequate values for the model (see Table 3).
PSI-SF Convergent Validity
Correlations between BDI-II (depressive symptomatology), B-CAPI (child abuse potential), and ECBI (child behaviour problems), and PSI-SF Total and subscales scores were analysed in both samples (see Table 4). Total PSI-SF and Parental Distress subscale scores were strongly, positively correlated with BDI-II and B-CAPI scores in both samples, indicating that mothers reporting more parental distress also reported more depressive symptomatology and a higher risk for physical child abuse. Total PSI-SF and Difficult Child subscale scores were also strongly positively correlated with ECBI scores in both samples, indicating that mothers who reported greater stress due to having a difficult child also reported more child behaviour problems. In addition, Parent-Child Dysfunctional Interaction subscale scores, although with less strength, were also positively correlated with both BDI-II and ECBI scores in both samples.
Table 4. Spearman Correlations between PSI-SF Total and Subscales Scores, and Mother Depressive Symptomatology (BDI-II), Child Abuse Potential (B-CAPI) and Child Behaviour Problems (ECBI) Scores

Note. S = skewness; K = kurtosis; SE = standardized errors; α = alpha; ω = omega; ωh = hierarchical omega; CI = confidence interval 95%.
*p < .05.
PSI-SF Differences between Baseline and 6-Month Measures
The repeated-measures MANOVA (see Table 5) revealed statistically significant differences between baseline and 6-month scores for the total PSI-SF and the Parental Distress, Parent-Child Dysfunctional Interaction, and Difficult Child subscales in the clinical sample of mothers (Wilks' lambda = .68, F(3, 138) = 21.65, p < .0001). As expected, 6-month scores (after receiving support or treatment services) were lower than baseline scores.
Table 5. Comparisons of PSI-SF Total and Subscales Scores between (1) Clinical and Community Samples, (2) Baseline and 6-month Measures in the Clinical Sample, (3) Children's age in the Clinical Sample, and (4) Economic Difficulties in the Family in the Clinical Sample

Note. PSI-SF = Parental Stress Index-Short Form Total; PD = Parental Distress subscale; PCDI = Parent-child Dysfunctional Interaction subscale; DC = Difficult Child subscale;d = Cohen's d effect size.
***p < .001.
Comparison between Clinical and Community samples
Statistically significant differences between the PSI-SF scores of both samples were found (Table 5). Mothers of the clinical sample obtained higher scores on the total PSI-SF, Parental Distress subscale, Parent-Child Dysfunctional Interaction subscale, and Difficult Child subscale scores (Wilks' lambda = .79, F(3, 306) = 26.99, p < .0001) than mothers from the community sample, suggesting that mothers with significant difficulties managing their children's behaviour felt more stress associated to their parenting role than mothers from the general population.
PSI-SF and Sociodemographic Variables
Differences in the PSI-SF scores based on sociodemographic characteristics (see Table 1) were assessed in both samples using two MANOVAs. Significant differences for child's age (Wilks' lambda = .87, F(3, 398) = 4.64, p < .0001) and economic difficulties (Wilks' lambda = .89, F(3, 164) = 6.45, p < .0001) were observed only in the clinical sample.
Differences between mothers with children of different ages were statistically significant for the total PSI-SF, Parent-Child Dysfunctional Interaction subscale, and Difficult Child subscale scores, but not for the Parental Distress subscale score (Table 5). Mothers of children between 0-3 years old reported lower scores than mothers of children between 4-6 and 7-8 years old. No differences between mothers with children 4-6 years old and mothers with children 7-8 years old were observed.
Mothers who reported economic difficulties also reported significantly higher scores on Parental Distress and Difficult Child subscales than mothers no reporting economic difficulties. No statistically significant differences were observed between both groups on Parent-Child Dysfunctional Interaction subscale and Total PSI-SF scores.
Discussion
The purpose of the present study was to analyse factor structure and psychometric properties of the Spanish version of the Parenting Stress Index-Short Form (PSI-SF) with two different samples of mothers with children under 8 years old.
The results showed that the original PSI-SF three-factor model was the most appropriate for mothers with significant difficulties managing their children's behaviour as well as for mothers from the general population. Adequate internal consistency was found for the PSI-SF total score, and for the Parental Distress (PD), Parent-Child Dysfunctional Interaction (PCDI), and Difficult Child (DC) subscales. Further, correlations between the three subscales showed significant values but lesser than .80, supporting their discriminant validity (Brown, 2015). Convergent validity with measures of depressive symptomatology, child abuse potential, and child behaviour problems also supported the PSI-SF three-factor model for both samples. In line with previous studies, the Parental Distress (PD) subscale was highly associated to mothers' depressive symptomatology, whereas the Difficult Child (DC) subscale showed a stronger association with mothers' reports of child behaviour problems (Barroso et al, 2016; Lee et al, 2016; Reitman et al, 2002).
Findings of our clinical sample were consistent with previous studies conducted with mothers of children aged between 0 to 12 years old of similar sociodemographic characteristics (low socioeconomic status), that concluded that PSI-SF three-factor model was the most adequate (Aracena et al, 2016; Lee et al, 2016; Reitman et al, 2002). Conversely, findings of our sample of mothers from the general population differed from those obtained by Díaz-Herrero et al. (2010), which supported a two-factor model. Differences between both studies can be related to sample characteristics—whereas the study by Díaz-Herrero et al. (2010) was conducted with mothers of children under 3 years old, the present study was conducted with mothers of children between 4 and 8 years old. Both used convenience samples, so additional studies with broader and representative samples are necessary for a better understanding of the psychometric characteristics of the PSI-SF Spanish version with mothers from the general population.
Taken together, our findings suggested that the Spanish version of the PSI-SF with three factors is appropriate to measure parenting stress in mothers having difficulties to manage their children's behaviour, and is also useful to detect changes following interventions designed to improve parenting skills. Also, the assessment of the three dimensions of parenting stress could be used to focus treatment strategies and for clinical decision-making.
The present study has some limitations that should be taken into account. First, small samples sizes did not allow testing invariance across samples and subgroups. Larger samples of mothers are necessary in order to confirm the influence of children's age and economic difficulties on parenting stress. Second, we only collected data from mothers, and differences in parenting stress between mothers and fathers can exist. The two studies that explored this issue yielded mixed results: whereas Deater-Deckard and Scarr (1996) did not found significant differences in PSI-SF scores, Delvecchio et al. (2015) found mothers reporting higher levels of parenting stress than fathers. These studies, however, did not test for measurement invariance (MI) across groups, a recommended analysis to test that the factor structure of an instrument is equivalent across groups and that is not conditioned by sample characteristics (for more information, see Putnick & Bornstein, 2016). Thus, further studies confirming the equivalence of PSI-SF factor structure across mothers and fathers are needed. This equivalence is required before conducting comparison analyses between groups. Only one study (Luo et al, 2019) analysed the factor structure of the PSI-SF and examined the measurement invariance (MI) across mothers and fathers in a community sample from China. They found that fathers reported significantly higher scores than mothers only in the Parent-Child Dysfunctional Interaction subscale (PCDI). However, the PSI-SF version of Luo et al. (2019) only included 15 items, so their findings cannot be generalized to the 36-item original version of the PSI-SF.
Based on our findings and the findings of previous studies with Spanish samples, it can be concluded that the Spanish version of the Parenting Stress Index-Short Form (PSI-SF) is useful to measure parenting stress with mothers with children under 8 years old. Further analyses with larger samples and including mothers and fathers are necessary to compare PSI-SF validity for the general population.