Mi SciELO
Servicios Personalizados
Revista
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Accesos
Accesos
Links relacionados
-
 Citado por Google
Citado por Google -
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO -
 Similares en Google
Similares en Google
Compartir
Medicina Oral, Patología Oral y Cirugía Bucal (Ed. impresa)
versión impresa ISSN 1698-4447
Med. oral patol. oral cir. bucal (Ed.impr.) vol.10 no.5 nov./dic. 2005
|
Bermejo-Fenoll A, Sáez-Yuguero R. Diferential diagnosis of temporomandibular joint disorders. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2005;10:468-9. |
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF TEMPOROMANDIBULAR DISORDERS (TMD)
CONCEPT
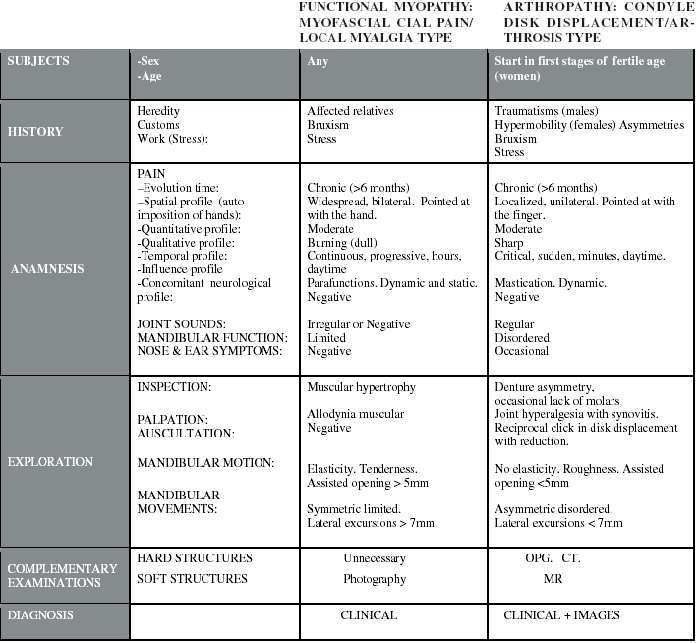
TDM comprise myopathies and arthropathies of the craniomandibular join system. They cause the largest amount of orofacial pain after the dental and periodontal pain.
The most frequent myopathies are myofascial pain (strong bodily pain with trigger points and reference areas), local myalgia (without reference areas) and myospasm. The most frequent arthropathies are disk displacement and its consequence, arthrosis.
Myopathies and arthropathies could come together. These pathologies are more frequent in women (5/1-9/1) and in their pathogenesis are implied other factors (genetic or acquired), parafunction (stress with stimulation of the dopaminergic system) and maybe occlusal disorders.
REFERENCES
-Clark GT, Seligman DA, Solberg WK, Pullinger AG. Guidelines for the examination and diagnosis of temporomandibular disorders. J Craniomand Dis 1989;3:7-14.
-McNeill C, Bell WE, Delaat A, Dworkin SF. Craniomandibular disorders: Guidelines for evaluation, diagnosis and management. In: The American Academy of raniomandibular Disorders. Chicago: Quintessence; 1990.
-Dworkin SF, LeResche L, DeRouen T, Von Korff M. Assessing clinical signs of temporomandibular disorders: reliability of clinical examiners. J Prosthet Dent 1990;63:574-9.
-De Wijer A, Lobbezoo-Scholte AM, Steenks MH, Bosman F. Reliability of clinical findings in temporomandibular disorders. J Orofac Pain 1995;9:181-91.
-Marguelles-Bonnet RE, Carpentier P, Yung JP, Defrennes D, Pharaboz C. Clinical diagnosis compared with findings of magnetic resonance imaging in 242 patients with internal derangement of the TMJ. J Orofac Pain 1995;9:244-53.
- Clark GT, Seligman DA, Solberg WK, Pullinger AG. Guidelines for the examination and diagnosis of temporomandibular disorders. J Craniomand Dis 1989;3:7- 14. [ Links ]
- McNeill C, Bell WE, Delaat A, Dworkin SF. Craniomandibular disorders: Guidelines for evaluation, diagnosis and management. In: The American Academy of raniomandibular Disorders. Chicago: Quintessence; 1990. [ Links ]
-Dworkin SF, LeResche L, DeRouen T, Von Korff M. Assessing clinical signs of temporomandibular disorders: reliability of clinical examiners. J Prosthet Dent 1990;63:574-9. [ Links ]
-De Wijer A, Lobbezoo-Scholte AM, Steenks MH, Bosman F. Reliability of clinical findings in temporomandibular disorders. J Orofac Pain 1995;9:181-91. [ Links ]
-Marguelles-Bonnet RE, Carpentier P, Yung JP, Defrennes D, Pharaboz C. Clinical diagnosis compared with findings of magnetic resonance imaging in 242 patients with internal derangement of the TMJ. J Orofac Pain 1995;9:244-53. [ Links ]











 texto en
texto en 


