1. INTRODUCTION
It has been defined as “localized skin and/or subcutaneous tissue damage, usually over bony prominences, caused by decubitus alone or in combination with shear and pressure” is the definition by the National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP) and the European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (EPUAP) in 2009 [1]. Bedsore, decubitus ulcer, decubitus, pressure sore, and pressure ulcer (PU) are the most commonly used terms among many synonyms for this disorder caused by pressure in the momenclature of tissue integrity [1, 2].
Although decubitus ulcers are mostly preventable health problem, they have many negative consequences for the patient, hospital and healthcare workers when they develop. From the patient's point of view, these disorders not only threaten the life of the patient by affecting the physical health of the patient, but also cause psychological problems such as loss of independence and social isolation. In addition, the patient who develops PU suffers from wound care, infections, debridement and grafting-related pain; increased hospitalizations time, and causes extra costs for the health system. PUs are also an important health problem that increases the workload of healthcare professionals. There are many risk factors that will lead to the development of PUs. Immobility, nutritional disorders, lack of hygiene of the patient's bed or laundry, obesity, edema, vascular pathologies, urinary or fecal incontinence, exposure to radiation, catheterization, mechanical equipment (plaster, bandage, etc.), injuries, irritations due to friction are the most common causes [3, 4].
While the recent increase in medical care has led to an increase in human lifespan, the number of nursing patients may also have increased and PUs development can be expected to increase. It is expected that the number of scientific publications on this subject, which concerns many common areas in health (surgery, internal medicine, infection diseases, nursing, dietitianity, etc.) also increase.
In this study, we aimed to analyze the developments in PUs and to add perspective to future studies by examining the research articles published on PUs, which is an increasing health problem worldwide.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bibliometric analysis method was used in this study. The data was obtained by a search conducted on the Elsevier Scopus database (https://www.scopus.com/home.uri). The Scopus database covers approximately 36,377 titles from approximately 11,678 publishers, of which 34,346 are peer-reviewed journals in different disciplines (life sciences, social sciences, physical sciences, and health sciences).
2.1. SEARCH CRITERIA
In this study data was retriewed from the beginning of records until October 12, 2021 containing the keywords “pressure ulcer” or “bedsore” or “decubitis ulcer” or “decubitus” or “pressure sore”, typed into the search box in the title section of the basic research. Only research articles included to the study as their scientific values are higher than other publications (letters, abstracts, congress papers, reviews, case presentations did not included). The articles were sorted by the authors, journals, countries, afiliations where the studies were published, publication dates, being open access status and citing numbers.
The searches were performed at the date October 12, 2021. The search was made in single day to avoid bias, since the database is still open and has daily updates. The graphics of the Scopus database were used for visualition and additionally Microsoft Office 2010 was used to create graphics. The tables were created by the researchers on the word file.
Canakkale On Sekiz March University's online library and digital resources were used to access information.
2.2. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The data in the tables were given as absolute values (percentage and frequency) by using Microsoft Excell 2010. Only absolute frequencies were used. No advanced statistical method (mean, median and fashion, dispersion measures, standard deviation or statistical tests) were used.
3. RESULTS
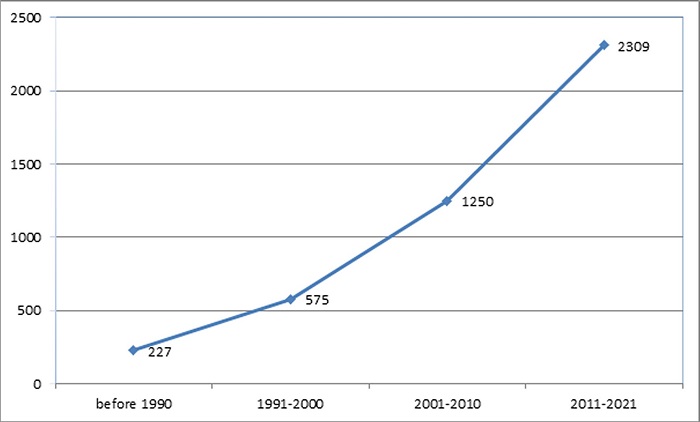
Five thousand nine hundred thirty publications included the study according to search criteria 4,361(73.54%) of them research articles. Only research articles were analyzed in terms of study criteria. The first article was published in the year 1849 [5], but after the 1990s the number of publications has increased. 52.94 % of articles were published after the year 2011 (Figure 1).
Most of the articles were written in English (n=3820, 87.6%) language. Also Spanish (n=177, 4.08%), Japanese (n=83, 1.92%), Portuguese (n=82, 1.91%), French (n=57, 1.31%), German (n=47, 1.10%), Chinese (n=45, 1.05%), Korean (n=20, 0.48%), Italian (n=18, 0.43%) and Czech (n=10, 0.25%) were top preferred languages. The majority (n=1278, 29.32%) of articles were produced by authors from the United States of America, while United Kingdom and Japan were among the top three countries. Spain, China, Brazil, Netherlands, Australia, Germany and Sweden were also in the top ten countries in PUs publications. 995 (22.81%) of the articles were published in open access (OA) journals. 3830 (87.82%) of the publications were not funded by any institution. Most of the funding sponsors were The United States Department of Health and Human Services [n=108, 2.47%], National Institutes of Health [n =103, 2.36%] and National Institute on Aging [n=49, 1.12%]. The most frequent keywords were ‘Human’ (n=3580), ‘decubitis (n=3167), ‘Pressure Ulcer’ (n=3059). Most of the articles were in the area of medicine [n=2896 (66.4%)] and nursing [n=1903 (43.63%)].
The highest number of articles on PUs were published in the journals of Ostomy Wound Management (n=177, 4.05%), Journal of Wound Care (n=156, 3.57%), International Wound Journal (n=144, 3.3%), Journal of Wound Ostomy and Continence Nursing (n=141, 3.23%) and Journal of Tissue Viability (n=126, 2.88%).
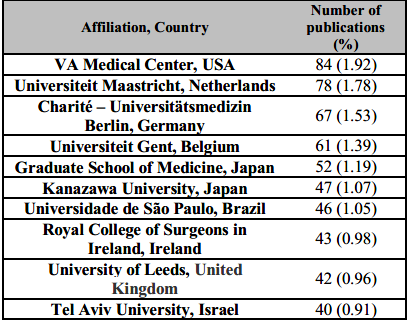
Hiromi Sanada, from The University of Tokyo (n=68), Theo W.N. Dassen from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, German (n=45) and Junko Sugama from Kanazawa University, Japan (n=41) were the most productive researches on PUs. Most of the publications were from VA Medical Center (USA) [n=84], Universiteit Maastricht (Netherlands) [n=78] and Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin (Germany) [n=67] (Table 1).
3.1. CITING ANALYSIS
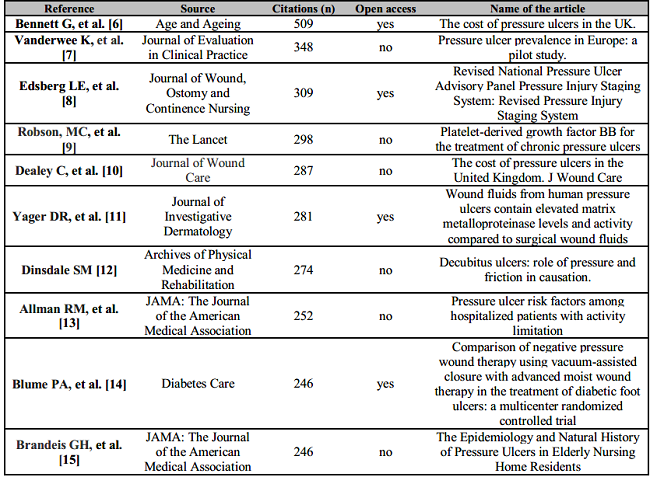
Eight hundred forty-one of the articles were not cited yet. Gerry Bennett from Queen Mary's School of Medicine and Dentistry (London, United Kingdom) was the most cited author (Table 2).
4. DISCUSSION
The effectiveness of scientific publications can be determined by bibliometric studies. With these studies, the most productive authors, countries or afiliations on certain topics can be identified. Bibliometric analysis can be used in many areas such as medicine [16, 17]. Many studies using bibliometric analysis methods can be found in the literature [16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31]. Although PU is among the popular topics in medicine due to the increasing number of patients, recent studies using bibliometric analysis arent identified in the literature. There are only three bibliometric studies, which were published more than 10 years ago [29, 30, 31]. As the publication rates are rapidly changing the information of this studies were out of date. The aim of our study was to assess the current publication trends on PUs literature with bibliometric analysis method.
In bibliometric studies, theses or any type of documents can be examined. In our study, we evaluated research articles as they have higher scientific features.
While the Web of Science (WoS) database was the only database for bibliometric studies until the year 2004, the number of bibliometric databases increased with the establishment of the Scopus and Google Scholar in the year 2004 [32]. The Scopus database, which has the largest content for bibliometric analyses, was preferred in our study. In addition, a commonly preferred bibliometric database is the WOS database as it allows free output for visualization or mapping by using other visualization programmes. We did not use visualization and mapping techniques in this study.
Because of our study, the majority (29.32%) of articles were from the USA, United Kingdom and Japan. Spain, China, Brazil, Netherlands, Australia, Germany and Sweden were also the top ten publishing countries. No publications originating from Turkey were found in the Scopus database. As in many bibliometric analysis studies examining scientific studies, the USA was found to be the most scientifically productive country in our study [19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 30]. The reason for this can be attributed to the USA origin of the institutions that finance scientific researches in the first 3 ranks, or the fact that there is a large number of institutions as a result of the wide geographical distribution in the USA.
Halfens et al. [29] were used bibliometric study on some topic in the year 2001. This study was conducted on Medline database. In this study, the United States and European countries were found to be the most productive countries. Our results / findings are similar, but in our current suty, in which the last 20 years are added to the precious study [29], the number of publications from Japan, Israel and Brazil has increased to the top 10 ranking. This proves that the issue of PUs is a global health problem. Halfens et al. [29] compared the research subjects examined in the USA and European countries in their study. It has been determined that publications in the USA paid more attention to the treatment of PUs, dressings, the etiology of PUs and basic research, while European researchers paid more attention to the prevention of PUs. In our study, this comparison was not made. In the recent study [29], research articles were also found in only 49% of all publications. In our study, 73.54% of the publications on PUs were research articles. This can prove that the quality of studies on this subject has increased in the last 20 years.
Chen et al. [30] were found that most of the publications were in surgery and nursing areas and from the USA. Our study results were similar. Compared with this study [30], we found that the number of publications increased even more after 2011, 52.94% of the articles are dated after 2011.
The number of publications on PUs are increasing, but especially studies from development countries. Studies outside of European and the USA should also be supported and the number of publications should be increased, especially from other developed countries.