Introduction
Epidemiologic data show that sleep duration impacts human physical health.1 Both short and long durations of sleep were reported to be predictors, or markers, of cardiovascular outcomes.2 Short and long sleep durations were associated with poor self-rated health, and the association persisted in subgroup analysis of gender.3 In a large representative sample of the general adult population, compared with a sleep duration of 7 hours, it was found a positive association between short and long sleep durations and poor self-rated health in Korean adults.3 The relationship between quantity of sleep and incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus was evaluated in a previous study, and it was shown that higher relative risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus was noted both for short duration of sleep (≤5-6hours/night) and long duration of sleep (>8-9hours/night).4 Another meta-analysis of prospective studies showed that both short and long durations of sleep are significant predictors of death in prospective population studies.5 Sleep disturbances, including insomnia, independently contribute to the risk of inflammatory disorders and major depressive disorder.6 Sleep loss induces a functional alteration of the monocyte proinflammatory cytokine response, resulting in alteration of immune cell physiologic characteristics.7 8 Chronic sleep deprivation markedly affects bone health by decreasing bone mineral density and 25-hydroxyvitamin D, deteriorating the bone microarchitecture and decreasing bone formation and bone resorption markers.9 Moreover, it was shown that gender differences in sleep become apparent after the onset of puberty.10
Previous reports showed that non-apnea sleep disorder increased the risk of periodontal disease.11 Sleep disordered breathing is defined as the number of apnea plus hypopnea events associated with ≥3% desaturation of oxygen per hour of estimated sleep and was shown to be associated with periodontitis, which was most pronounced in young adults.12 Similarly, higher Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index scores, representing worse sleep quality, were associated with severity of periodontal disease.1 Previous reports also evaluated the relationship of routine inadequate sleep duration and periodontitis in a nationally representative sample.13 However, limited information is available regarding the relationship between long sleep duration and periodontal disease. It was hypothesized that there is no significant association between long sleep duration and periodontitis. Thus, this study was performed to assess the association between long sleep duration and periodontitis among men and women using nationally representative data.
Methods
Survey and subjects
This study used data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), which was conducted between 2012 and 2014. The data were obtained by the Division of Chronic Disease Surveillance under the Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare.14 15 The sampling units of KNHANES were based on the population and housing consensus from the National Census Registry in the Republic of Korea. Sample weights with complex survey design and poststratification were applied in KNHANES.
Initially, a total of 23,626 individuals were candidates in the KNHANES survey. The analysis in this study was confined to a total of 18,382 respondents over 19 years of age. Finally, 14,675 individuals -without missing values for the outcome variables- were analyzed for the analysis. Informed consent was obtained from all participants of KNHANES, and this survey was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Sociodemographic and health behaviors variables
All participants were asked about sociodemographic and health behaviors variables by trained interviewers. Smoking status was categorized into two groups: current smoker or non-current smoker. Participants were also categorized into two groups according to alcohol consumption within one month from the interview: current drinker or noncurrent drinker.16 Individuals were regarded as a regular exerciser if they performed walking at least five times per week for over 30minutes per session. Sleep duration was self-reported. In this study, “short sleep” was considered 5hours or less, and “long sleep” was defined as 9hours; the reference category was 6 to 8hours.17
Anthropometric and biochemical measurements
Trained staff members performed the anthropometric measurements. Body weight was measured to the nearest 0.1kg, and height was measured to nearest 1mm. Body mass index (kg/m2) was defined as body weight (kg) divided by the square of the height (m2). Waist circumference was measured at the narrowest point between the lowest rib and the iliac crest. Cut-offs for defining general and abdominal obesity were applied to be suitable for the Asian population: a body mass index ≥25kg/m2 was defined as general obesity,18 and abdominal obesity was defined as a waist circumference ≥90cm in men or ≥80cm in women.19
Systolic and diastolic blood pressure was measured twice using a standard mercury sphygmomanometer (Baumanometer; W.A. Baum Co., Inc., Copiague, NY, USA) at intervals of 5minutes, and the average was used for the analysis.
A blood sample was obtained from the antecubital vein of each participant after fasting for more than 8hours to measure white blood cell count and the total concentration of cholesterol, triglycerides, serum fasting plasma glucose, and high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol with Automatic Analyzer 7600 (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) using the kits (Daiichi, Tokyo, Japan).20
If three or more of the following criteria were fulfilled, the participants were considered to have metabolic syndrome21 waist circumference of 90cm or greater in men and 80cm or greater in women, fasting triglycerides 150mg/dL or greater or use of lipid-lowering medication, high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol lower than 40mg/dL in men and lower than 50mg/dL in women or use of medication, blood pressure of 130/85mm Hg or greater or use of antihypertensive medication in a patient with a history of hypertension, and fasting blood glucose of 100mg/dL or greater or current use of antidiabetic medication. Participants were considered to have diabetes when fasting plasma sugar was 126mg/dL or greater and/or hemoglobin A1c was 6.5% or greater or when they were currently using antidiabetic medications or had physician-diagnosed diabetes.22 Hypertension was defined as a systolic blood pressure of 140mmHg or greater, a diastolic blood pressure of 90mmHg or greater, or the current use of antihypertensive medication.23
Oral health behaviors, periodontitis, and number of natural teeth
The time of day when participants brushed their teeth and used secondary oral products was recorded as oral health behaviors.24 We calculated the frequency of daily tooth brushing by the total number of times the teeth were brushed per day. Secondary oral products included the following: dental floss, mouthwash, interdental brushes, electric toothbrushes, irrigation devices, tongue cleaners, end-tufted brushes, and any special device for dentures. Self-reported oral state was categorized into favorable, average, and problematic.
The presence of periodontal disease was evaluated using the World Health Organization community periodontal index (CPI). Periodontitis was defined if the CPI score was ≥3. When more than one site had a >3.5mm pocket in the index teeth, which are 11, 16, 17, 26, 27, 31, 36, 37, 46, and 47, according to the Federation Dentaire Internationale system, it indicated a CPI score of code 3.25 The mouth was divided into sextants and a CPI probe (PWHO, Osung MND, Seoul, Korea) with a 0.5mm ball tip was used. An average probing force was approximately 20g.25
Trained and calibrated dentists examined the periodontal status of the participants. Training was provided to minimize the errors in the measurement of periodontal pocket depth by each examiner during the examination, as a part of quality control. In 2012 KNHANES, 29 and 27 dentists performed the evaluation in the first and second half, respectively. Twenty-nine dentist and 27 dentists performed the evaluation in the first and second half of 2013, respectively. In 2014 KNHANES, 26 dentists examined the periodontal status.
Statistical analyses
We used the appropriate survey procedures to take into account the complex sampling design used in KNHANES. All data are presented as mean±standard error or percentage (standard error). We performed logarithmic transformation to achieve normal distribution when necessary. We performed a Rao-Scott chi-square test for categorical variables or an independent t-test for continuous variables to assess the differences in characteristics according to the presence of periodontitis. Interactions between sex and sleep and interactions between menopause and sleep were evaluated and the p-interaction values were calculated. In addition, subgroup analyses were performed. We used multivariable logistic regression analyses to evaluate the risk of periodontitis in relation to sleep duration and calculated odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (95%CI) after adjusting for potential confounders. Model 1 was unadjusted, and model 2 was adjusted for age. In model 3, adjustments were made for the variables in model 2, plus smoking, drinking, exercise, frequency of tooth brushing, and self-reported oral status. In model 4, adjustments were made for the variables in model 3, plus white blood cell count. model 5 was adjusted for the variables in model 4, plus income and education.
Results
Table 1 describes the sex-specific baseline characteristics of the study population by presence of periodontitis. Significant differences were noted between men and women in the mean age, body mass index, waist circumference, sleep duration, smoking, drinking, and exercise. The number of individuals who brushed their teeth three times or more per day, used floss, and used interdental brushes was higher in women (p <0.05). The interactions between sex and sleep, and the interactions between menopause and sleep were evaluated, and the p-interaction values were 0.02 and 0.14, respectively.
Table 1 The baseline characteristics of the study individuals according to diagnosis of periodontitis, categorized by men and women.
| Men | Women | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Periodontitis | ||||||
| No | Yes | p | No | Yes | pa | |
| Unweighted (n) | 3,914 | 2,203 | 6,532 | 2,026 | ||
| Age (years) | 40.2±0.3 | 52.8±0.4 | <0.001 | 43.4±0.3 | 56.3±0.4 | <0.001 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 24.2±0.1 | 24.3±0.1 | 0.14 | 22.9±0.1 | 24.4±0.1 | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 83.4±0.2 | 85.3±0.2 | <0.001 | 76.4±0.2 | 81.2±0.3 | <0.001 |
| Number of natural teeth | 26.1±0.1 | 24.1±0.1 | <0.001 | 25.6±0.1 | 23.6±0.2 | <0.001 |
| White blood cell count (×103/μL) b | 6.19 (6.13-6.25) | 6.52 (6.43-6.61) | <0.001 | 5.56 (5.51-5.61) | 5.73 (5.64-5.82) | <0.001 |
| Sleep duration (hours) | 6.81±0.03 | 6.77±0.03 | 0.38 | 6.81±0.02 | 6.68±0.04 | 0.002 |
| Smoking (current) | 35.3 (0.9) | 44.5 (1.3) | <0.001 | 4.5 (0.4) | 5.6 (0.6) | 0.12 |
| Smoking (no) | 64.7 (0.9) | 55.5 (1.3) | 95.5 (0.4) | 94.4 (0.6) | ||
| Drinking (current) | 75.2 (0.8) | 72.9 (1.1) | 0.10 | 44.9 (0.8) | 32.5 (1.3) | <0.001 |
| Walking (yes) | 44.4 (1.1) | 37.2 (1.2) | <0.001 | 37.1 (0.8) | 34.4 (1.3) | 0.07 |
| Frequency of tooth brushing per day | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| ≤1 | 10.8 (0.5) | 17.5 (0.9) | 5.8 (0.3) | 11.7 (0.8) | ||
| 2 | 38.2 (1) | 42.6 (1.3) | 34.4 (0.7) | 44.1 (1.4) | ||
| ≥3 | 51.1 (1) | 40.0 (1.3) | 59.9 (0.8) | 44.2 (1.3) | ||
| Self-reported oral status | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| Favorable | 17.2 (0.8) | 10.4 (0.7) | 13.8 (0.5) | 10.5 (0.8) | ||
| Average | 42.8 (1) | 30.7 (1.1) | 47 (0.8) | 35.1 (1.4) | ||
| Problematic | 40 (1) | 58.9 (1.2) | 39.2 (0.8) | 54.4 (1.4) | ||
| Floss (yes) | 18.4 (0.8) | 10.6 (0.8) | <0.001 | 28.8 (0.7) | 14.6 (1) | <0.001 |
| Interdental brush (yes) | 17 (0.8) | 18.7 (1.1) | 0.17 | 21.4 (0.6) | 17.9 (1.1) | 0.006 |
| Mouth rinse (yes) | 18.9 (0.8) | 17.2 (1) | 0.21 | 22.6 (0.6) | 20.4 (1.1) | 0.07 |
| Electric toothbrush | 6.8 (0.5) | 5.6 (0.6) | 0.14 | 5.9 (0.3) | 3.6 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| Other oral products | 4.4 (0.4) | 3.7 (0.5) | 0.27 | 5.9 (0.3) | 4.7 (0.5) | 0.08 |
| Body mass index ≥25 (kg/m2) | 36.4 (0.9) | 39.7 (1.1) | 0.02 | 24.1 (0.7) | 38.5 (1.4) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus (yes) | 6.4 (0.4) | 16.8 (1) | <0.001 | 5.2 (0.3) | 16 (1.1) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension (yes) | 21.9 (0.8) | 38.1 (1.3) | <0.001 | 17.3 (0.6) | 38.8 (1.4) | <0.001 |
Data are presented as means±standard error or percentages (standard error).a p-values were obtained by independent t-test for continuous variables or chi-square test for categorical variables.b Log transformation was applied to the value, and the geometric mean (95% confidence interval) is shown.
Figure 1A displays the prevalence of periodontitis in men according to the sleep duration after adjusting for potential confounders (p >0.05). The prevalence of periodontitis in women, according to sleep duration, is shown in Figure 1B. Increase in the prevalence of periodontitis was noted with longer sleep duration after adjusting the covariates (p <0.05).
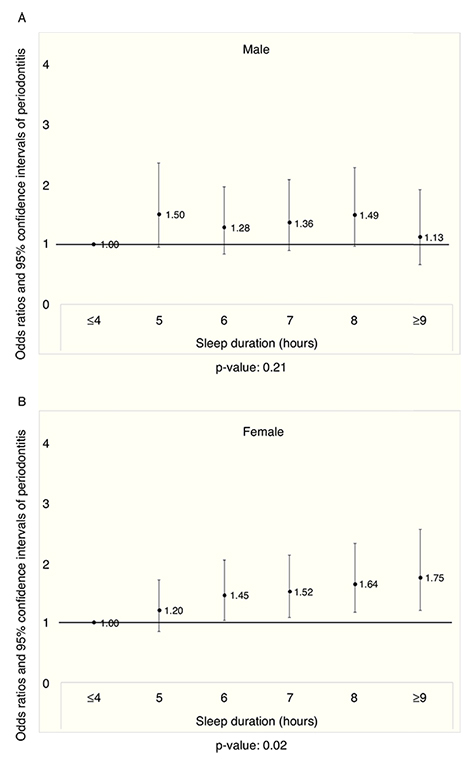
Figure 1 A) The prevalence odds ratio of periodontitis in men according to sleep duration after adjusting for the covariates (p=0.21). B) The prevalence odds ratio of periodontitis in women according to sleep duration after adjusting for the covariates (p=0.02).
Table 2 shows the subgroup analysis regarding the sleep duration, categorized by sex, using health behaviors variables and oral health behaviors. Women with long sleep durations of 9hours or more showed a higher prevalence of smoking and drinking. These trends were not seen in men with long sleep durations. Women with long sleep durations showed lower prevalence of tooth brushing three times a day or more, lower use of floss, and lower use of interdental brushes (p <0.05). However, statistically significant differences were not seen in men.
Table 2 The subgroup analysis regarding sleep duration, using health behaviors variables and oral health behaviors, categorized by men and women.
| Variables | Sleep duration (hours) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤5 | 6 to 8 | ≥9 | pa | ≤5 | 6 to 8 | ≥9 | pa | |
| Men | Women | |||||||
| Unweighted n | 798 | 4,948 | 371 | 1,559 | 6,351 | 648 | ||
| Smoking (current) | 40.2 (2.2) | 37.9 (0.9) | 37.8 (3.4) | 0.64 | 6.7 (0.8) | 4.0 (0.3) | 7.8 (1.5) | <0.001 |
| Smoking (no) | 59.8 (2.2) | 62.1 (0.9) | 62.2 (3.4) | 92.3 (0.8) | 96.0 (0.3) | 92.2 (1.5) | ||
| Drinking (current) | 74.2 (1.8) | 75.0 (0.7) | 68.2 (3.1) | 0.06 | 35.7 (1.5) | 43.5 (0.8) | 43.9 (2.4) | <0.001 |
| Walking (yes) | 45.9 (2.2) | 41.8 (0.9) | 39.1 (3.1) | 0.12 | 36.2 (1.6) | 37.4 (0.8) | 29.1 (2.2) | 0.001 |
| Frequency of tooth brushing per day | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| ≤1 | 17.0 (1.6) | 11.8 (0.5) | 20.3 (2.6) | 9.3 (0.9) | 6.2 (0.4) | 10.3 (1.3) | ||
| 2 | 37.2 (2.1) | 40.1 (0.9) | 36.9 (3.2) | 40.2 (1.5) | 35.1 (0.7) | 41.1 (2.3) | ||
| ≥3 | 45.8 (2.1) | 48.1 (0.9) | 42.8 (3.7) | 50.6 (1.6) | 58.8 (0.8) | 48.6 (2.3) | ||
| Self-reported oral status | 0.02 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Favorable | 14.4 (1.7) | 15.3 (0.7) | 12.0 (1.7) | 10.2 (0.9) | 13.8 (0.5) | 13.4 (1.3) | ||
| Average | 35.7 (2.0) | 39.7 (0.9) | 34.8 (2.5) | 39.3 (1.5) | 45.8 (0.8) | 40.7 (2.1) | ||
| Problematic | 49.9 (2.3) | 45 (0.9) | 53.1 (2.6) | 50.5 (1.5) | 40.4 (0.8) | 45.9 (2.0) | ||
| Secondary oral products | ||||||||
| Floss (yes) | 15.3 (1.5) | 16 (0.6) | 14.3 (2.3) | 0.71 | 20.9 (1.3) | 27.4 (0.7) | 19.7 (1.8) | <0.001 |
| Interdental brush (yes) | 16.5 (1.6) | 17.9 (0.7) | 13.5 (2.6) | 0.23 | 20.1 (1.3) | 21.1 (0.6) | 16.3 (1.7) | 0.04 |
| Mouth rinse (yes) | 19.1 (1.9) | 18.5 (0.7) | 13.3 (2.1) | 0.12 | 20.0 (1.2) | 22.6 (0.6) | 20 (1.8) | 0.09 |
| Electric toothbrush | 6.3 (1.0) | 6.6 (0.4) | 3.8 (1.2) | 0.18 | 5.7 (0.7) | 5.5 (0.3) | 3.4 (0.8) | 0.09 |
| Other oral products | 5 (0.9) | 4.1 (0.3) | 3.9 (1.2) | 0.64 | 5.1 (0.6) | 5.9 (0.3) | 4.2 (0.9) | 0.17 |
| Body mass index ≥25 | 40.2 (2.1) | 37.4 (0.8) | 34.7 (2.5) | 0.23 | 34.2 (1.4) | 25.7 (0.8) | 28.0 (1.7) | <0.001 |
Data are presented as percentages (standard error).a p-values were obtained via Rao-Scott chi-square test for categorical variables.
Table 3 shows the adjusted OR and their 95%CI from multivariable logistic regression analyses for individuals with periodontitis, according to sleep duration. Adjusted OR and their 95%CI of men with periodontitis were 1, 0.99 (0.78-1.25), and 0.83 (0.57-1.22) after adjustment for age, smoking, drinking, exercise, frequency of tooth brushing, self-reported oral status, body mass index, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and white blood cell count for sleep durations of 5hours or less, 6 to 8hours, and 9hours or more, respectively (p >0.05). Adjusted OR and their 95%CI of women with periodontitis were 1, 1.29 (1.06-1.56), and 1.45 (1.07-1.96) after adjustment for sleep durations of 5hours or less, 6 to 8hours, and 9hours or more, respectively (p <0.05).
Table 3 The adjusted odds ratios and their 95% confidence intervals from multivariable logistic regression analyses for individuals with periodontitis, according to sleep duration.
| Men | Women | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sleep duration (hours) | ≤5 | 6 to 8 | ≥9 | P trend | ≤5 | 6 to 8 | ≥9 | p trend |
| Model 1 | 1 | 0.78 (0.65-0.94) | 0.80 (0.57-1.11) | 0.03 | 1 | 0.72 (0.62-0.83) | 0.77 (0.61-0.99) | <0.001 |
| Model 2 | 1 | 0.93 (0.75-1.15) | 0.94 (0.68-1.30) | 0.79 | 1 | 1.15 (0.97-1.36) | 1.33 (1.05-1.68) | 0.05 |
| Model 3 | 1 | 0.97 (0.77-1.21) | 0.75 (0.51-1.09) | 0.27 | 1 | 1.25 (1.05-1.49) | 1.45 (1.10-1.92) | 0.01 |
| Model 4 | 1 | 1.00 (0.79-1.28) | 0.82 (0.56-1.21) | 0.52 | 1 | 1.27 (1.05-1.54) | 1.44 (1.07-1.95) | 0.006 |
| Model 5 | 1 | 0.99 (0.78-1.25) | 0.83 (0.57-1.22) | 0.50 | 1 | 1.29 (1.06-1.56) | 1.45 (1.07-1.96) | 0.005 |
Model 1: no adjustment.Model 2: age adjusted.Model 3: model 2+smoking, drinking, exercise, frequency of tooth brushing, and self-reported oral status adjusted. Model 4: model 3+white blood cell count adjusted. Model 5: model 4+income and education adjusted.
Figure 2A Displays the prevalence of periodontitis according to sleep duration, categorized by general obesity, after adjusting the covariates. Statistically significant association was only noted in women (p <0.05).Figure 2B displays the prevalence of periodontitis according to sleep duration, categorized by abdominal obesity. Statistically significant association was only noted in women (p <0.05).

Figure 2 A) The prevalence odds ratio of periodontitis according to sleep duration, categorized by general obesity, after adjusting for the covariates. B) The prevalence odds ratio of periodontitis according to sleep duration, categorized by abdominal obesity, after adjusting for the covariates.
Table 4 shows the adjusted OR and their 95%CI from multivariate logistic regression analyses for individuals with periodontitis, according to sleep duration, categorized by premenopause and postmenopause. Adjusted OR and their 95%CI of periodontitis in premenopause women were 1, 1.25 (1.04-1.51), and 1.58 (1.13-2.21) after adjustment for sleep durations of 5hours or less, 6 to 8hours, and 9hours or more, respectively (p <0.05). Adjusted OR and their 95%CI of periodontitis in postmenopause women were 1, 1.17 (0.79-1.73), and 1.52 (0.86-2.68) after adjustment for sleep durations of 5hours or less, 6 to 8hours, and 9hours or more, respectively (p >0.05).
Table 4 The adjusted odds ratios and their 95% confidence intervals from multivariable logistic regression analyses for individuals with periodontitis, according to sleep duration, categorized by menopausal status.
| Premenopause | Postmenopause | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sleep duration (hours) | ≤5 | 6 to 8 | ≥9 | P trend | ≤5 | 6 to 8 | ≥9 | P trend |
| Model 1 | 1 | 1.02 (0.86-1.21) | 1.49 (1.09-2.03) | 0.03 | 1 | 0.87 (0.63-1.19) | 0.80 (0.52-1.24) | 0.58 |
| Model 2 | 1 | 1.14 (0.96-1.35) | 1.54 (1.13-2.10) | 0.02 | 1 | 1.00 (0.70-1.41) | 1.38 (0.85-2.24) | 0.21 |
| Model 3 | 1 | 1.20 (1.01-1.42) | 1.57 (1.13-2.17) | 0.01 | 1 | 1.15 (0.79-1.68) | 1.62 (0.96-2.71) | 0.14 |
| Model 4 | 1 | 1.21 (1.00-1.46) | 1.56 (1.11-2.20) | 0.004 | 1 | 1.16 (0.79-1.71) | 1.53 (0.87-2.68) | 0.17 |
| Model 5 | 1 | 1.25 (1.04-1.51) | 1.58 (1.13-2.21) | 0.002 | 1 | 1.17 (0.79-1.73) | 1.52 (0.86-2.68) | 0.18 |
Model 1: no adjustment.Model 2: age adjusted.Model 3: model 2+smoking, drinking, exercise, frequency of tooth brushing, and self-reported oral status adjusted.Model 4: model 3+white blood cell count adjusted.Model 5: model 4+income and education adjusted.
Discussion
This study aimed to identify associations between periodontitis and long sleep duration among men and women. The results showed that an increased risk of periodontitis was statistically significantly associated with longer sleep duration in women, especially in premenopause women.
The following issues should be considered when interpreting the results. Because of this study's cross-sectional design, the causal direction of the associations between sleep duration and periodontitis cannot be ascertained.26 It is therefore possible that long duration of sleep might be a consequence of, rather than a causative risk factor for, periodontal disease.27 Another limitation of this study is that individuals’ sleep habits were obtained via recall and that they may not have recalled their habits correctly.28 Also, long sleep duration may be part of an unhealthy health behaviors, which in turn may impair oral health.27 This study used partial mouth recording protocols of CPI because it was not feasible to conduct the traditional full-mouth examination in nationally performed health survey due to limited resources including manpower, funds, number of examiners and time.29 However, the limitations of CPI are its inability to provide an adequate assessment of prevalence of periodontal disease and partial mouth recording protocols may underestimate the prevalence of periodontitis with the amount of underestimation varies depending on the number and type of sites examined.30 31 32 Additionally, sleep duration is reported to be associated with depressive symptoms and the use of antidepressants,33 but the information was not available for this study. However, the data used in this study were a nationally representative sample based on the National Census Registry, and a multistage clustered probability design was applied for the recruitment of the participants.34 Selection bias was overcome by applying survey sample weights adjusted for participation rate and response rate.35 The association between the sleep duration and periodontitis was evaluated using multiple logistic regression analyses after adjusting for confounding factors.26 Collectively, this study can be considered representative and reliable.
The definitions of short and long sleep duration vary among different studies. In this study, short sleep was considered 5hours or less, long sleep was defined as 9hours, and the reference category was 6 to 8hours. Other studies have defined short sleep as ≤4hours,36 ≤5hours,17 ≤6hours,37 and <7hours,38 and long sleep as >8hours,37 ≥9hours,17 10hours,38 and 12hours,39 while the reference category has been defined as 7hours,37 7 to 8hours,40 7 to 9hours,41 6 to 8hours,42 and 9hours.39
Several researches have been performed to evaluate the association between sleep duration and health outcomes.13 27 36 Previous observational epidemiologic studies suggest that both short and long durations of sleep may be associated with an increased risk of adverse health outcomes, including total mortality, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, obesity, respiratory disorders, and poor general health.27 36 However, other population-based data suggest that only short sleep duration was associated with adverse health issues.43 In a previous study using a nationally representative sample, no statistically significant relationship between inadequate sleep duration and periodontitis was found.13 The different results may be due to the design of the studies and characteristics of the study population, including culture.27
The association between long sleep duration and periodontitis may be explained by the following. Sleep habits in the general population are reported to be the result of a complex interaction between different kinds of factors, including social, behavioral, psychological, and comorbid conditions.27 One study found significant consistent associations of long sleep duration with age and poorer physical health status.27 Low socioeconomic status, unemployment, poor general health, undiagnosed health condition, and depression may also be associated with long sleep duration.4 44 Moreover, this study clearly showed that health behaviors variables and oral health behaviors were associated with long sleep duration, and this may have produced a higher prevalence of periodontitis in individuals with longer sleep duration. However, there is possibility that both, sleeping time and periodontitis, are cross-sectionally associated because both are consequences of the same group of risk factors (life style and health behavior).
Previous reports have shown sex differences in the risk associated with duration of sleep. This study clearly showed association only in women. Biological conditions unique to women, including menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and menopause, may alter sleep pattern.10 45 Similarly, modest associations between sleep and incident myocardial infarction were seen in middle-aged women but not men from the general population.46 The association between sleep duration and the prevalence of hypertension was only noted in women and not in men.47 The effect was stronger among premenopausal women than among postmenopausal women.48 However, another report showed that long sleep duration was associated with age, especially among men.27 Female hormones, including estrogen and progesterone, are suggested to be related to sleep patterns.49 50 It should also be considered that there may be sex differences in stress and reaction and there may be differences in genetics that may affect sleep.46
Conclusion
Conclusively, the association between long sleep duration and periodontitis was proven by multiple logistic regression analyses after adjusting for confounding factors among Korean women, especially in premenopausal women. Long sleep duration may be considered an independent risk indicator of periodontal disease among Korean women.
What is known about the topic?
Epidemiologic data show that sleep duration impacts human physical health
What does this study add to the literature?
There is now epidemiological evidence that supports a possible association between long sleep duration and periodontal disease among Korean female adults. Long sleep duration may be associated with periodontitis, after adjusting for potential confounding factors, among Korean female adults, especially in premenopausal women. Long sleep duration may be considered an independent risk indicator of periodontal disease, especially for women.














