Meu SciELO
Serviços Personalizados
Journal
Artigo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Acessos
Acessos
Links relacionados
-
 Citado por Google
Citado por Google -
 Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO -
 Similares em Google
Similares em Google
Compartilhar
Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas
versão impressa ISSN 1130-0108
Rev. esp. enferm. dig. vol.103 no.4 Madrid Abr. 2011
https://dx.doi.org/10.4321/S1130-01082011000400007
PICTURES IN DIGESTIVE PATHOLOGY
Kaposi's sarcoma of the rectum
Sarcoma de Kaposi del recto
Sheila Ferreira1, Bruno Arroja2, Manuela Canhoto2, Cristina Amado3 and Claudia Gonçalves2
Departments of 1Internal Medicine, 2Digestive Diseases, and 3Pathology. Hospital de Santo André, EPE. Leiria, Portugal
Case report
A 40-year old male patient, professor, without previous relevant medical history searched medical assistance for rectal bleeding for the previous two weeks associated with proctalgia. He denied perianal pruritus or secretions or other major complaints.
At physical examination he presented with an excellent general state, without skin lesions or palpable adenopathies. Rectal digital examination detected an irregular and painful rectal mass with rough consistence. Laboratory data: leucocytes 5.800 µL (58.2% neutrophils; 32.3% lymphocytes), haemoglobin 13.7 g/dL, platelets 247.000/ µL, creatinine 1.01 mg/dL, blood-urea nitrogen 20 mg/dL, C-reactive protein 44.8 mg/dL.
A colonoscopy was performed, revealing a polypoid vinous lesion occupying approximately 2/3 of the luminal circumference (Figs. 1 and 2). A macrobiopsy with a polipectomy snare was obtained. Histological analysis revealed multiple small blood vessels delimited by spindle cells displayed in a swirl pattern with areas of bleeding and hemosiderin deposits.
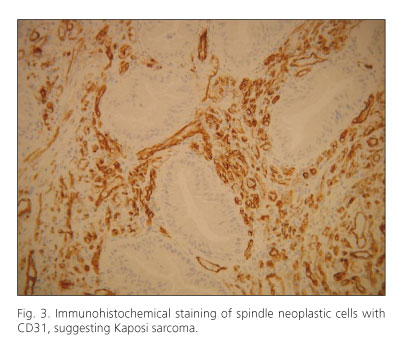
Immunohistochemical staining was positive for vimentin, CD 31 and CD 34 (Fig. 3). These findings were highly suggestive of Kaposi's sarcoma afflicting the rectum. HIV serologies were positive.
The subsequent investigation for other Kaposi's lesions was negative.
Discussion
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) is a vascular malignant neoplasm commonly found in immunocompromised patients, which carries high mortality and morbidity (1,2). It most frequently affects the skin with a slow progression although it has a visceral associated involvement as well. When the intestine is affected this usually precedes skin lesions. Histological typical findings are seen in the submucosa and deeper layers (3,4).
Solitary KS has been described in the appendix, mesentery and rectum as in our case (5).
Since the introduction of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), immunological reconstitution and viral load reduction has been possible thus enabling reduction and even total remission of KS (5).
In our case we emphasize the fact that the patient presented with an advanced AIDS despite the lack of significant clinical and analytical changes.
References
1. Zoufaly A, Schmiedel S, Lohse AW, Van Lunzen J. Intestinal Kaposi's sarcoma may mimic gastrointestinal stromal tumor in HIV infection. World Gastroenterology 2007;13(33):4514-6. [ Links ]
2. Svrcek M, Tiret E, Bennis M, Guyot P, Fléjou JF. KSHV/HHV8-Associated Kaposi's sarcoma in patient with ulcerative colitis receiving immunosuppressive drugs: report of a case. Dis of the Colon & Rectum 2009;52(1):154-8. [ Links ]
3. Salako AA, Adisa AO, Ojo OS, Arigbabu AO. Severe gastrointestinal haemorrhage due to primary intestinal Kaposi's sarcoma - a case report. Niger Postgrad Med J 2007;14(4):352-4. [ Links ]
4. Pantanowitz L, Mullen J, Dezabe BJ. Primary Kaposi sarcoma of the subcutaneous tissue. World J Surg Oncol 2008;2(6):94. [ Links ]
5. Pantanowitz L, Dezube BJ. Kaposi sarcoma in unusual anatomical locations. BMC Cancer 2008;8:190. [ Links ]











 texto em
texto em