My SciELO
Services on Demand
Journal
Article
Indicators
-
 Cited by SciELO
Cited by SciELO -
 Access statistics
Access statistics
Related links
-
 Cited by Google
Cited by Google -
 Similars in
SciELO
Similars in
SciELO -
 Similars in Google
Similars in Google
Share
Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas
Print version ISSN 1130-0108
Rev. esp. enferm. dig. vol.109 n.8 Madrid Aug. 2017
https://dx.doi.org/10.17235/reed.2017.4396/2016
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Colonic obstruction secondary to Actinomyces
Obstrucción colónica secundaria a Actinomyces
Key words: Actinomyces. Colonic obstruction. IUD.
Palabras clave: Actinomyces. Obstrucción colon. DIU.
Dear Editor,
Actinomycosis is an uncommon granulomatous infection by Gram-positive anaerobic bacteria of the genus Actinomyces. A. israelii is a major human pathogen (1).
The most frequent locations for colonization are cervicofacial (50%), abdominal (20%) and thoracic (15-20%). The abdominal actinomycosis predisposing factors include recent surgery, trauma and neoplasias. Certain cases have been associated with the intrauterine contraception device (IUD) (2,3).
Case report
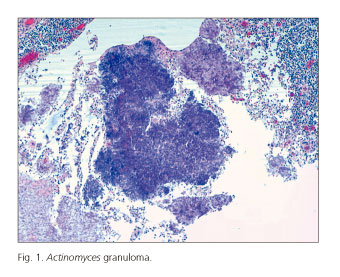
A 42-year old woman with an IUD was admitted due to colic pain, diarrhea without pathological products and abdominal distension of two months duration. The physical examination showed a slightly distended and tympanized abdomen. The blood analysis was unremarkable and co-cultures were negative. On colonoscopy, an extrinsic compression at 20 cm from the anal margin prevented progression. Afterwards, the patient presented abdominal pain with peritonism and was diagnosed with a pelvic tumor of 3 x 2.3 cm by computed tomography (CT) scan, suggestive of a teratoma dependent on the left ovary and perforation in the cecum. The patient underwent surgery and a stony tumor mass that infiltrated the retroperitoneum, uterus and both ovaries was resected. Ileocecal resection with ileocolic anastomosis and provisional colostomy was performed as well as removal of the IUD. A pathological anatomy study found Actinomyces on the IUD and in the resected tumor; there was no histological malignancy. After completing antibiotic treatment the patient remains asymptomatic.
Discussion
This is a very rare case of colonic subocclusion due to a pelvic mass, secondary to infection by Actinomyces caused by the IUD, with late diastaic perforation of the cecum.
Abdominal infection with Actinomyces is infrequent and has been previously associated with the use of an IUD. These cases may mimic neoplasia (3-5). The diagnosis is anatomopathological. Effective treatment consists of penicillin G 10-20 MU/24h in 4-6 daily doses for 4-6 weeks, followed by oral amoxicillin 2-4 g/24h for 6-12 months (2,5).
Manuel Alfonso Jiménez-Moreno1, Isabel Sánchez-Pedrique2 and Estíbaliz Obregón-Martínez3
Departments of de 1Digestive Diseases, 2General Surgery and 3Pathology.
Hospital Universitario de Burgos. Burgos, Spain
References
1. Wong VK, Turmezei TD, Weston VC, et al. Actinomycosis BMJ 2011;343. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.d6099. [ Links ]
2. Cintron JR, Del Pino A, Duarte B, et al. Abdominal actinomycosis. Dis Colon Rectum 1996:39(1):105. DOI: 10.1007/BF02048278. [ Links ]
3. Yeo Joo Kim, Jina Youm, Jee Hyun Kim, et al. Actinomyces-like organisms in cervical smears: The association with intrauterine device and pelvic inflammatory diseases. Obstet Gynecol Sci 2014:57(5):393-6. DOI: 10.5468/ogs.2014.57.5.393. [ Links ]
4. Nissi R, Blanco Sequeiros RB, Lappi-Blanco E, et al. Large bowel obstruction in a young woman simulating a malignant neoplasm: A case report of Actinomyces infection. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol 2013;2013:756768. DOI: 10.1155/2013/756768. [ Links ]
5. Bittencourt JA, Andreis EL, Lima EL, et al. Actinomycosis simulating malignant large bowel obstruction. Braz J Infect Dis 2004;8(2):186-9. DOI: 10.1590/S1413-86702004000200011. [ Links ]











 text in
text in