Mi SciELO
Servicios Personalizados
Revista
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Accesos
Accesos
Links relacionados
-
 Citado por Google
Citado por Google -
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO -
 Similares en Google
Similares en Google
Compartir
Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas
versión impresa ISSN 1130-0108
Rev. esp. enferm. dig. vol.110 no.11 Madrid nov. 2018
https://dx.doi.org/10.17235/reed.2018.5598/2018
PICTURE IN DIGESTIVE PATHOLOGY
String sign of Kantor in a patient with Crohn's disease
1Servicios de Aparato Digestivo. Hospital Universitario de La Princesa. Madrid. Spain
2Servicios de Radiodiagnóstico. Hospital Universitario de La Princesa. Madrid. Spain
CASE REPORT
We report the case of a 29-year-old male with structuring ileocolic Crohn's disease (CD), diagnosed in 2007 and treated with oral azathioprine, oral mesalazine and intravenous infliximab, without any other surgical or medical history of interest. He presented to the Emergency Room with abdominal distention and pain, nausea, vomiting and motility problems of a three-day duration. An abdominal computerized tomography using intravenous contrast was performed (Fig. 1 and Fig. 2).

Fig. 1 Significant transverse colon dilatation (7 cm) with air-fluid level and inflammatory changes in the pericolic fat (blue arrow).
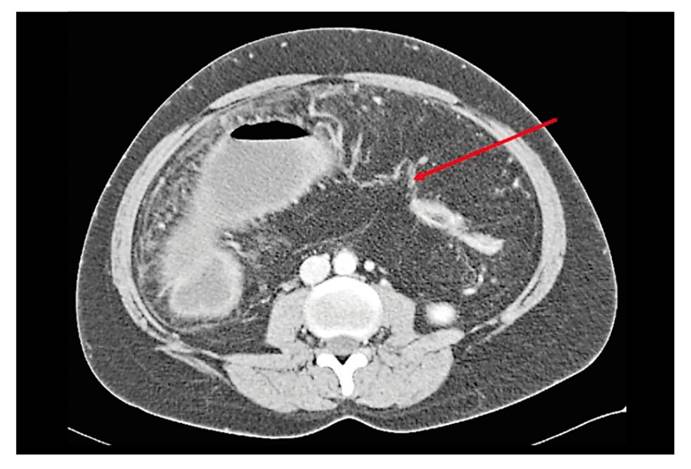
Fig. 2 An 8 cm stenotic bowel in the splenic flexure is seen in the distal bowel; the image of string sign of Kantor is shown (red arrow).
The stenosis was de novo, with a predominance of fibrostenotic strictures, wider than 5 cm in length. Thus, medical treatment or endoscopic intervention could not be performed. Finally, the patient required surgery; an extended right hemicolectomy was performed. There were no complications after the procedure.
DISCUSSION
Stricturing CD can be classified according to whether or not there is a previous history of surgery (de novo or anastomotic) and according to the composition of strictures (inflammatory, fibrotic and mixed types) 1. It is the second indication for surgery, after failure of medical treatment. The approach to stricturing CD includes endoscopic balloon dilation and metallic biodegradable or removable stents, when the stenosis is less than 5 cm in length or there is an anastomotic postoperative recurrence stenosis. Surgery including strictureplasty and intestinal resection may also be performed. The latter must be as minimally invasive as possible and focused on relieving the stenosis 2,3.
BIBLIOGRAFÍA
1. Wo WCP, Mourad F, Leong RWL. Crohn's disease associated strictures. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.14119 [ Links ]
2. Bettenworth D, Gustavsson A, Atreja A, et al. A pooled analysis of efficacy, safety, and long-term outcome of endoscopic balloon dilation therapy for patients with stricturing Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2017;23(1):133-42. DOI: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000988 [ Links ]
3. Rieder F, Fiocchi C, Rogler G. Mechanisms, management, and treatment of fibrosis in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 2017;152(2):340-50.e6. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.09.047 [ Links ]











 texto en
texto en 


