CASE REPORT
We present the case of a 79-year-old patient with multiple cardiovascular morbidities, classified as ASA III (American Society of Anesthesiology). An upper digestive endoscopy was performed due to chronic anemia and a subepithelial lesion was identified in the subcardial region of 30 x 25 mm, without other relevant findings (Fig. 1A). A radial echoendoscopy was performed to characterize the lesion. A hypoechoic nodular lesion of 25 x 28 mm was identified with a central hyperechoic area with well-defined edges, which was dependent on the muscularis mucosae that extended to the submucosa in an area of 5.8 mm. A single incision needle-knife biopsy (SINK) was accomplished. Pathological analysis showed presence of stromal fusiform cells, with a Ki67 of 2%, a low mitotic index. The patient was evaluated by the Department of General Surgery and was considered to be a non-surgical candidate due to his comorbidities. Thus, endoscopic management was programmed via the application of two endoloops (Fig. 1B), followed by an intralesional injection of cyanoacrylate plus 5 ml of liopidol using a 19G needle (Fig. 1C). Endoscopic control was performed after 12 weeks and a scarred area was identified, without local infiltration (Fig. 1D). Clinical and endoscopic follow-up has not identified evidence of residual lesions after three years of endoscopic intervention.
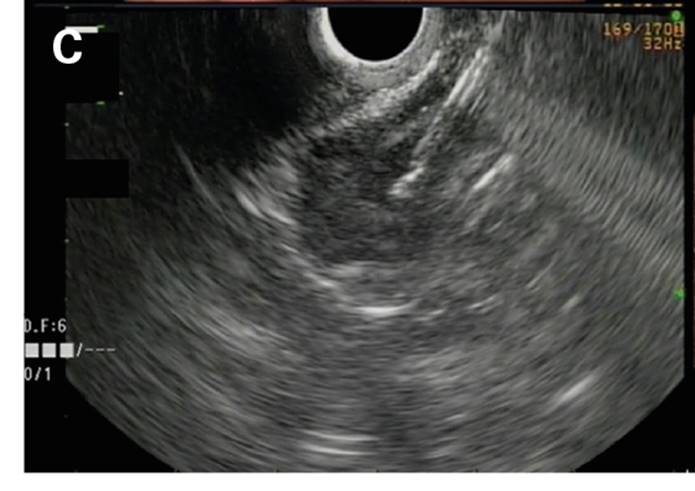



Fig. 1 A. Endoscopic vision of a subcardial gastric sub-epithelial lesion. B. Endoscopic management via the application of two endoloops. C. Intralesional EUS-guided application of cyanoacrylate. D. Endoscopic control 12 weeks after therapy. C. Intralesional EUS-guided application of cyanoacrylate. D. Endoscopic control 12 weeks after therapy.














