INTRODUCTION
Following the onset of COVID-19, there has been an apparent increase in the number of reported cases of acute invasive fungal rhino-sinusitis (mucormycosis), a rare but lethal fungal infection, particularly those with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus (DM) or on systemic corticosteroid therapy. Studies have shown that India has the highest incidence rate of mucormycosis in the world, with a significant proportion resulting from even a short course of DM treatment1. However, cases of COVID-19-associated mucormycosis in non-diabetic and non-steroid therapy patients are relatively less reported in literature. We report a rare case of acute invasive fungal rhino-sinusitis in a non-diabetic, non-steroid therapy patient with a recent history of COVID-19 infection. This report highlights the significance of considering mucormycosis as a plausible adverse effect of COVID-19 infection, even in patients who do not exhibit the traditional risk factors. The aim of this report is to provide a detailed description of the clinical features, diagnostic workup, and management of this rare case.
CASE DESCRIPTION
A male patient, aged 42, came to us with complaints of facial edema localized to the right side and teeth becoming loose over the past 2 weeks. The patient had tested positive for COVID-19 one month earlier. Initial diagnostic tests revealed a blood glucose level of 128 mg/dL, high levels of C-reactive protein (88.78 mg/dL), elevated serum ferritin (808 ng/mL), and reduced levels of blood urea (11 mg/dL) and creatinine (0.62 mg/dL). Other laboratory investigations included a complete blood count (CBC) within normal ranges, indicating no evidence of neutropenia, lymphocytosis, or lymphopenia. The ratio of CD4+ to CD8+ cells was 1.49, suggesting a balanced immune profile with negative serological markers for HIV and HCV. Immunoglobulin levels (IgG, IgM, and IgA) were normal, and complement levels (C3: 88mg/dL, C4: 32mg/dL) were within the expected range. Additionally, the patient's medical treatment history did not include long-term medications, immunosuppressive therapies, or chemotherapy drugs. Furthermore, there were no signs or symptoms of immunocompromised states such as frequent infections, poor wound healing, recurrent oral ulcers, or persistent fever. Based on these findings, the comprehensive history, examination, and laboratory investigations were deemed sufficient in excluding other potential causes of immunocompromised status in the patient.
Blood and urine cultures showed no growth of microorganisms. The patient was diagnosed with mild to moderate COVID-19 and hence systemic corticosteroids were not recommended as the literature suggests that it does more harm than good, by delaying viral clearance and increasing the risk of secondary infections.
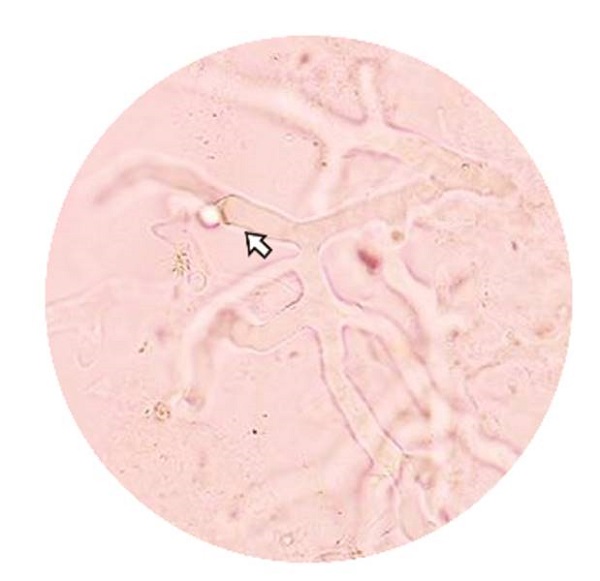
No comorbidities were reported. Physical examination showed a tender swelling on the right malar region, minimal discharge from the right nasal cavity, and mobile maxillary teeth with multiple draining sinuses (Figure 1A). CT-PNS showed eroded lateral walls of the maxillary sinus with peri-antral fat stranding and thickening of the sphenoidal sinus walls. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain with orbits and paranasal sinuses showed diffuse circumferential mucosal thickening of the maxillary, ethmoidal, and sphenoidal sinuses (Figure 2). The patient was given Liposomal Amphotericin B injections of 1.5-5 mg/kg body weight/day and underwent Functional Endoscopic Sinus surgery (FESS) using a modified Denker's approach after obtaining a signed informed consent. Necrosis of the posterior maxillary sinus mucosa and bony defects in the ethmoidal sinus walls were noted during the surgery. A bilateral maxillectomy was performed for the patient using an intra-oral approach (Figure 1). The excised tissue was sent for a frozen section and came out positive for mucor on KOH staining, confirming the diagnosis of mucormycosis (Figure 3). The patient tolerated the procedure well and was discharged after no residual lesion was noted on MRI. He was prescribed Tablet Posaconazole 300 mg orally once daily on discharge and showed satisfactory healing. A feeding plate was fabricated to assist with feeding in the interim, and a definite rehabilitation plan was being decided upon.
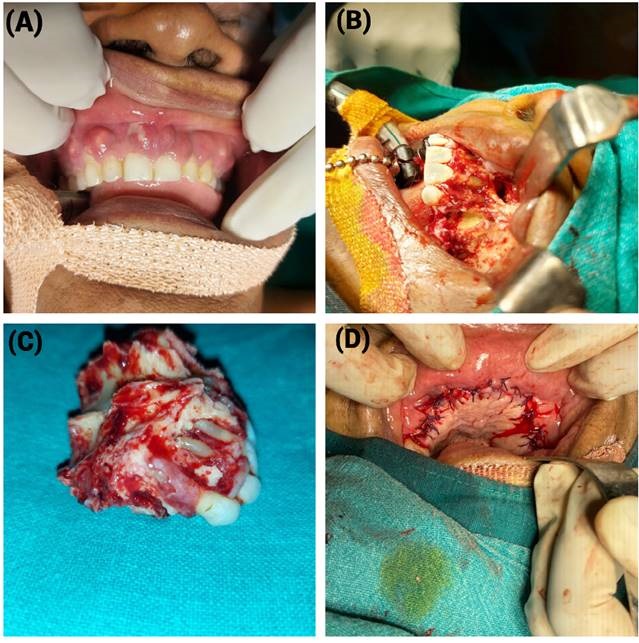
Figure 1. Clinical image and surgical management of the patient. A: preoperative image of the patient. B: intraoral approach for bilateral maxillectomy. C: image of resected specimen. D: closure of surgical site.

Figure 2. T2-weighted gadolinium MRI image of the patient. T2-weighted gadolinium MRI image of a rhinomaxillary mucormycosis patient, revealing soft tissue swelling and inflammation in the affected area, fungal invasion in the sinuses and maxillary bone, involvement of nearby structures and tissue necrosis.
DISCUSSION
The case report describes a rare case of acute invasive fungal rhino-sinusitis (mucormycosis) in a non-diabetic, non-steroid therapy patient with a recent history of COVID-19 infection. This highlights the importance of considering mucormycosis as a potential complication of COVID-19 infection, even in patients without traditional risk factors.
Fungal rhino-sinusitis (mucormycosis) is an acute, aggressive fungal infection emanating from a cluster of moulds called Mucorales, which are widely distributed and can be found in soil, decomposing foliage, compost, and the atmosphere. Mucormycosis is known to occur in people with reduced immunity, such as those with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, haematologic malignancies, and solid organ transplantations2. Feasible utilization of industrial grade oxygen, tap water in humidifiers, recycling of masks, and overutilization of antibiotics have also been described as potential reasons for the spread of this infection3. However, recent reports have shown an increasing incidence of COVID-19 linked mucormycosis, particularly in India1. The gravity of the situation is evident as eleven states and union territories in the country had declared it as an epidemic, under the Epidemic act of 1897.
The pathophysiology of COVID-19-associated mucormycosis is not fully understood. However, it is believed that COVID-19 infection may cause a dysregulated immune response, leading to a state of immune suppression and predisposing patients to opportunistic infections such as mucormycosis. In addition, COVID-19 may also induce hyperglycaemia, which can further increase the risk of this infection in patients with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus4.
Prompt detection and management of mucormycosis are crucial for improving patient outcomes. Diagnosis of mucormycosis involves a combination of clinical suspicion, imaging studies, and microbiological confirmation. It heavily relies on histopathological evidence as blood tests are relatively preliminary in nature. Mucorales exhibit a unique appearance under histological examination. They have irregular hyphae that do not contain any septa and branch at right angles.
In the present case, the patient presented with typical clinical features of rhinomaxillary mucormycosis, including a tender swelling on the right malar region, minimal discharge from the right nasal cavity, and mobile maxillary teeth with multiple draining sinuses. Literature suggests that fungal rhino-sinusitis typically presents with rapidly progressing symptoms such as swelling on one side of the face, fever, headache, inflammation, drooping of the eyelid, and the appearance of black lesions on the nasal area.
The recommended line of treatment for fungal rhino-sinusitis is an amalgamation of systemic antifungal therapy, surgical debridement, and management of subjacent comorbidities5. Early intervention by a multidisciplinary team is paramount for survival. The primary course of action is administering an injection of liposomal amphotericin B. However, if the patient exhibits intolerance to the treatment or weakened general health, alternative options such as Posaconazole and Isavuconazole, may be considered. It is crucial to perform aggressive and repeated surgical debridement, coupled with medical therapy, to ensure that the margins are clear of the disease. Microsurgical reconstruction in the early stages of the disease has been generally avoided because of the fungus's tendency to invade blood vessels, which can lead to infarction and necrosis.
CONCLUSION
This case report highlights the value of factoring in mucormycosis as a potential complication of COVID-19 infection, even in patients bereft of the common risk factors. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are paramount for improving patient outcomes. It is crucial for the healthcare providers to be vigilant and consider mucormycosis as a differential diagnosis in COVID-19 patients with suspected fungal infections. The relevance of a multidisciplinary management of these patients cannot be overemphasized.